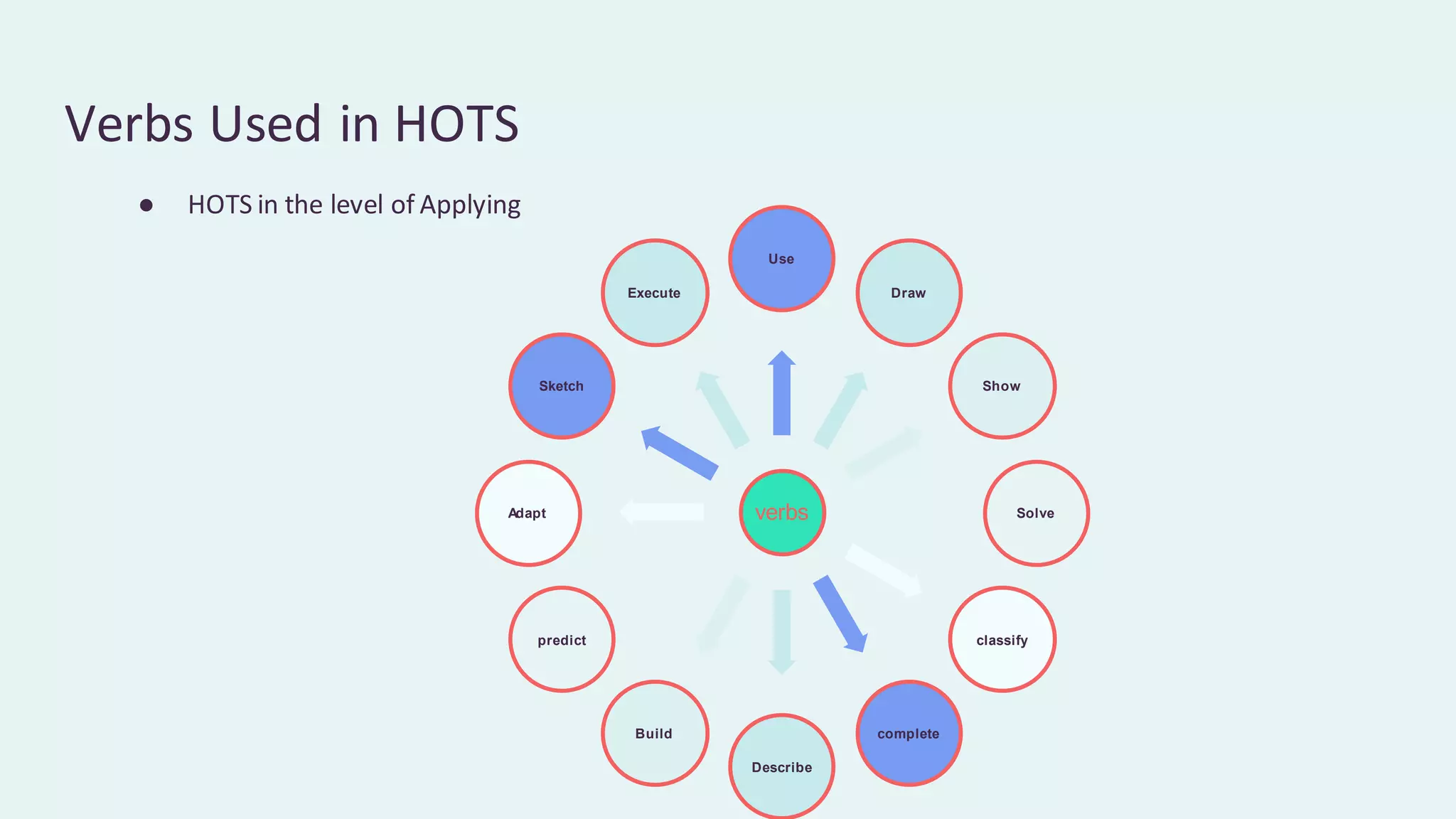
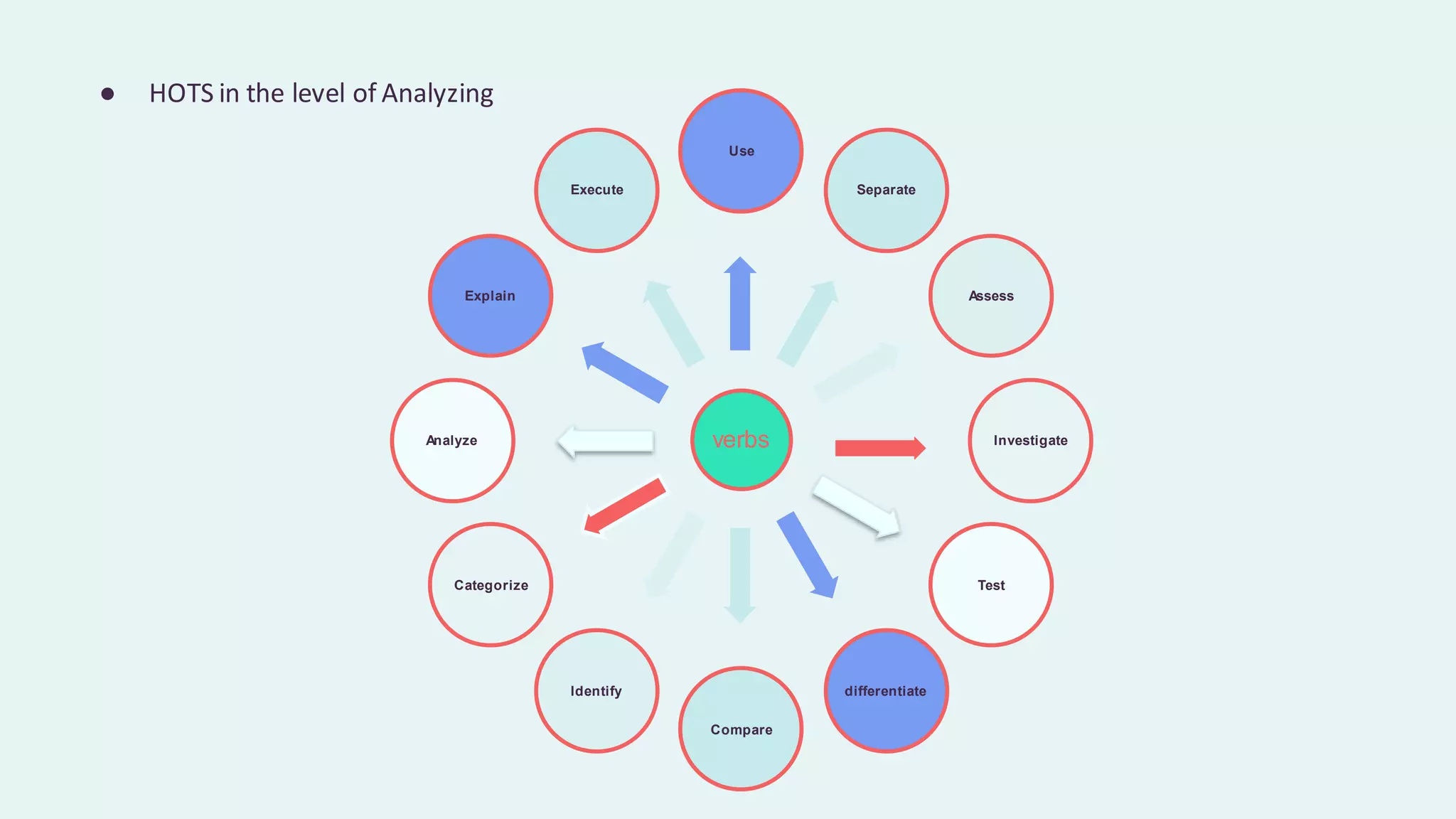
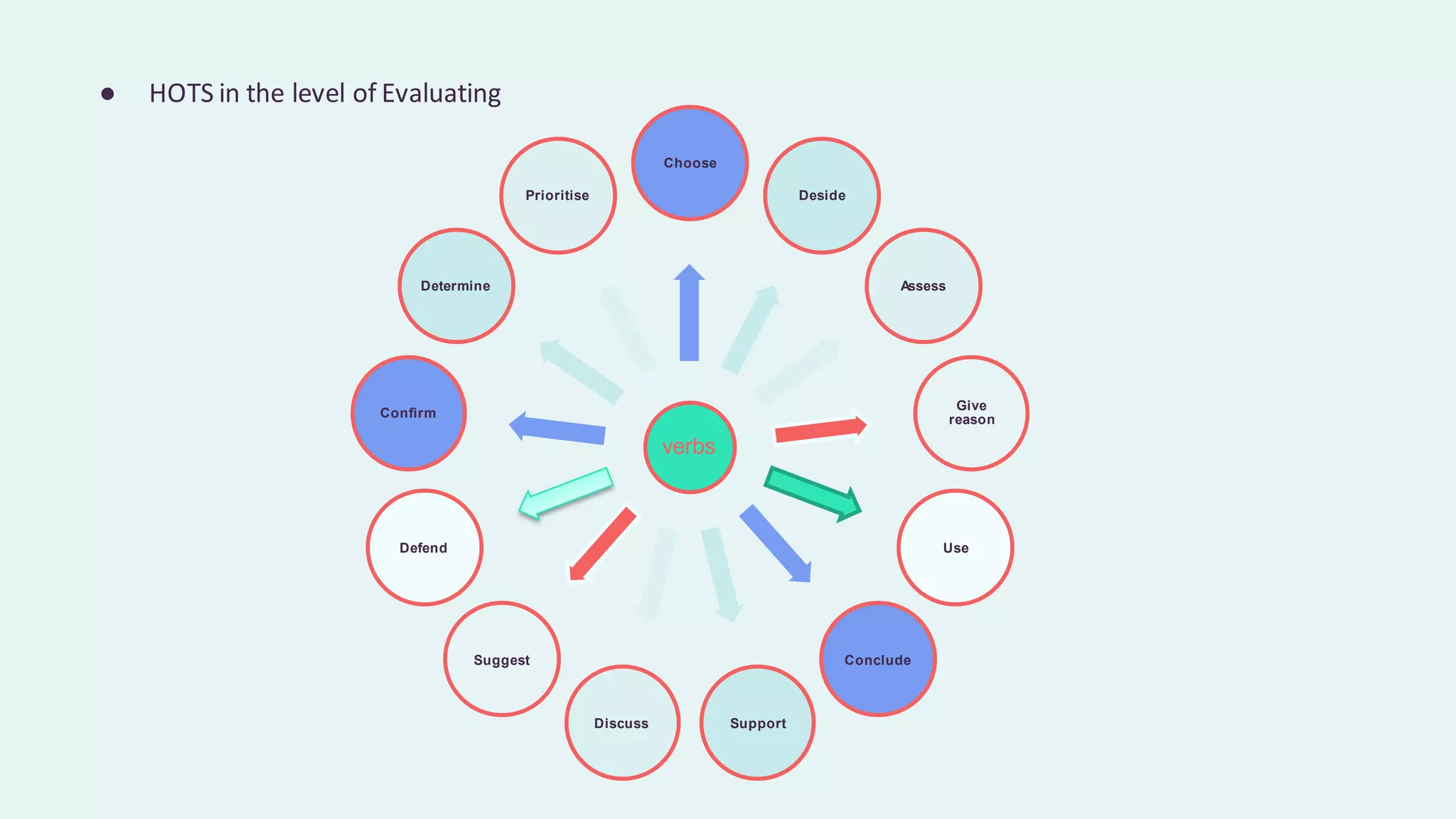
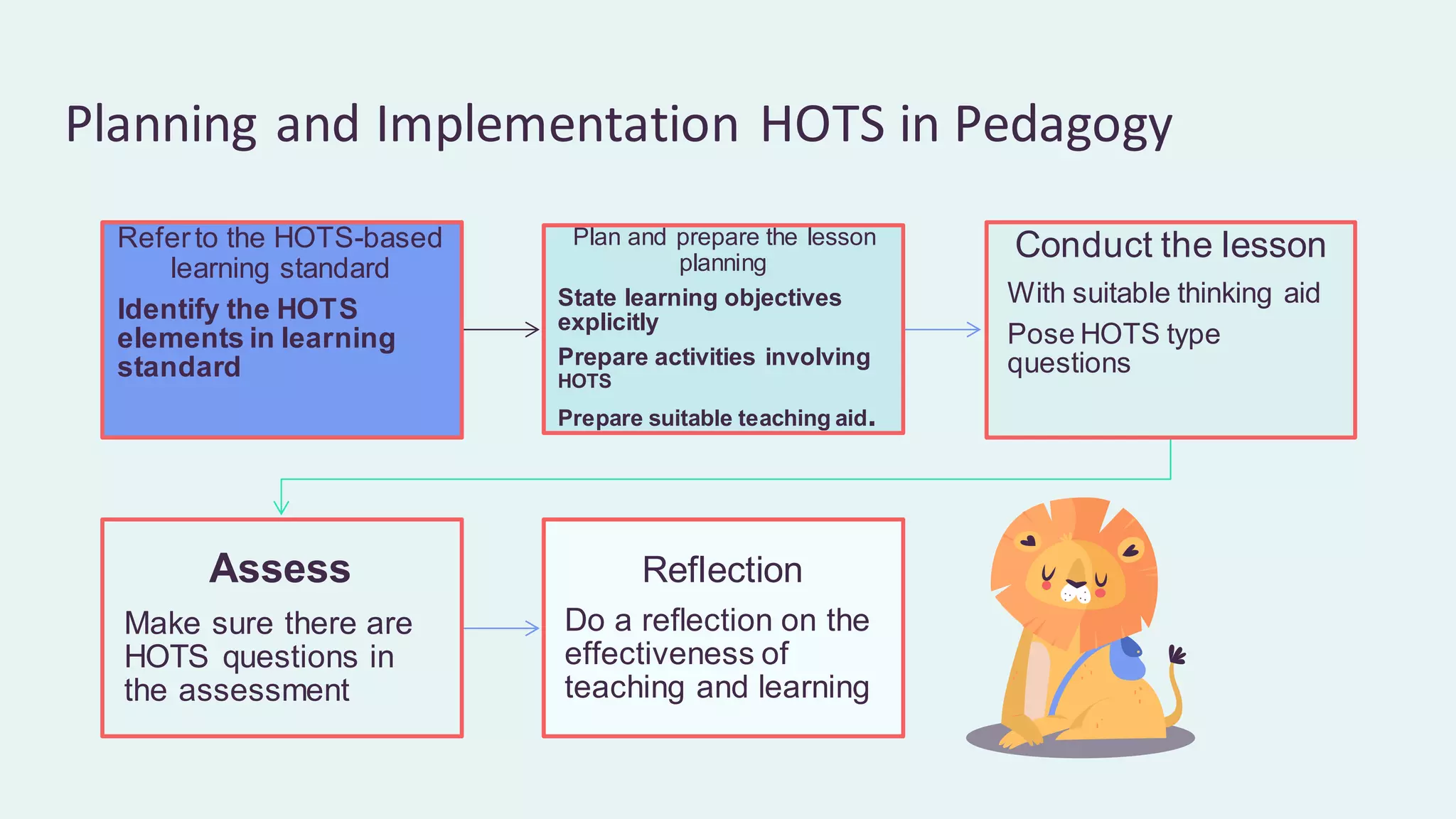
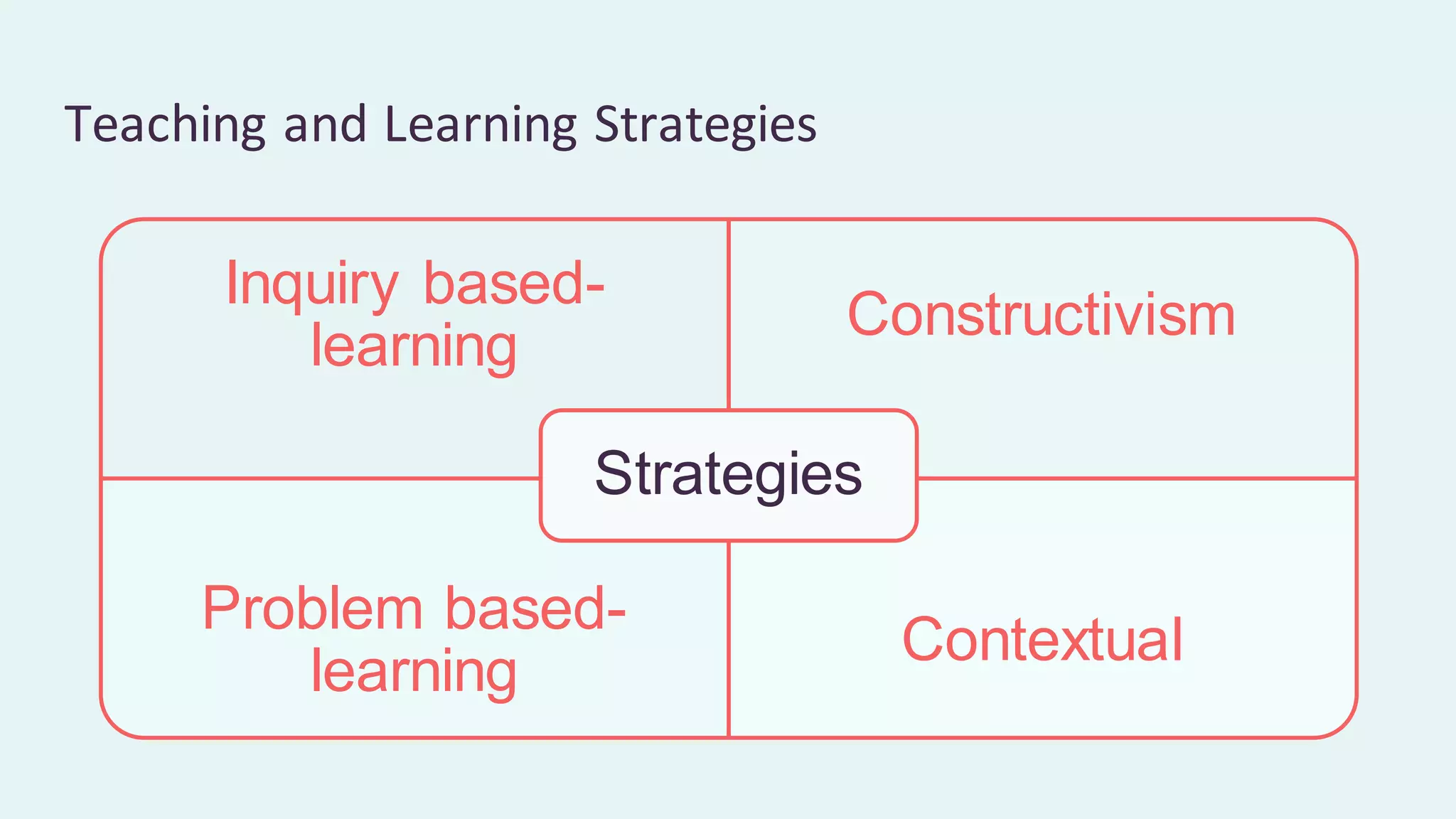
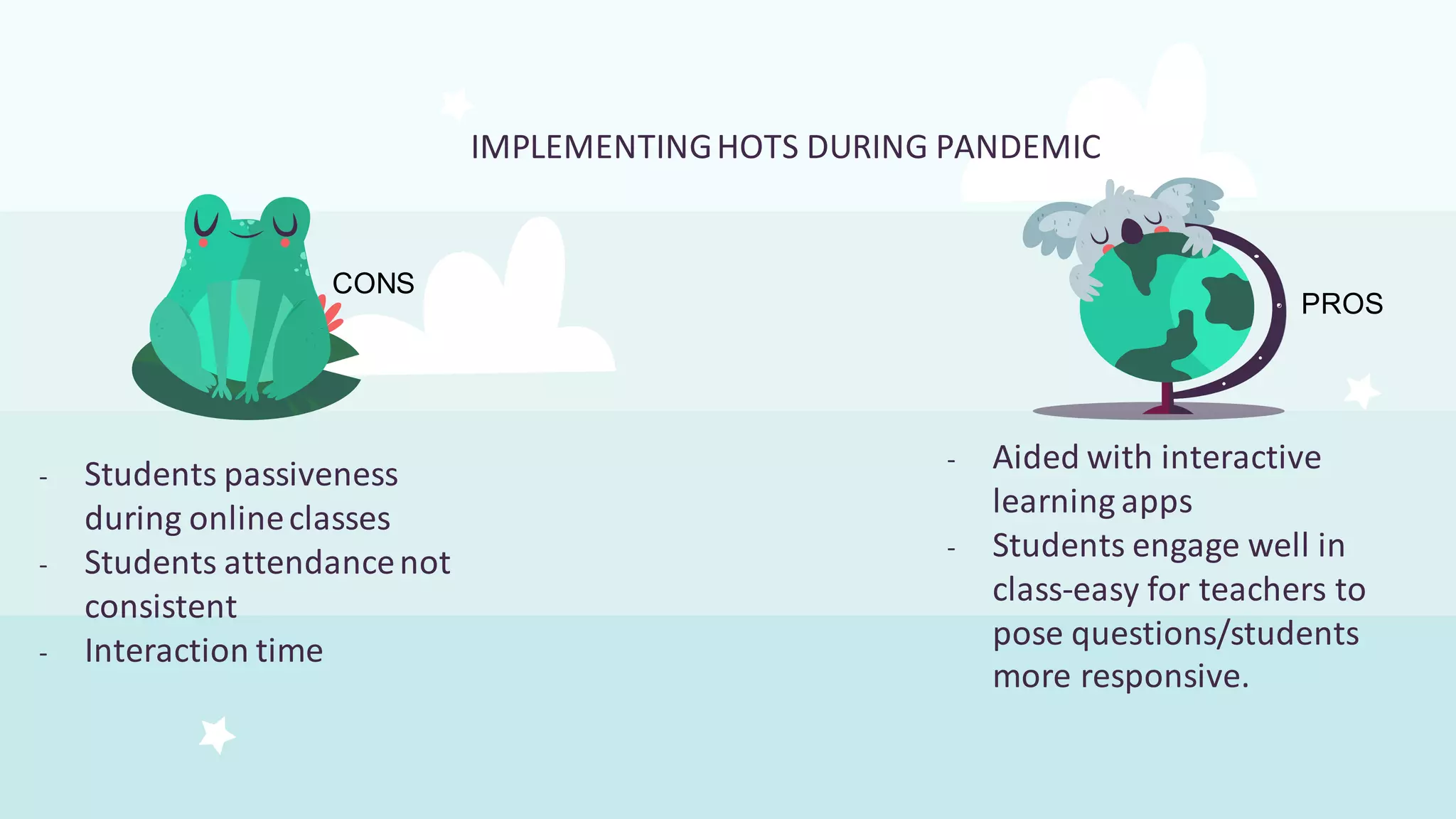
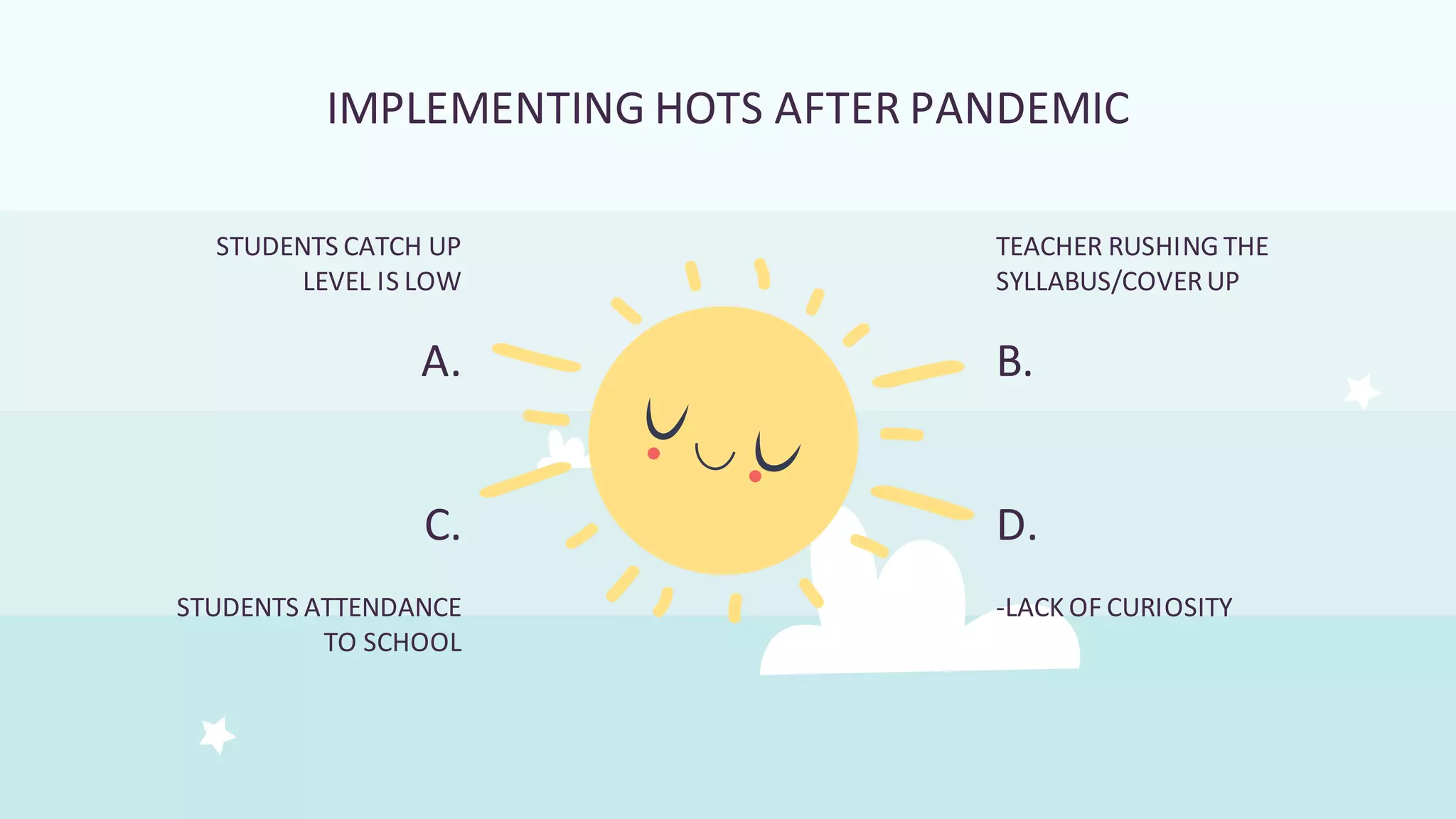
This document discusses higher order thinking skills (HOTS) in education. It defines HOTS as the ability to apply knowledge, skills, and values to solve problems, make decisions, innovate, and create. HOTS include skills like critical thinking, creative thinking, reasoning, and thinking strategies. The document outlines three important aspects of HOTS - applying knowledge, reasoning and reflecting, and problem solving and decision making. It also discusses verbs used to indicate different levels of HOTS. Finally, it discusses strategies for planning and implementing HOTS in pedagogy and some challenges, like time constraints and learning environments not conducive to active learning.