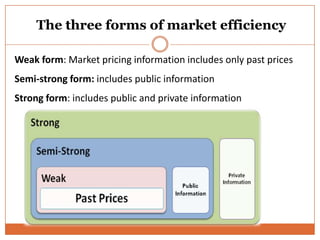
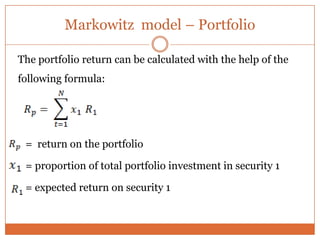
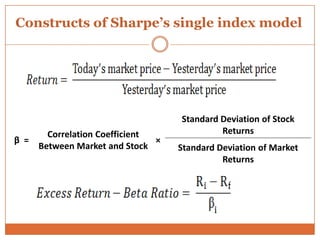
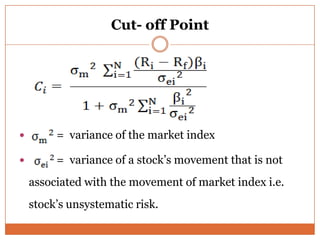
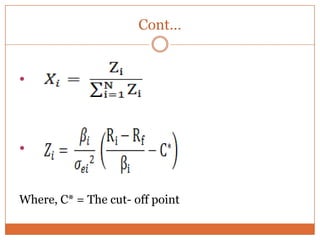
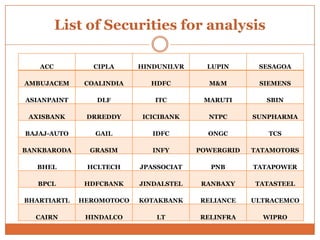
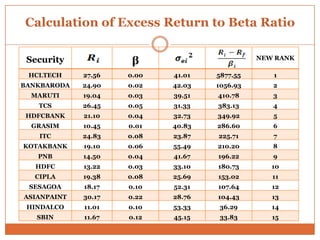
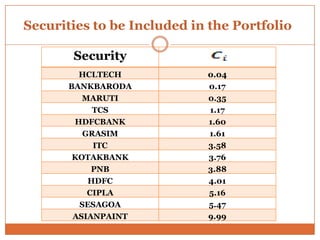
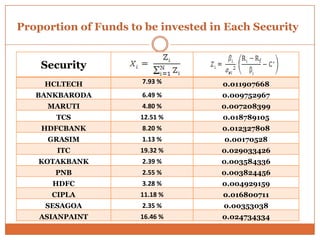
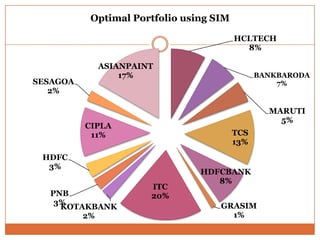
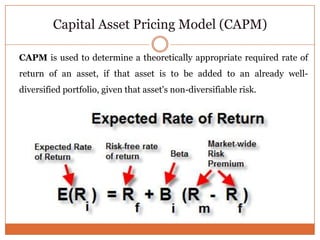
The document summarizes key concepts in portfolio theory including the efficient market theory, Markowitz portfolio analysis, Sharpe's optimum portfolio construction model, and the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM). It provides details on calculating excess return to beta ratios to select securities for an optimal portfolio using Sharpe's single index model. Specifically, it ranks 14 securities based on their ratios, includes the top 7 in the optimal portfolio, and calculates the proportion of funds to invest in each. In the end, it outlines the assumptions of CAPM for calculating the expected return of an asset given its beta, the risk-free rate, and expected market return.