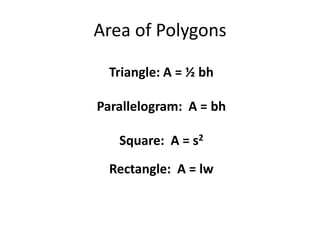
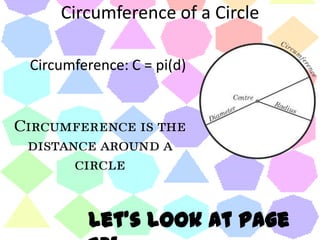
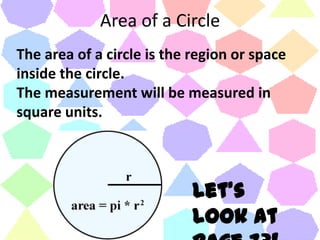
This document discusses formulas and strategies for computing the perimeter and area of basic shapes like triangles, parallelograms, trapezoids, and circles. It provides the formulas for finding the perimeter of squares, rectangles, and other polygons by adding the side lengths. Formulas are also given for finding the area of triangles, parallelograms, squares, rectangles, trapezoids, circles, and more complex irregular shapes by decomposing them into basic components. Examples are worked through on various pages and homework is assigned covering the material.