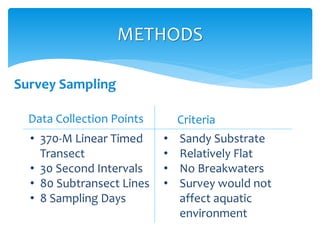
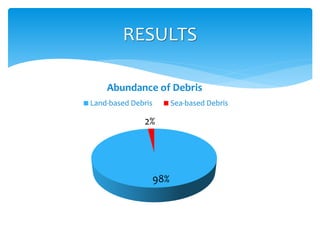
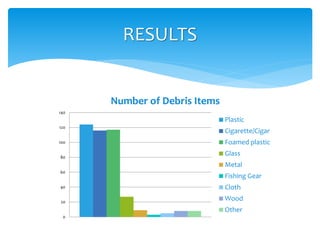
This document summarizes a study on marine debris found on beaches. The study hypothesized that land-based debris would be more abundant on beaches than sea-based debris. Through surveys of sandy beaches along saltwater and freshwater shorelines, the study found that 98% of debris was from land-based sources, primarily plastic. The document discusses the environmental and economic impacts of marine debris, such as threats to wildlife, contaminated water, and decreased tourism. It calls for global action through increased research, education, and efforts by communities and individuals to help address the growing problem of marine debris.