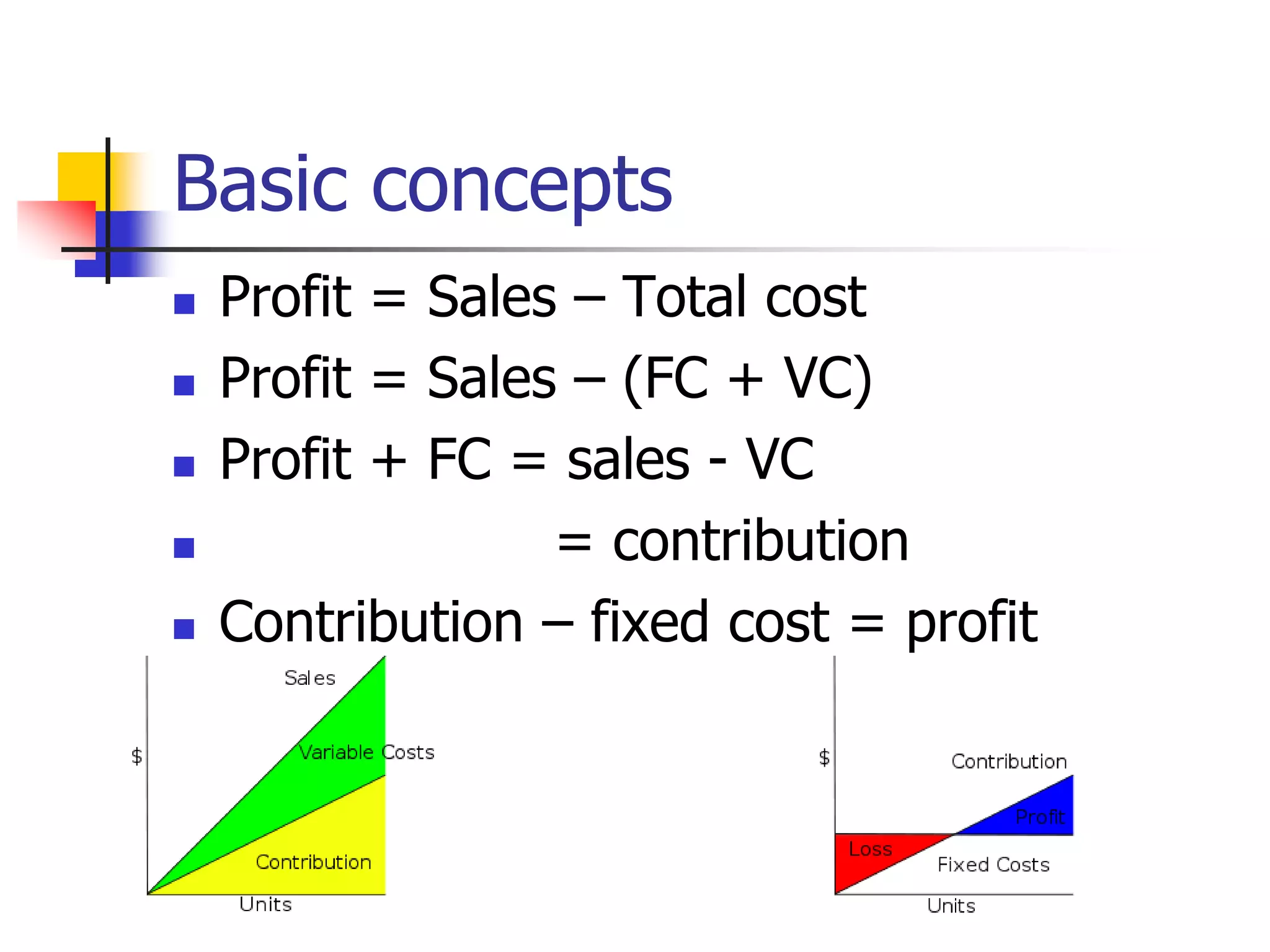
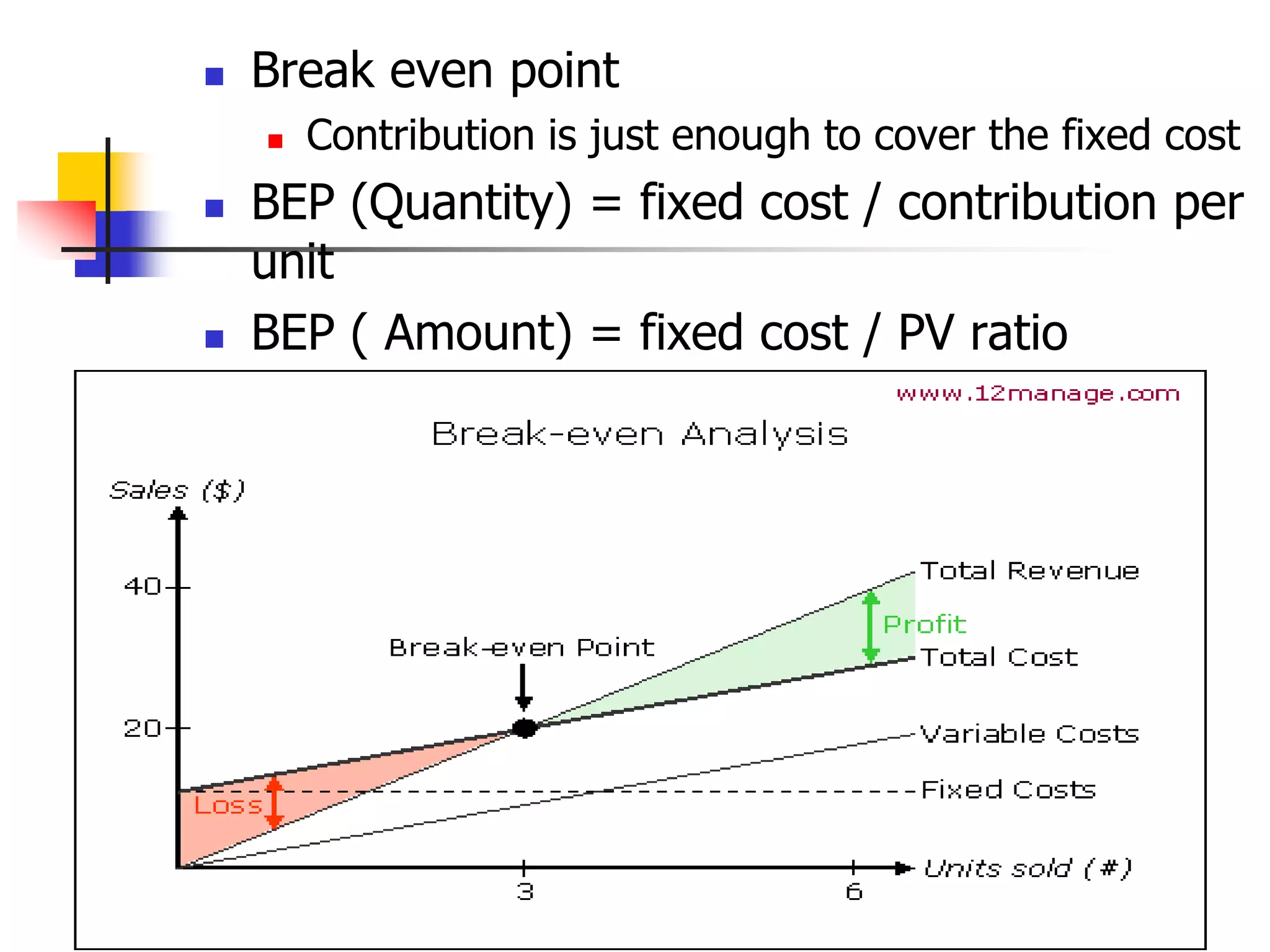
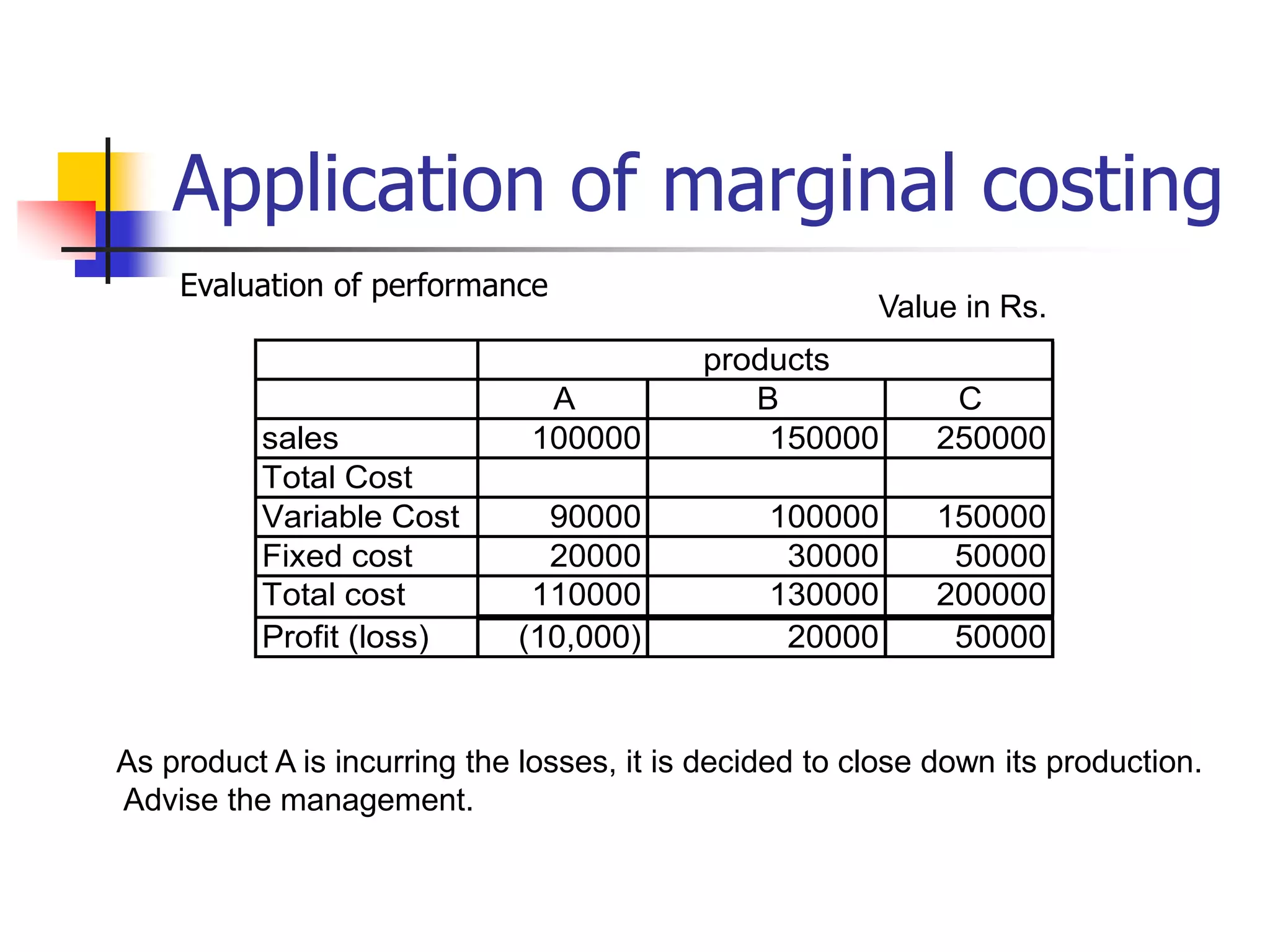
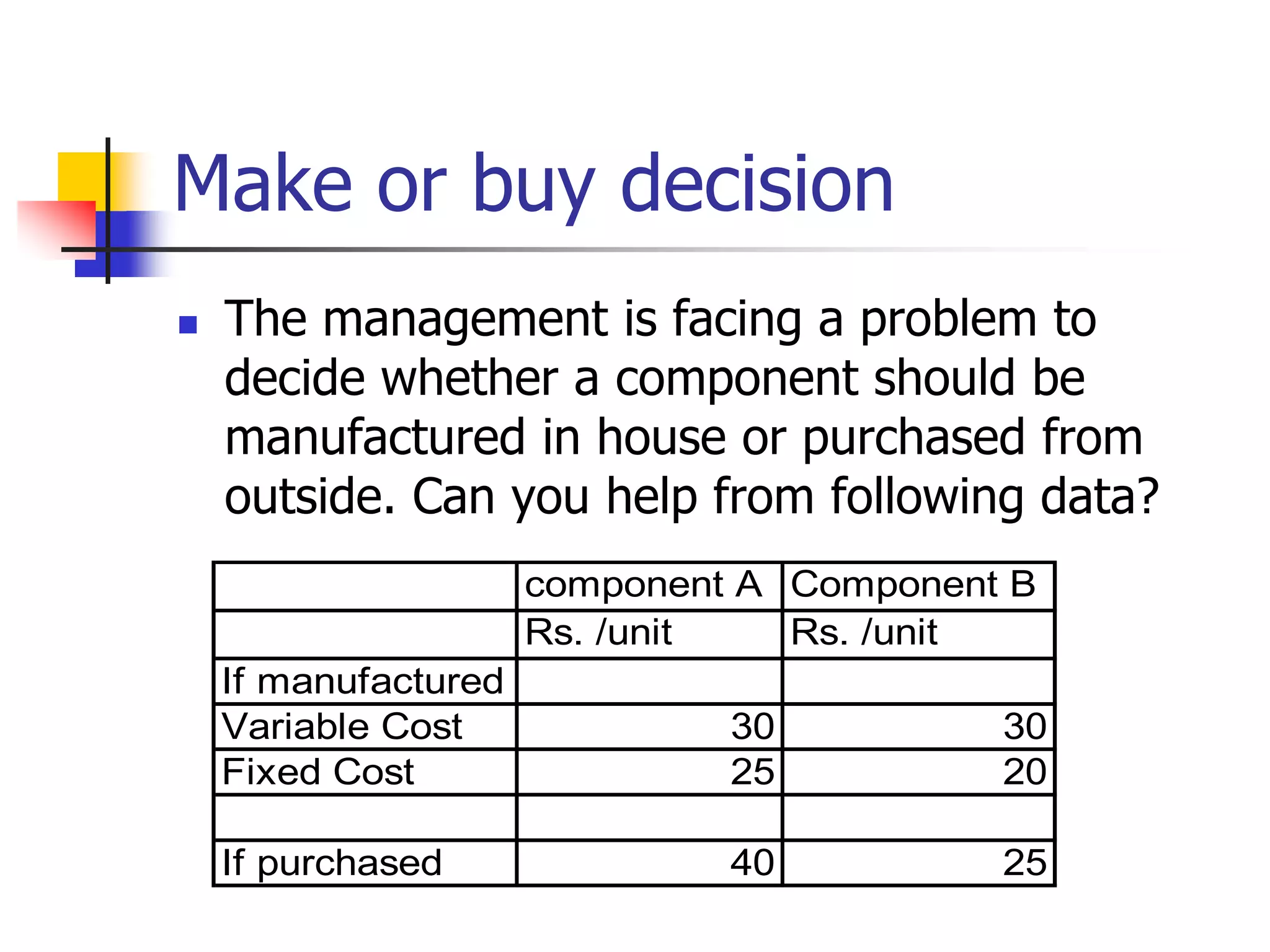
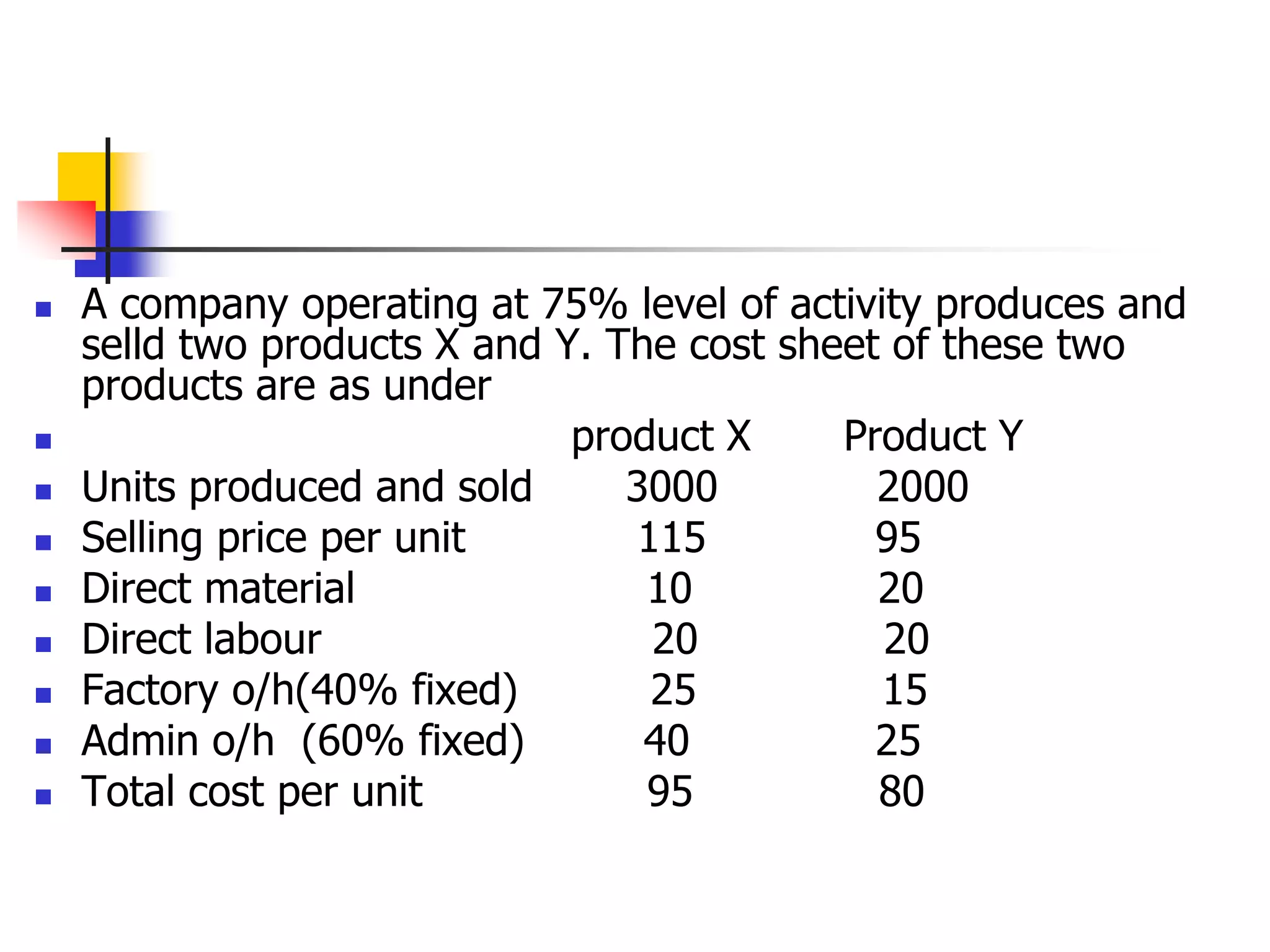
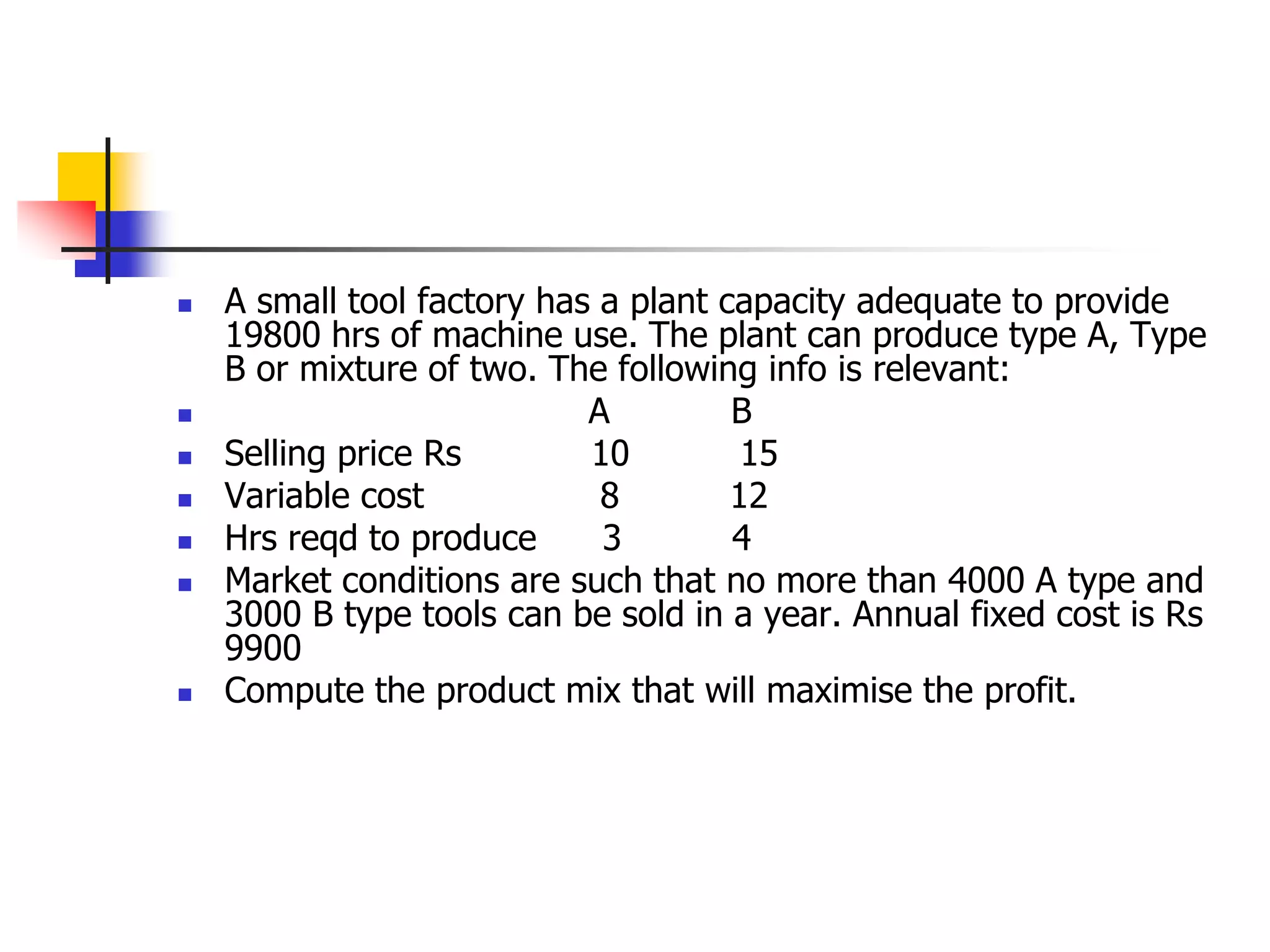
Marginal costing involves differentiating between fixed and variable costs to determine the marginal costs and the effect on profit of changes in output volume and type. An operating statement shows sales, marginal costs subtracted to get contribution, and fixed costs subtracted from contribution to get profit. Basic concepts include defining profit, contribution, profit volume ratio, break-even point, and margin of safety in determining production and pricing decisions.