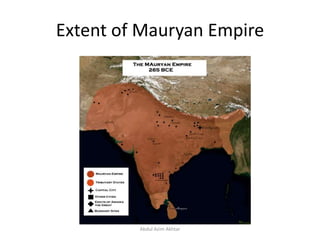
This document provides information on the Mauryan Empire from 325-185 BCE, including its founding and major rulers. It discusses Chandragupta Maurya, the founder of the empire, and his advisor Chanakya. It then focuses on the reign and accomplishments of Emperor Ashoka, considered one of India's greatest rulers, who expanded the empire and promoted Buddhism. Ashoka used his military to protect the empire while renouncing war, and instituted Dhamma or moral laws through edicts. The empire saw a period of peace, prosperity and trade under a strong centralized administration before its eventual dissolution.