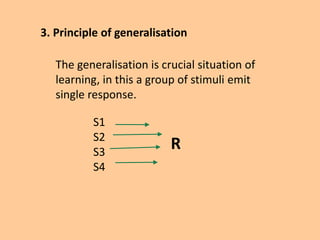
This document discusses mathematics programmed instruction. It begins by explaining that programmed instruction was developed by B.F. Skinner as a way to apply the scientific method to teaching using highly structured materials to replace the teacher. It then describes the basic idea of starting with motivating tasks and working backwards, called retrogressive chaining. The principles of mathematics programs are training responses to mastery, discrimination through different stimuli/responses, and generalization of a single response to a group of stimuli. The document outlines the steps to create a mathematics program and assumptions they are based on, and concludes by discussing advantages like being task-oriented and limitations like technical nature.