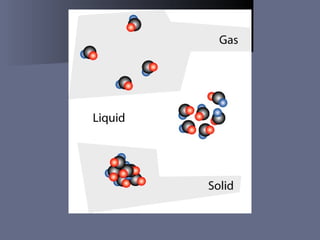
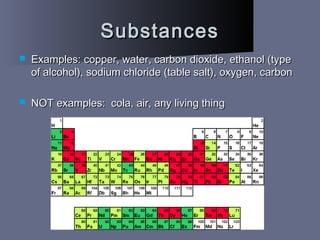
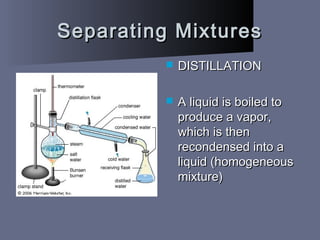
The document defines matter as anything that takes up space and has mass. It describes the three common states of matter - solids, liquids, and gases - based on how tightly or loosely packed the atoms are and how they move. Physical properties can be observed without changing a substance's identity, while chemical properties involve changing its identity through a chemical reaction. Physical changes alter a substance's properties but not its chemical makeup, while chemical changes produce different substances. Mixtures are combinations of two or more substances that can often be separated using physical properties like density, solubility, or melting/boiling points.