This document provides guidance for teachers on using the internet and websites in the classroom in three main ways:
1) It discusses how websites can be used as printed pages, with one computer and internet connection, or in a computer lab.
2) It recommends that using the internet be an integral part of learning rather than an occasional activity. Both ELT and authentic websites have benefits depending on the teaching goals.
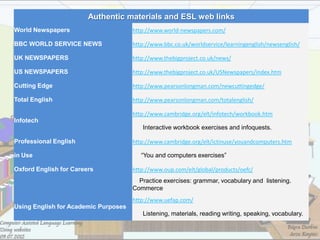
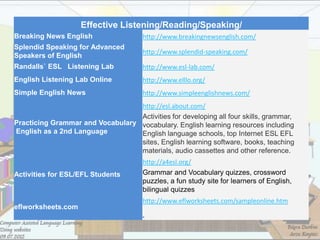
3) It provides examples of search engines and categories of websites for images, video, audio and podcasts that can be used for different classroom projects. Specific ESL website resources are also listed.