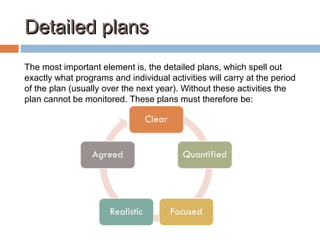
The document provides an overview of key components to include in a marketing plan, such as market and product definitions, competition analysis, positioning, communication strategies, launch plans, pricing, distribution, and a 12-month schedule. It also outlines different marketing strategies like single market, multi market, total market strategies as well as strategies based on market dominance including leader, challenger, follower, and nicher.