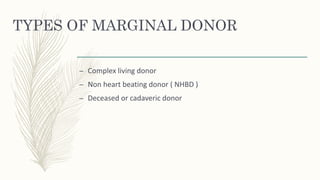
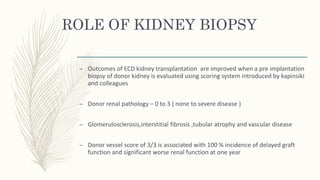
Renal transplant is crucial for patients with end-stage renal disease, yet there is a significant gap between the demand for and supply of donor kidneys, leading to the use of marginal donors to increase availability. These marginal donors include those with suboptimal kidney function or health risks, and while they may result in inferior outcomes compared to standard criteria donors, they still provide a survival advantage over patients awaiting transplants. Effective management protocols are essential for the transplantation of these kidneys, focusing on nephron protection and tailored immunosuppression strategies to improve outcomes.