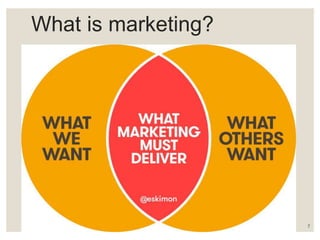
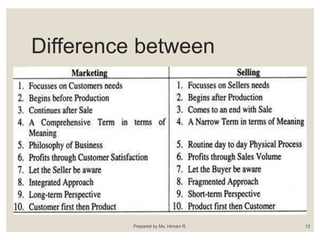
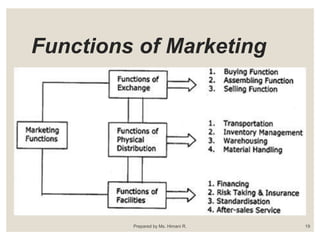
This document provides an introduction to marketing. It defines marketing as a social process of identifying and meeting human needs through the exchange of products and values. The document outlines the key concepts of marketing including the market, marketing goals, traditional and modern approaches, and the 4Ps of the marketing mix. It also discusses recent trends in marketing such as e-business, telemarketing, and customer relationship management.