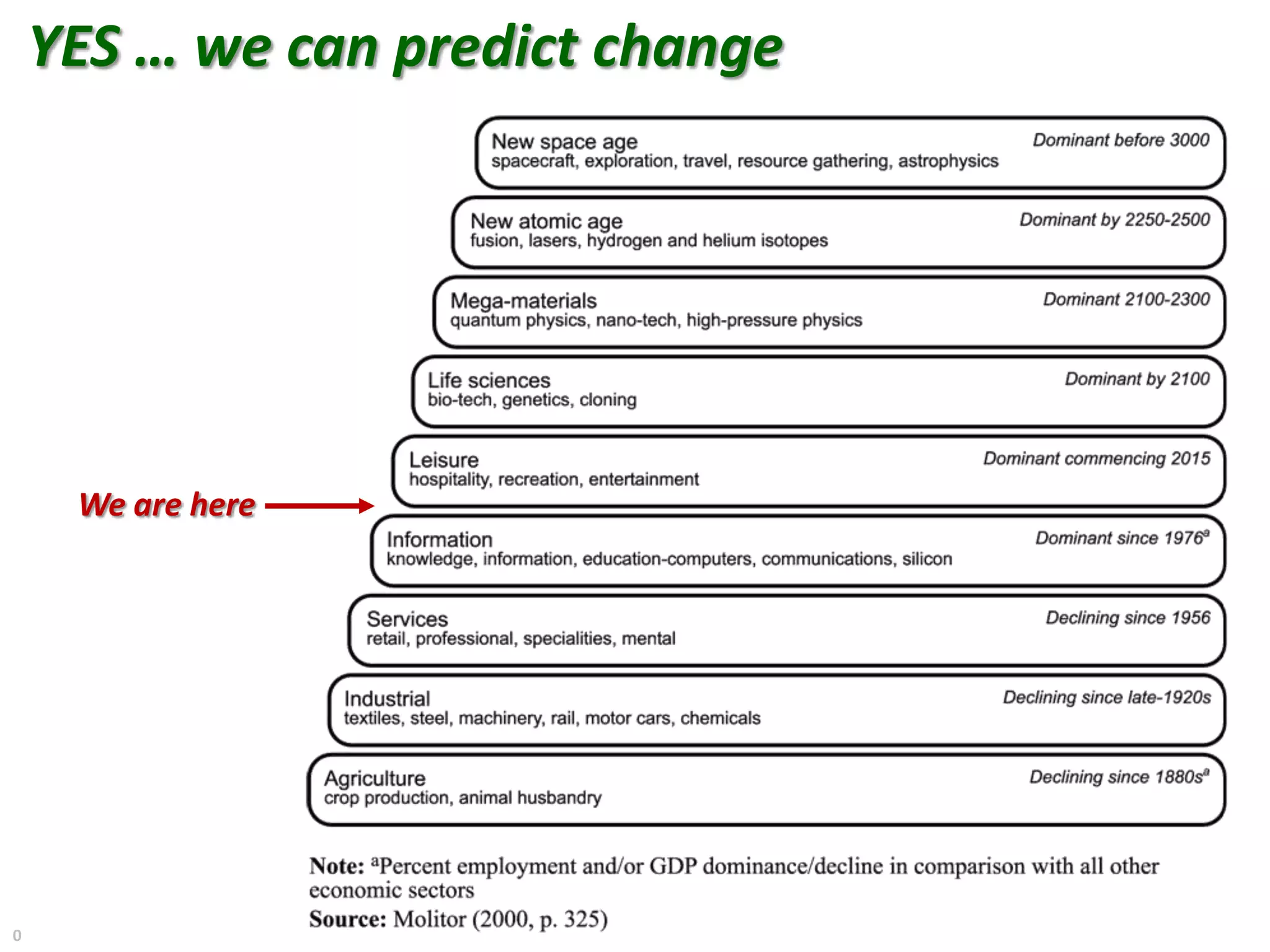
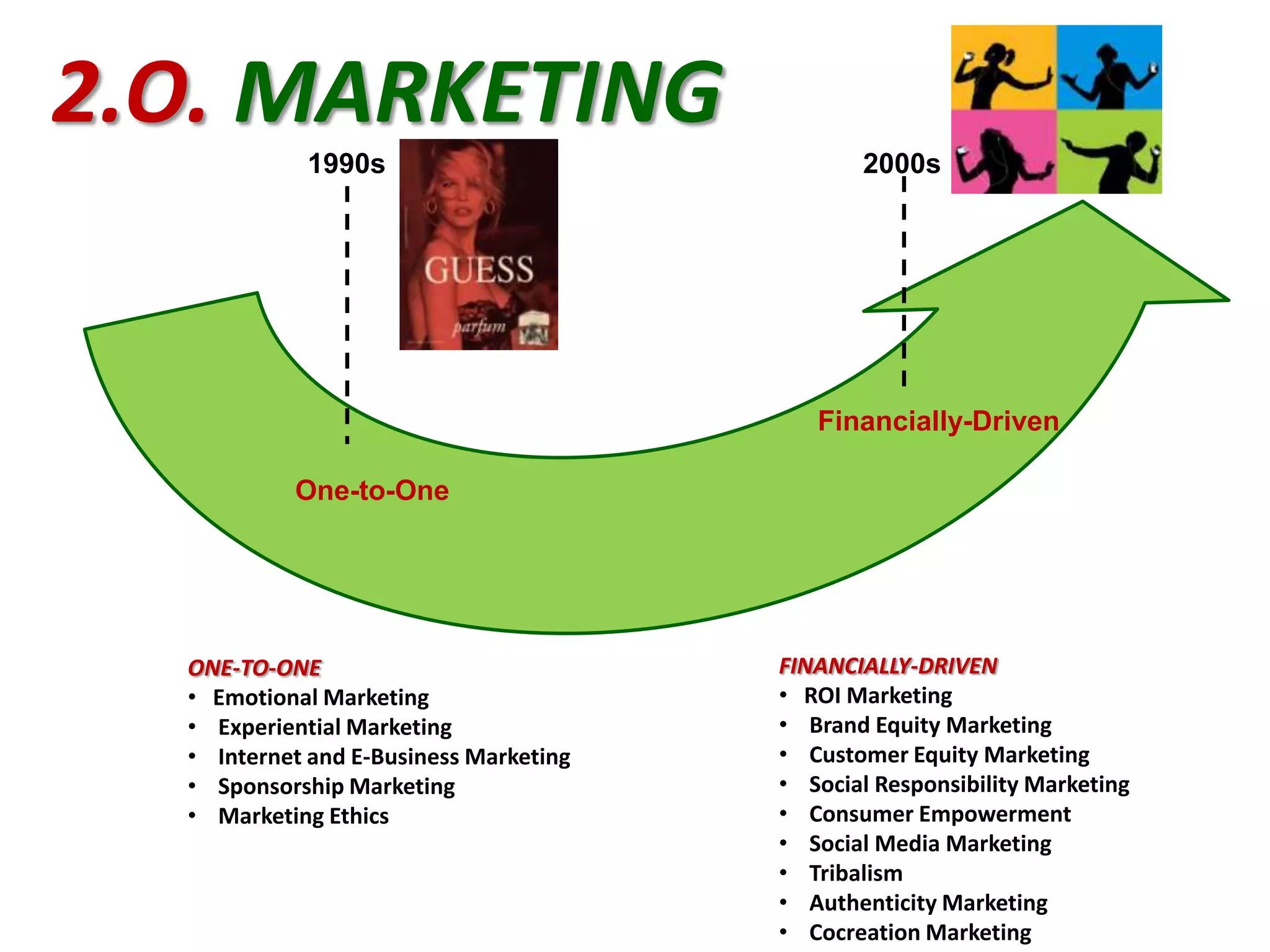
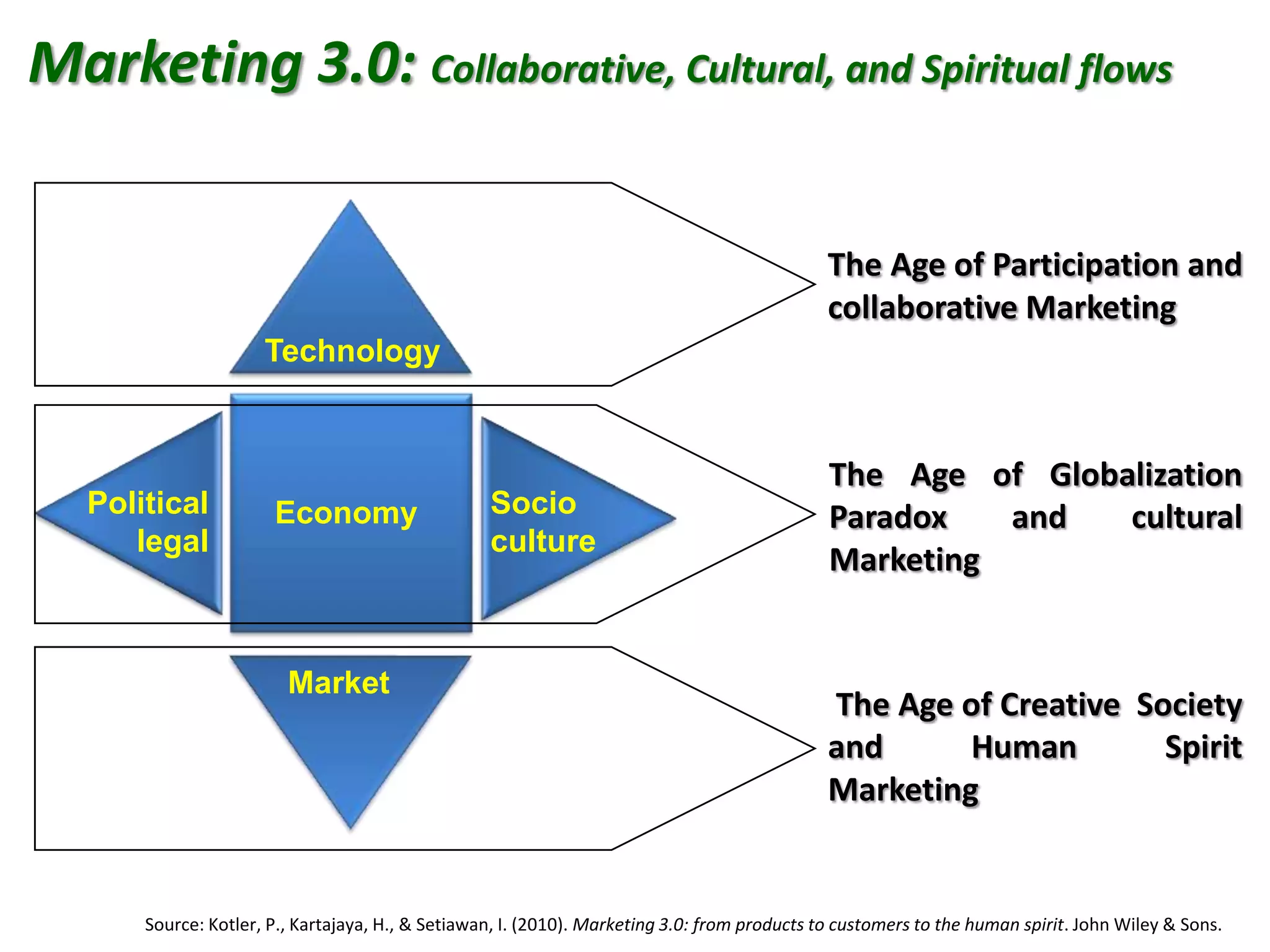
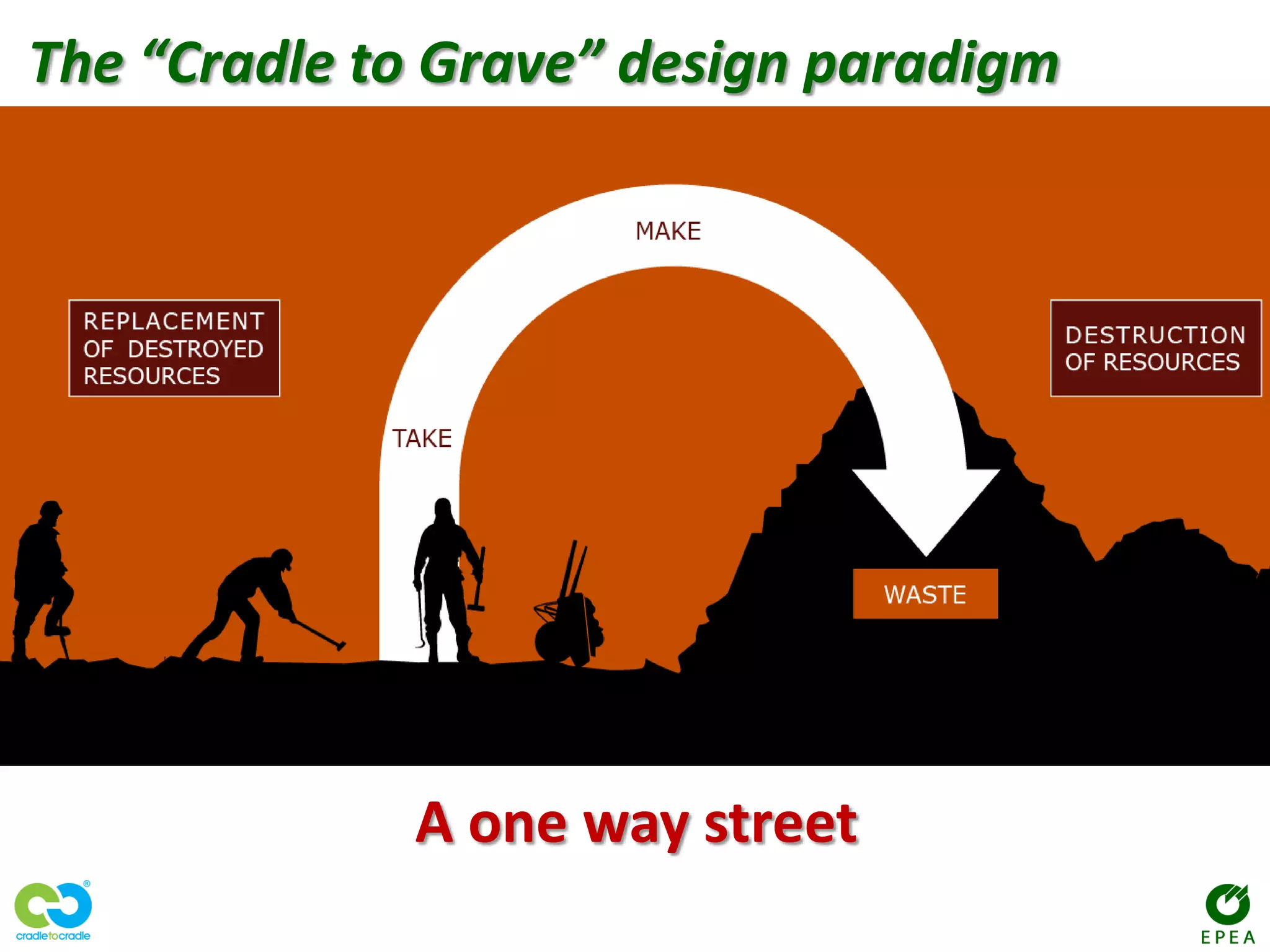
The document discusses the evolution of marketing from versions 1.0 to 3.0. Marketing 1.0 was product-centric and focused on mass production and sales. Marketing 2.0 became more consumer-oriented and enabled by new technologies. Marketing 3.0 aims to make the world a better place by aligning business values with social values and enabling collaboration. It emphasizes sustainability, social responsibility and spiritual well-being over short-term financial goals. The document also outlines some of the changes driving this evolution and examples of companies adopting a Marketing 3.0 approach.