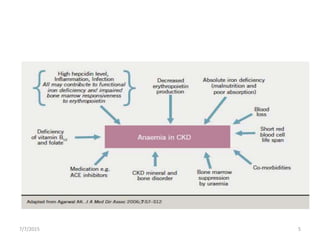
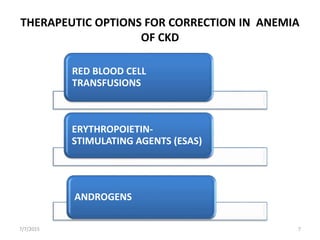
This document discusses the management of anemia in chronic kidney disease (CKD). It begins by defining anemia and its causes in CKD, which include reduced erythropoietin production and decreased red blood cell survival due to kidney failure. Left untreated, anemia in CKD can lead to deterioration in cardiac function, impaired cognition, and increased fatigue and mortality risk. The main therapeutic options for treating anemia in CKD are red blood cell transfusions, androgens, and erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs). ESAs such as epoetin alfa and darbepoetin alfa are now the standard treatment as they reduce transfusion needs and risks while helping to mobilize