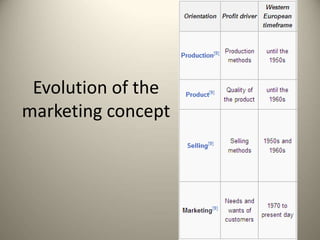
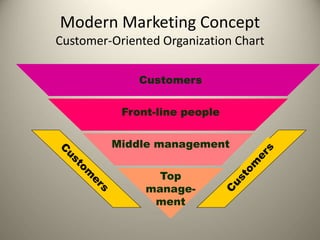
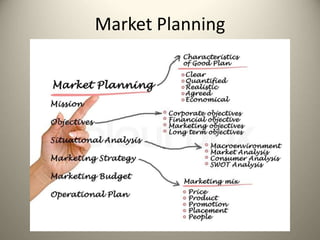
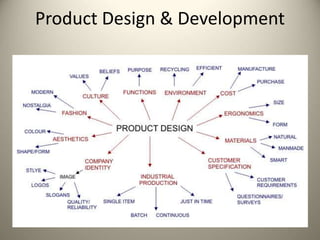
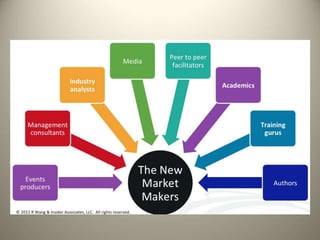
This document provides an overview of the history and evolution of marketing as a field. It discusses how marketing began with early trade and markets, but it was not until the early 1900s that "marketing" emerged as a defined term with the publication of early marketing textbooks. It notes that Aristotle is considered the first marketer for his skills in rhetoric and persuasion. The document also outlines some of the key early contributors who helped develop marketing into the discipline it is today. Finally, it discusses the core concepts that constitute modern marketing management frameworks.