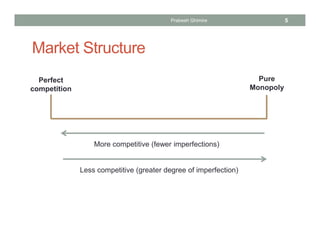
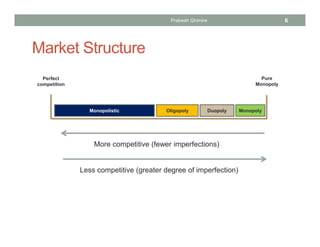
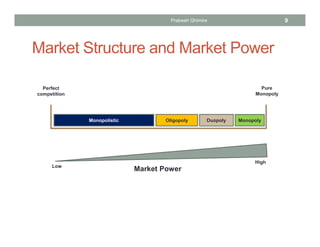
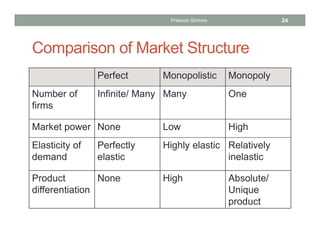
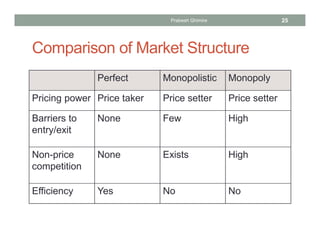
The document discusses different market structures and their corresponding market power, detailing concepts like perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, and monopoly. It evaluates factors that influence market dynamics such as the number of firms, product differentiation, barriers to entry, and non-price competition. The text concludes by comparing characteristics of these market structures in terms of pricing power, elasticity of demand, and efficiency.