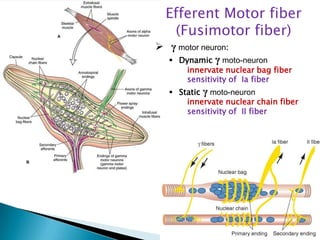
This document discusses the common terminal motor pathway which involves the anterior horn cell (A1) and its axon (the alpha motoneuron). It describes the major descending pathways that influence motor activity, including the corticospinal tract, rubrospinal tract, reticulospinal tract, and vestibulospinal tract. These pathways terminate on the alpha motoneurons and gamma motoneurons, which influence the muscle spindles. Afferent fibers from the muscle spindles and tendon organs provide feedback to complete the reflex loop.