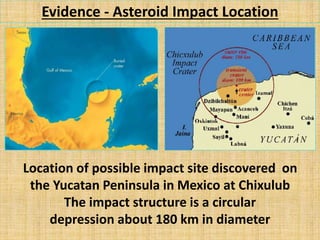
The document discusses the concept of mass extinction, detailing five major events in Earth's history where significant species loss occurred due to various factors, including climate changes and major geological events. It highlights the ongoing Holocene extinction, attributing it to human activities such as habitat destruction and pollution, which threatens around 30,000 species annually. Suggestions for mitigating these impacts are provided, such as energy conservation and wildlife protection efforts.