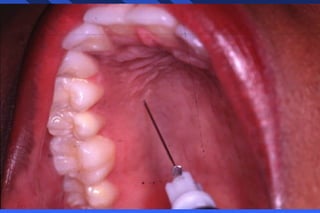
The document discusses maxillary anesthesia techniques. It describes the basic injection technique which includes checking the local anesthetic, positioning the patient, preparing the tissue, communicating with the patient, and establishing a hand rest. It also discusses infiltration of the palate specifically, including the nerves and area, indications and contraindications, advantages and disadvantages, and the technique. Signs and symptoms of successful anesthesia and possible failures or complications are outlined.