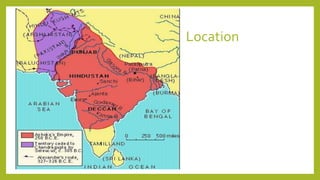
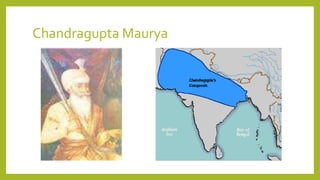
Ashoka was an emperor of the Mauryan Dynasty who ruled most of northern and central India from 268 to 232 BCE. After conquering the kingdom of Kalinga in a brutal war, Ashoka converted to Buddhism and renounced violence, instead following a policy of non-violence, tolerance, and respect. He erected pillars with edicts promoting dharma and established hospitals, rest houses, roads, and wells across his empire. The Mauryan Empire had a large administrative structure and military to govern its vast territories during Ashoka's reign.