Embed presentation
Downloaded 11 times
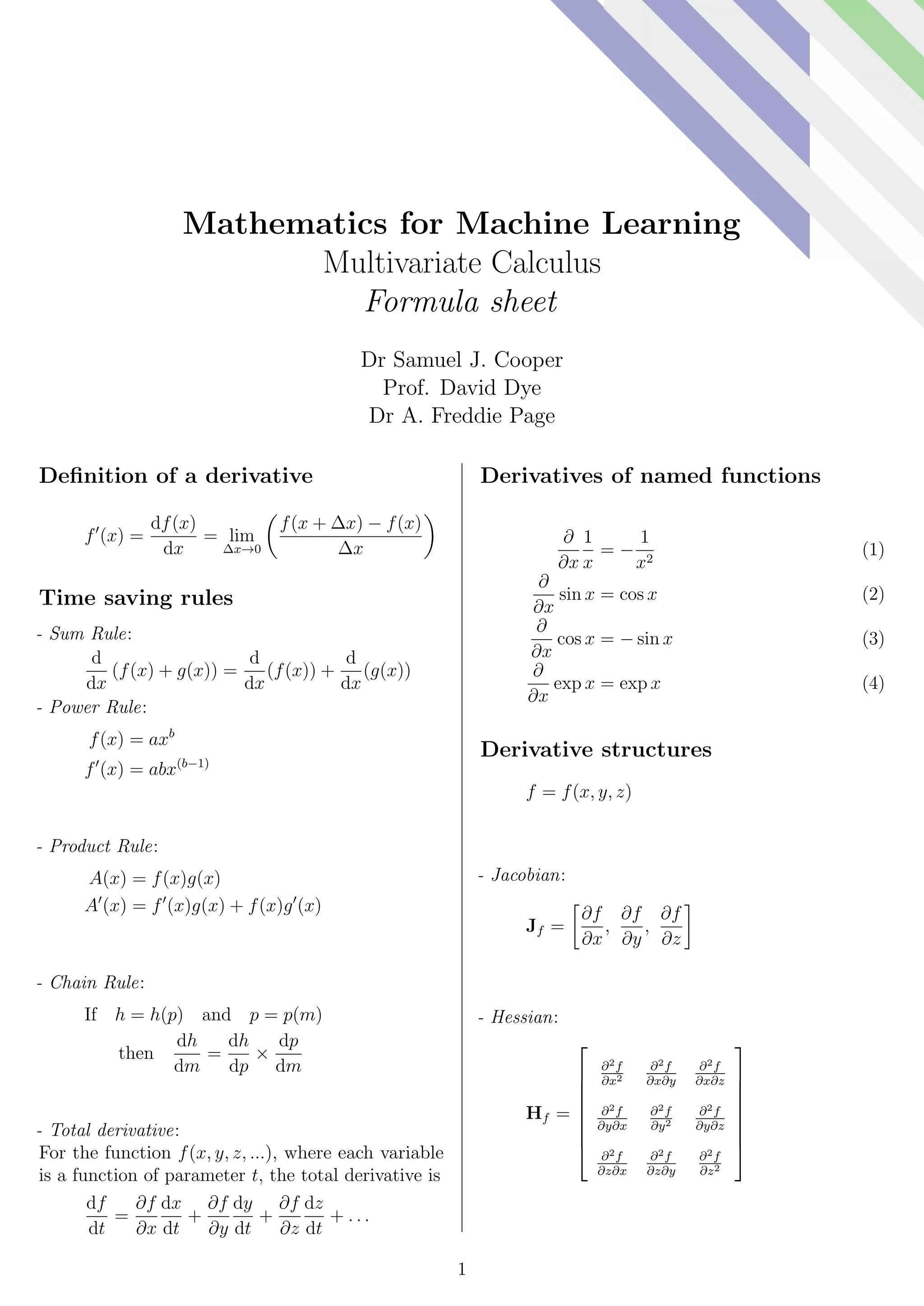


This document provides formulas and definitions for concepts in multivariate calculus and machine learning. It defines the derivative and lists time-saving rules like the sum, product, and chain rules. It also defines the Jacobian and Hessian matrices, Taylor series, optimization techniques like Newton-Raphson and gradient descent, and concepts like Lagrange multipliers and least squares minimization. The document is a formula sheet for a course on mathematics for machine learning.

