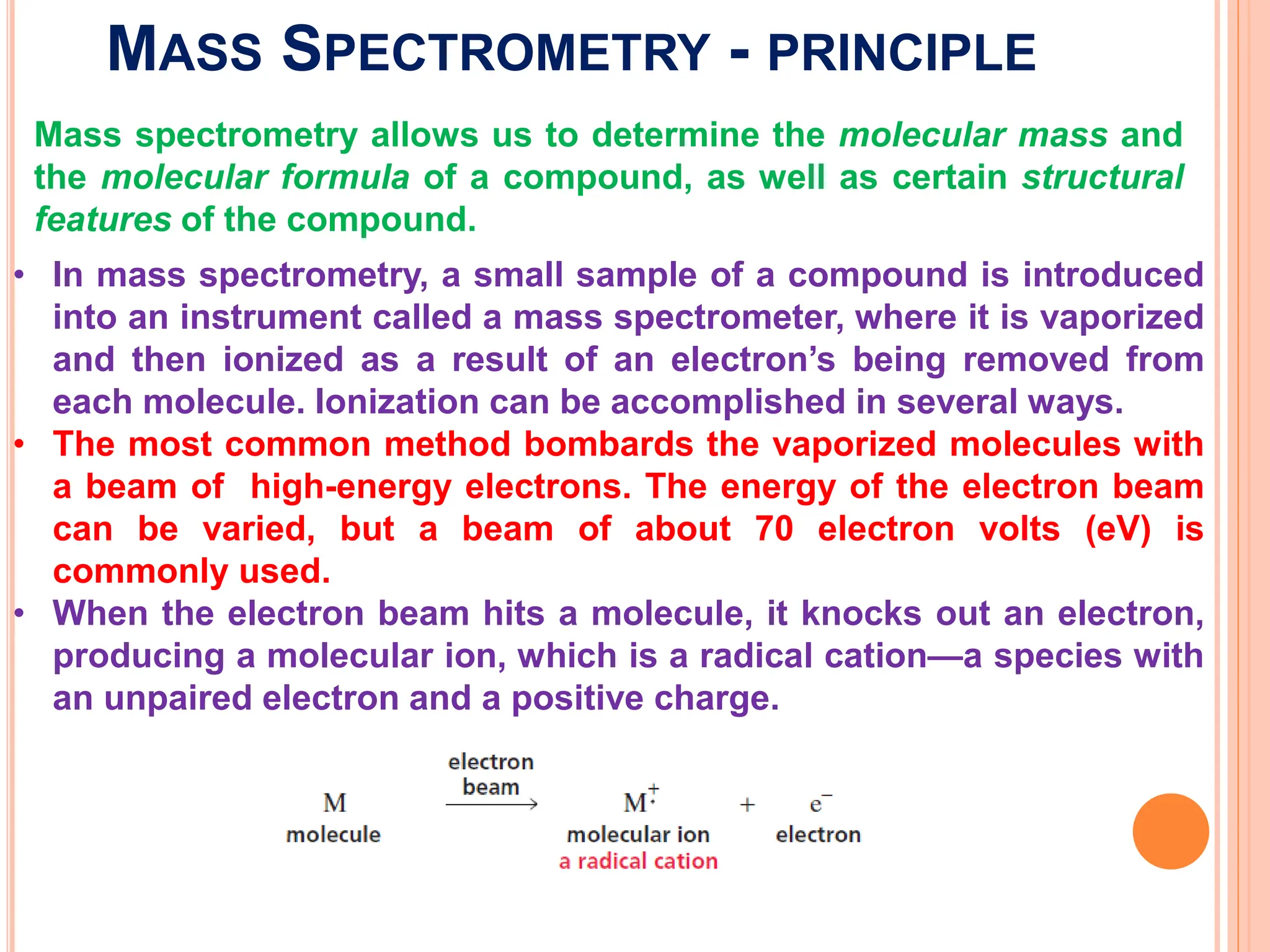
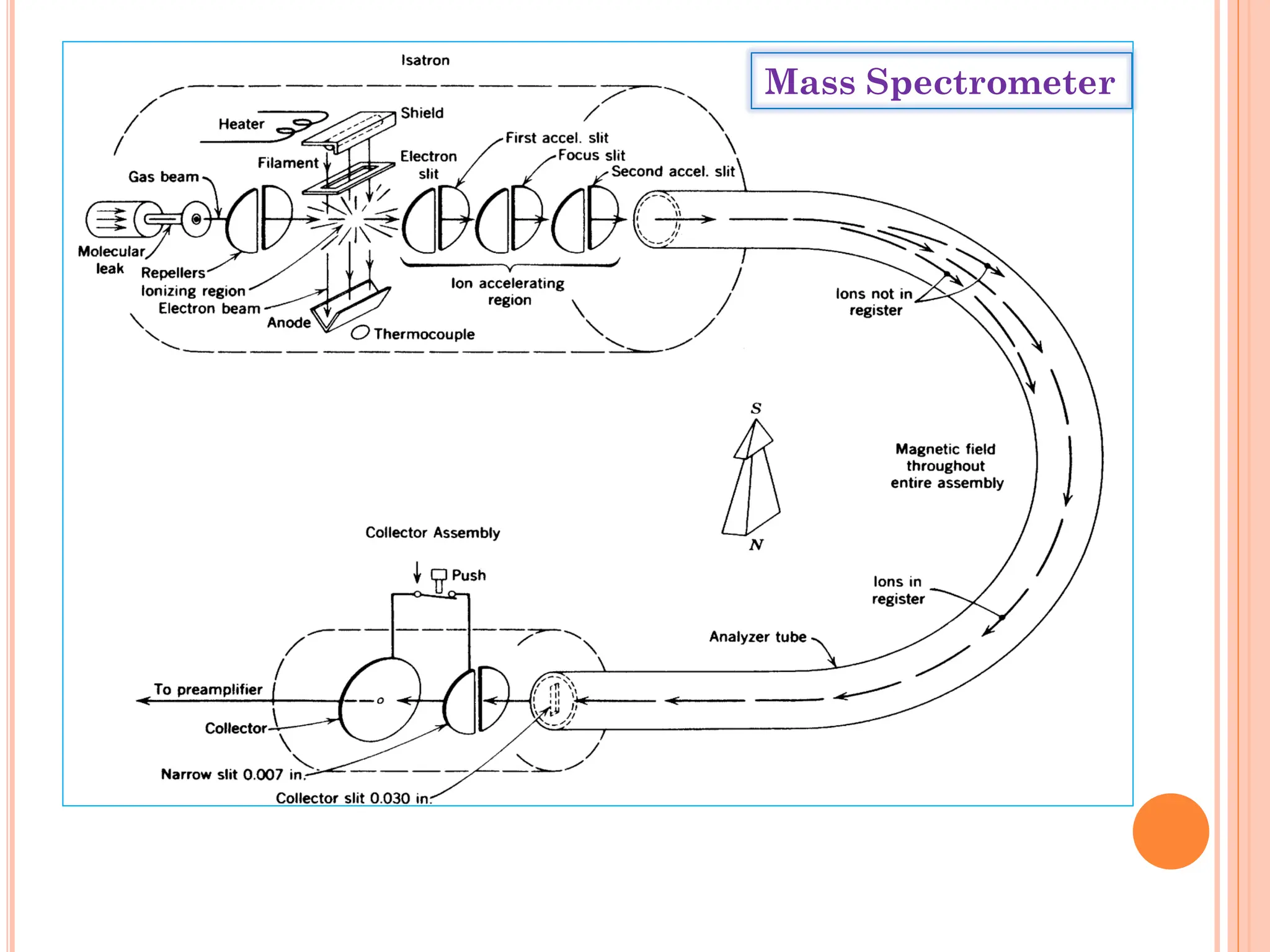
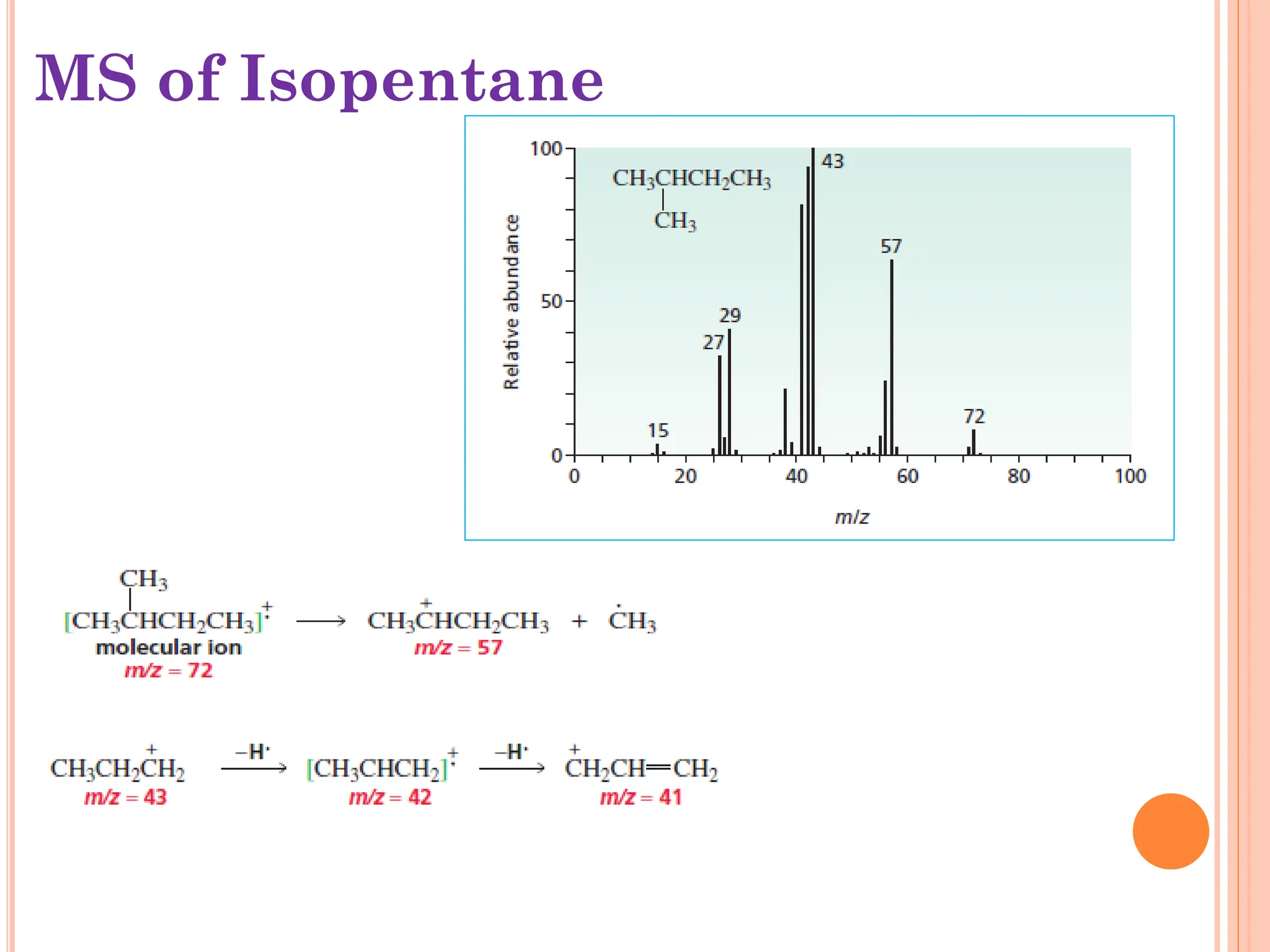
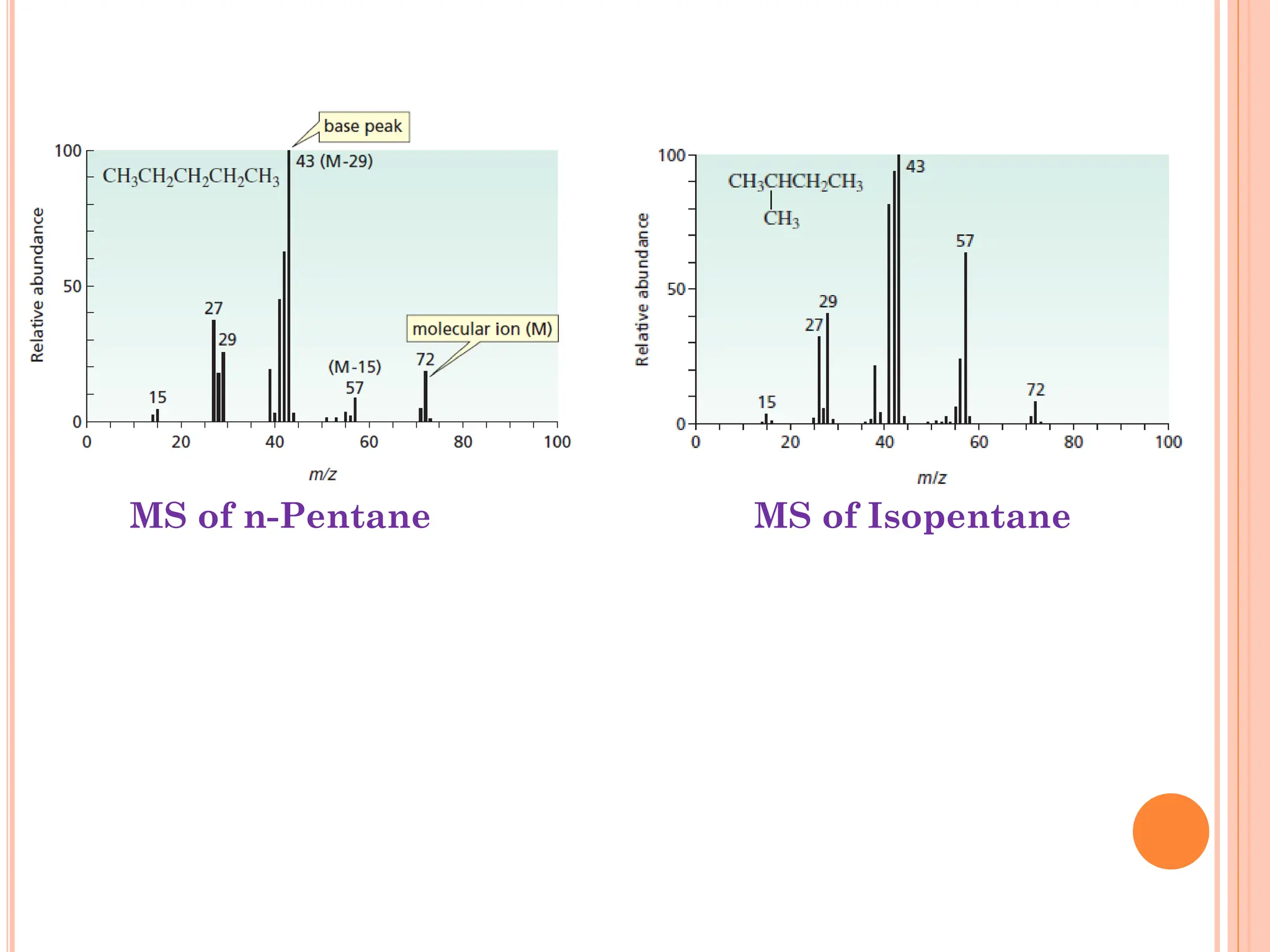
Mass spectrometry allows determination of molecular mass, molecular formula, and some structural features. It works by vaporizing and ionizing a sample using electron bombardment, which knocks an electron off each molecule to produce a molecular ion. The mass spectrometer then separates the ions based on their mass-to-charge ratio, which allows identification of the molecular ion peak corresponding to the molecular weight. Isotope peaks from elements like carbon can provide structural information. Fragmentation patterns are also used for structural analysis.





![Isotope Peaks: [M+1]
[M+2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/massspectrometry-231019171405-fb96f838/75/Mass-Spectrometry-pdf-10-2048.jpg)































![Field Desorption (FD)
Stable molecular ions are obtained from a sample of low
volatility, which is placed on the anode of a pair of electrodes,
between which there is an intense electric field.
Desorption occurs, and molecular and quasimolecular ions are
produced with insufficient internal energy for extensive
fragmentation.
Usually the major peak represents the [M+H]+ ion.
Synthetic polymers with molecular weights on the order of
10,000 Da have been analyzed, but there is a much lower
molecular weight limit for polar biopolymers.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/massspectrometry-231019171405-fb96f838/75/Mass-Spectrometry-pdf-46-2048.jpg)



