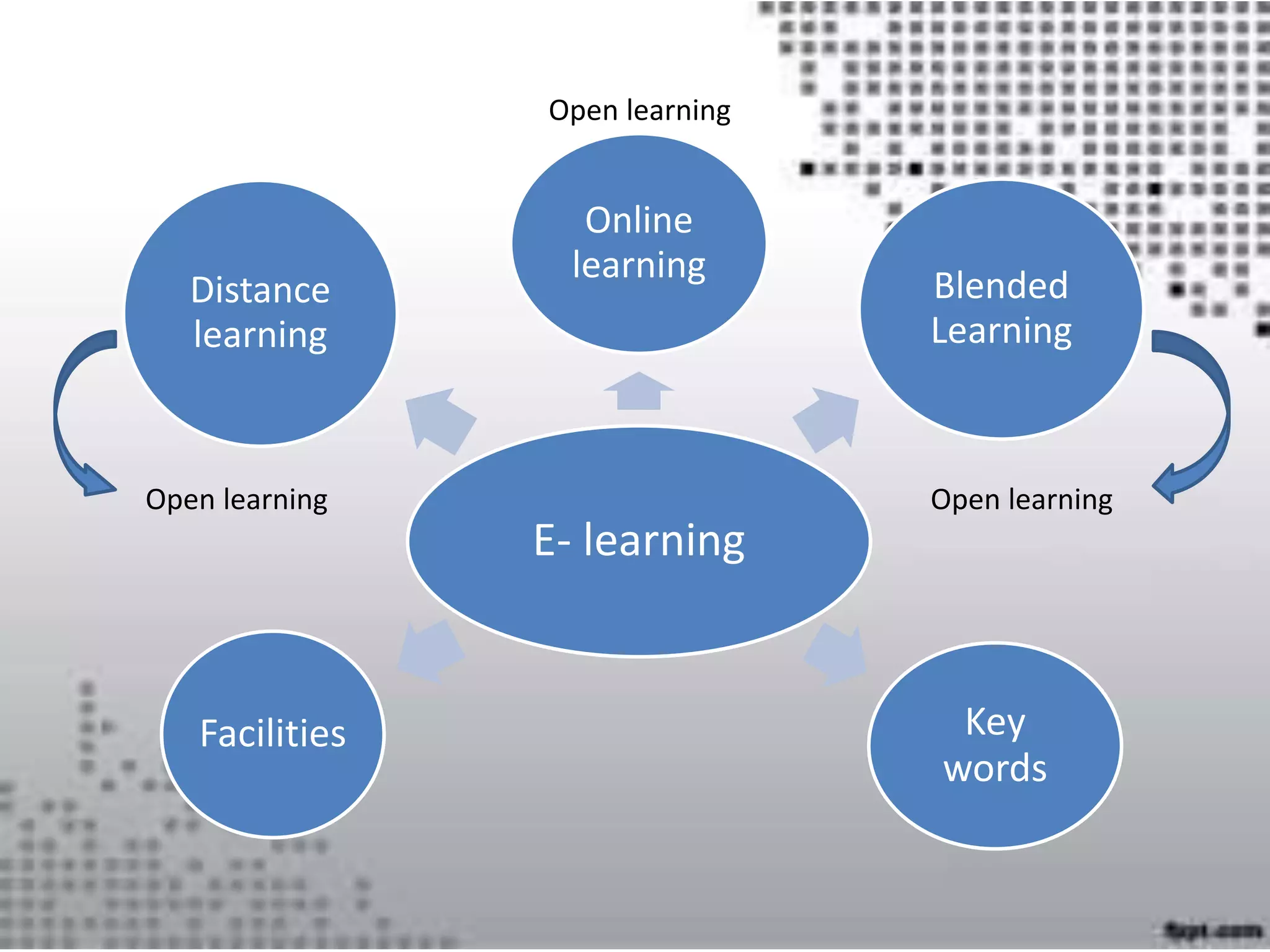
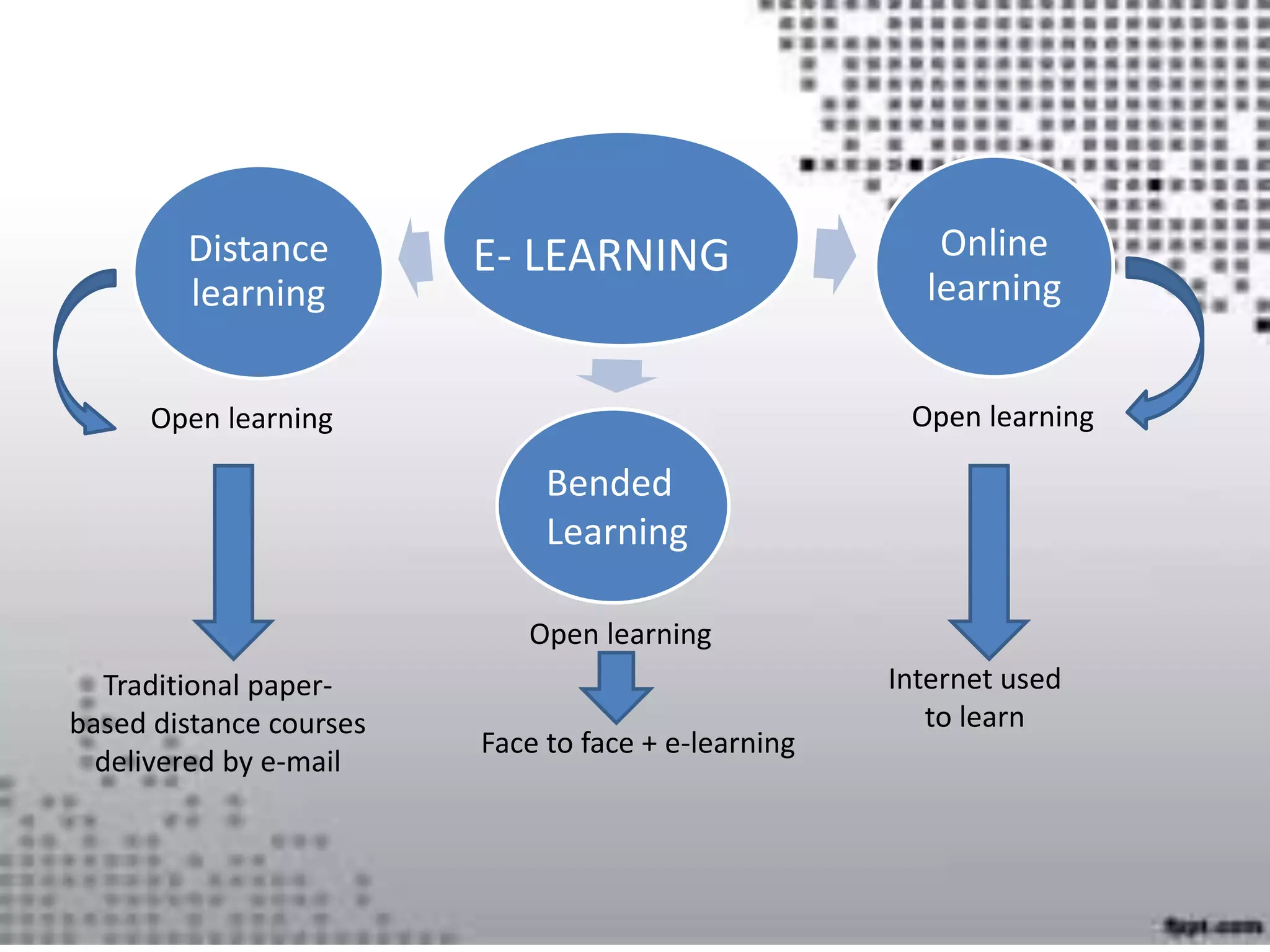
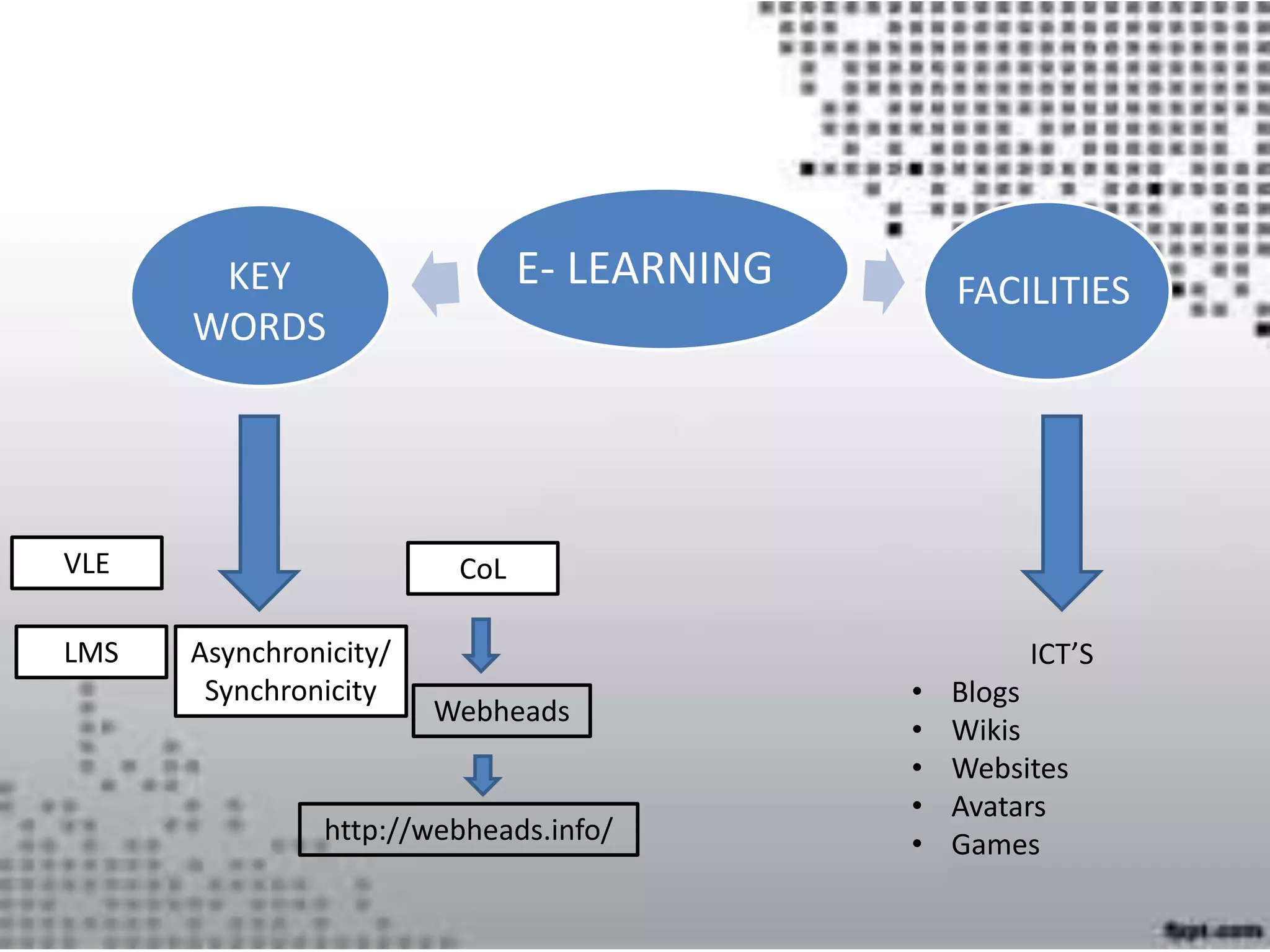
This document discusses various approaches to using technology in teaching, including e-learning, online learning, blended learning, and distance learning. It covers facilitating online classes through learning management systems, communication tools like blogs and wikis, and considering learners' needs, technical skills, and educational backgrounds. The roles of an online teacher as coach, leader, tutor and facilitator are outlined. Effective online lesson planning, input, activities, assessment and ensuring understanding are also discussed. Authentication of student identity is noted as a challenge for online assessment.