This document provides an overview of MATLAB, including:
- MATLAB is a programming language and environment used for scientific and engineering calculations. It is matrix-oriented and supports graphical programming.
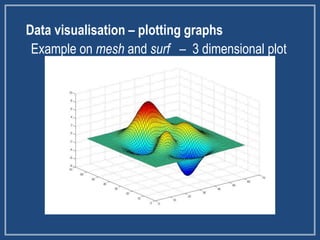
- MATLAB can be used for 3D plotting, vector and matrix operations, and modeling dynamic systems using Simulink. It includes tools for variables, functions, loops, and plotting graphs.
- MATLAB has applications in fields like aerospace, biomedicine, signal processing, and more. Companies like NASA, GE, and Bosch utilize MATLAB.









![Vectors
a = [1 2 3 4 5 6 9 8 7] ;
t = 0:2:20
t = 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
b = a + 2
b = 3 4 5 6 7 8 11 10 9
c = a + b
c = 4 6 8 10 12 14 20 18 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matlab-150730195834-lva1-app6892/85/Matlab-12-320.jpg)
![Matrices
B = [1 2 3 4;5 6 7 8;9 10 11 12] ;
B = 1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
9 10 11 12
C = B'
C = 1 5 9
2 6 10
3 7 11
4 8 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matlab-150730195834-lva1-app6892/85/Matlab-13-320.jpg)






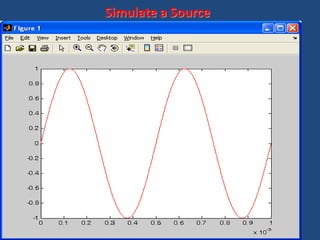
![Complete MATLAB Script [Prog1.m]
tmin = 0; tmax = 10^(-3); step = (tmax-tmin)/1000;
t = tmin:step:tmax;
fm = 2*10^3;
Vm = 1;
m = Vm*sin(2*pi*fm*t);
plot(t,m,'r');
Simulate a Source](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matlab-150730195834-lva1-app6892/85/Matlab-20-320.jpg)