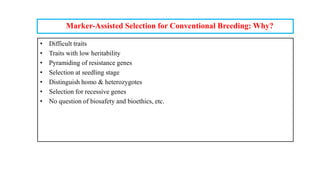
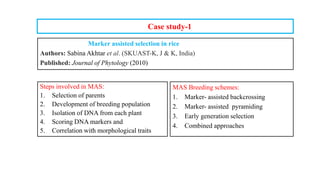
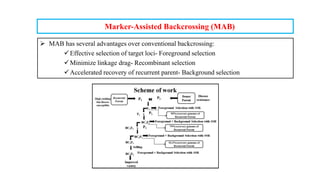
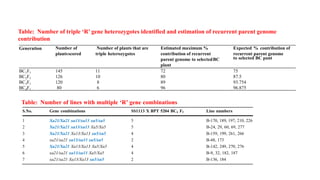
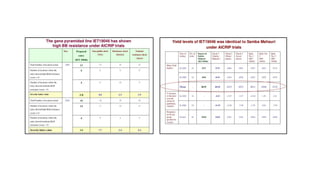
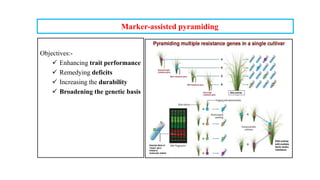
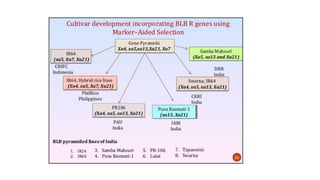
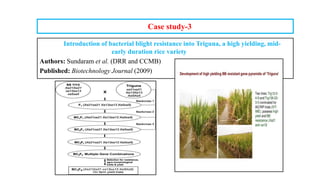
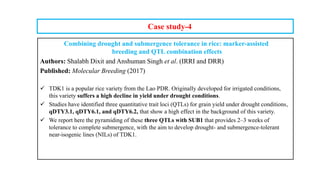
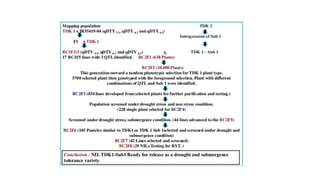
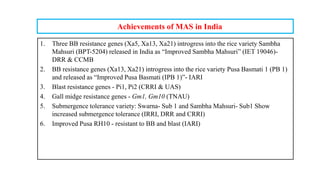
The document discusses marker-assisted breeding methods in rice, highlighting their advantages for selecting desirable traits and increasing efficiency in breeding programs. It presents multiple case studies on the successful integration of disease resistance genes into prominent rice varieties in India, showcasing techniques like marker-assisted backcrossing and pyramiding. The research emphasizes the importance of early generation selection and combining traits to enhance yield and resilience against environmental stressors.