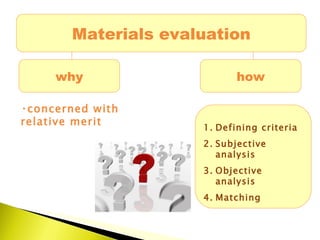
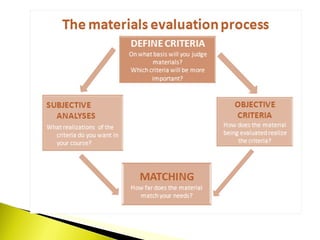
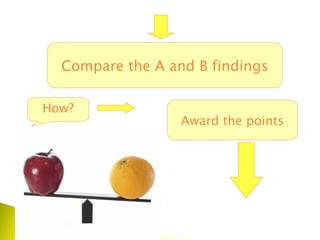
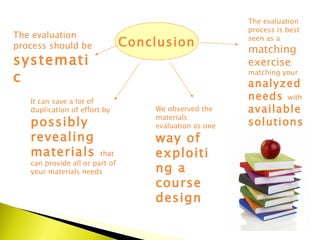
The document outlines a systematic process for evaluating existing teaching materials based on the needs and requirements of a target audience and course. Key steps include:
1) Identifying requirements based on audience, aims, content, skills, methodology, and other factors.
2) Analyzing existing materials based on the same criteria.
3) Comparing requirements against existing materials and awarding points to materials based on how closely they match requirements.
4) Selecting materials that receive the highest scores across important criteria and documenting the decision.