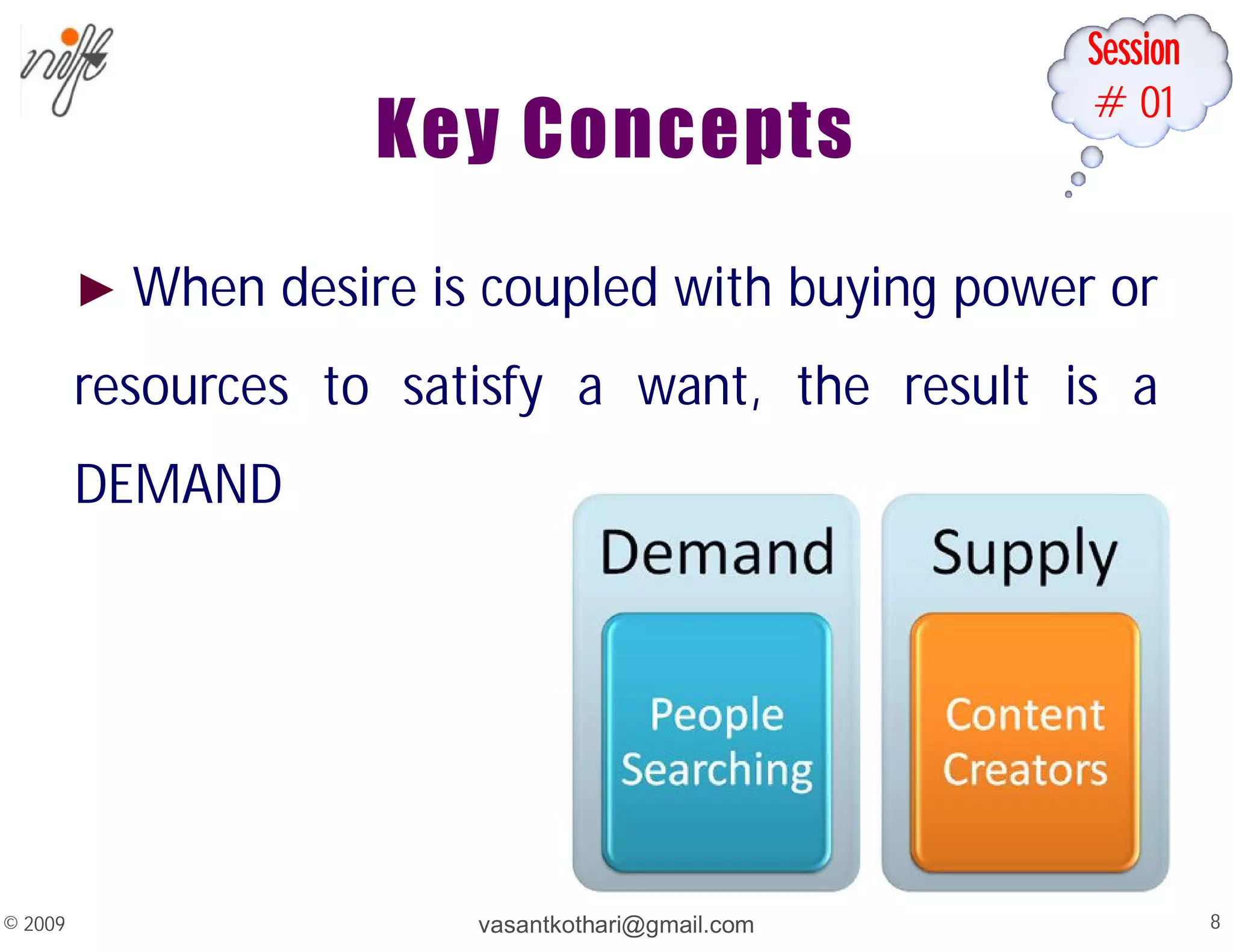
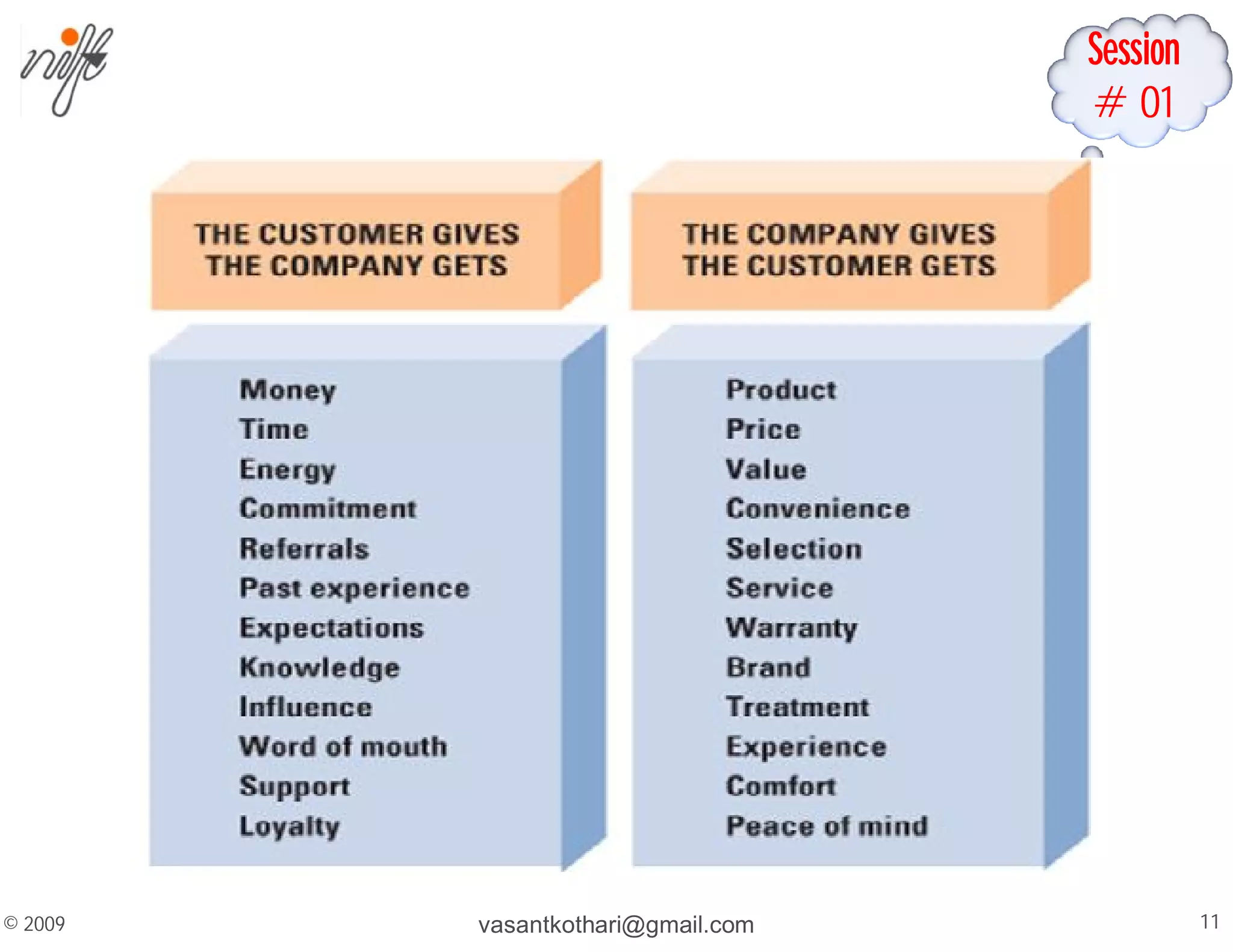
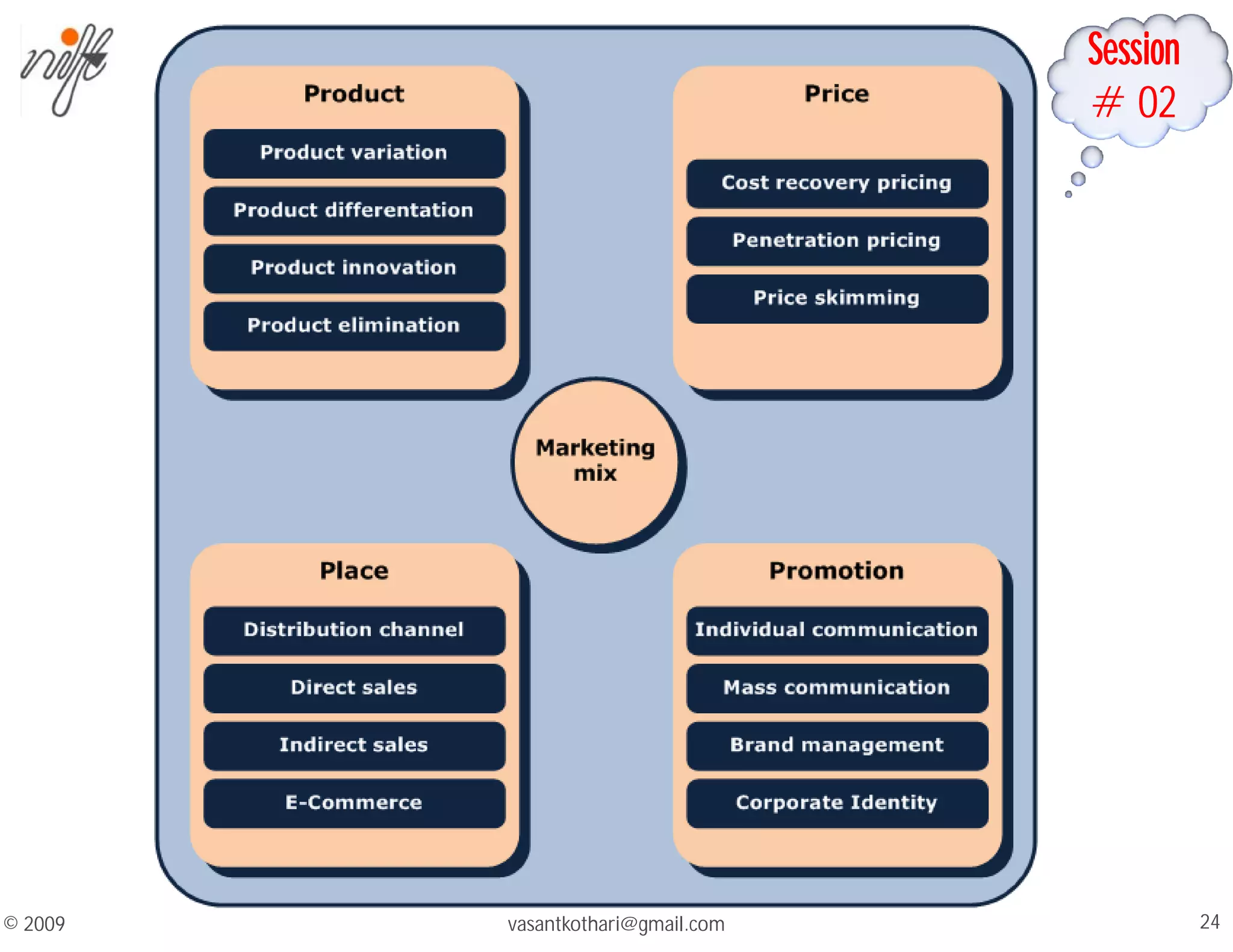
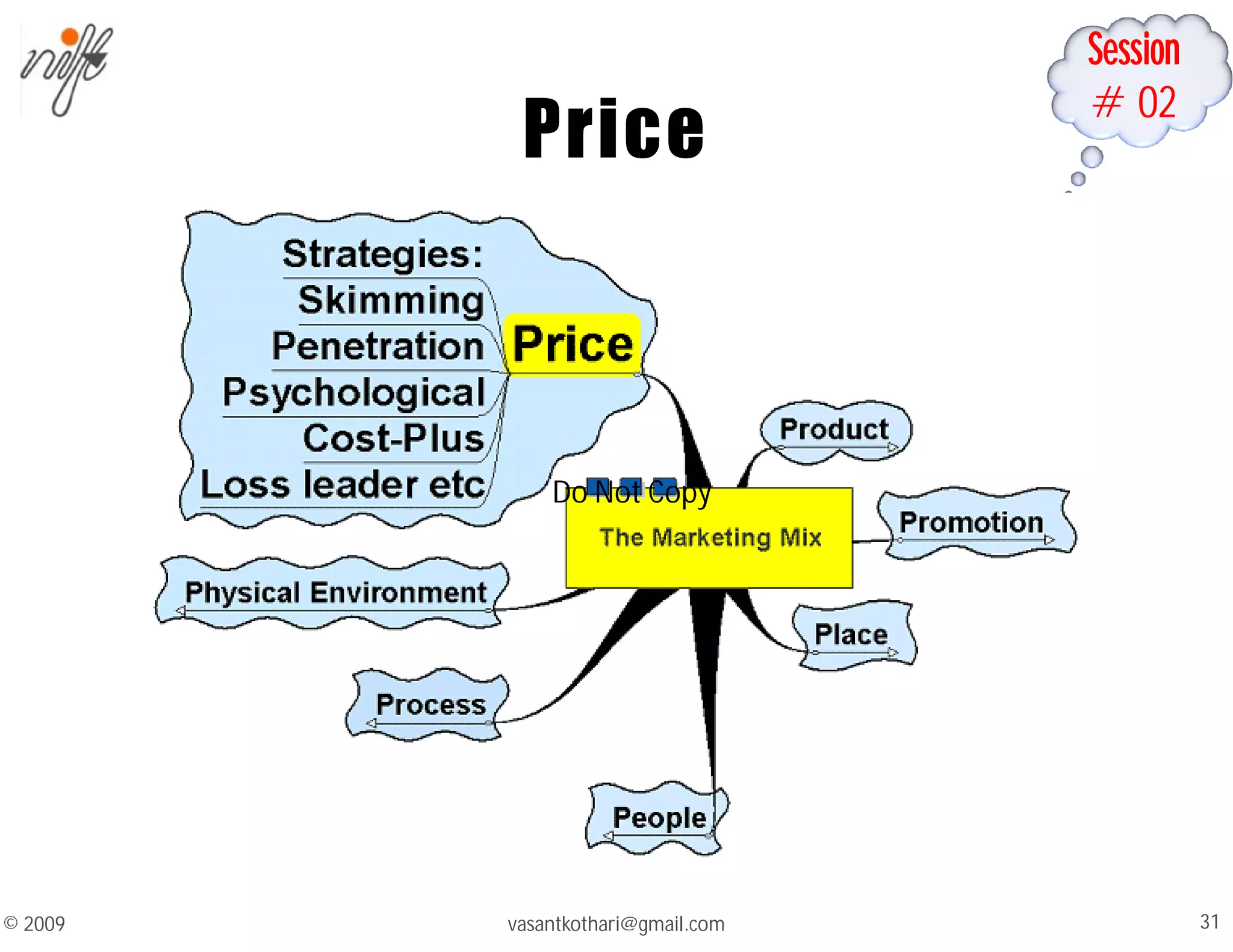
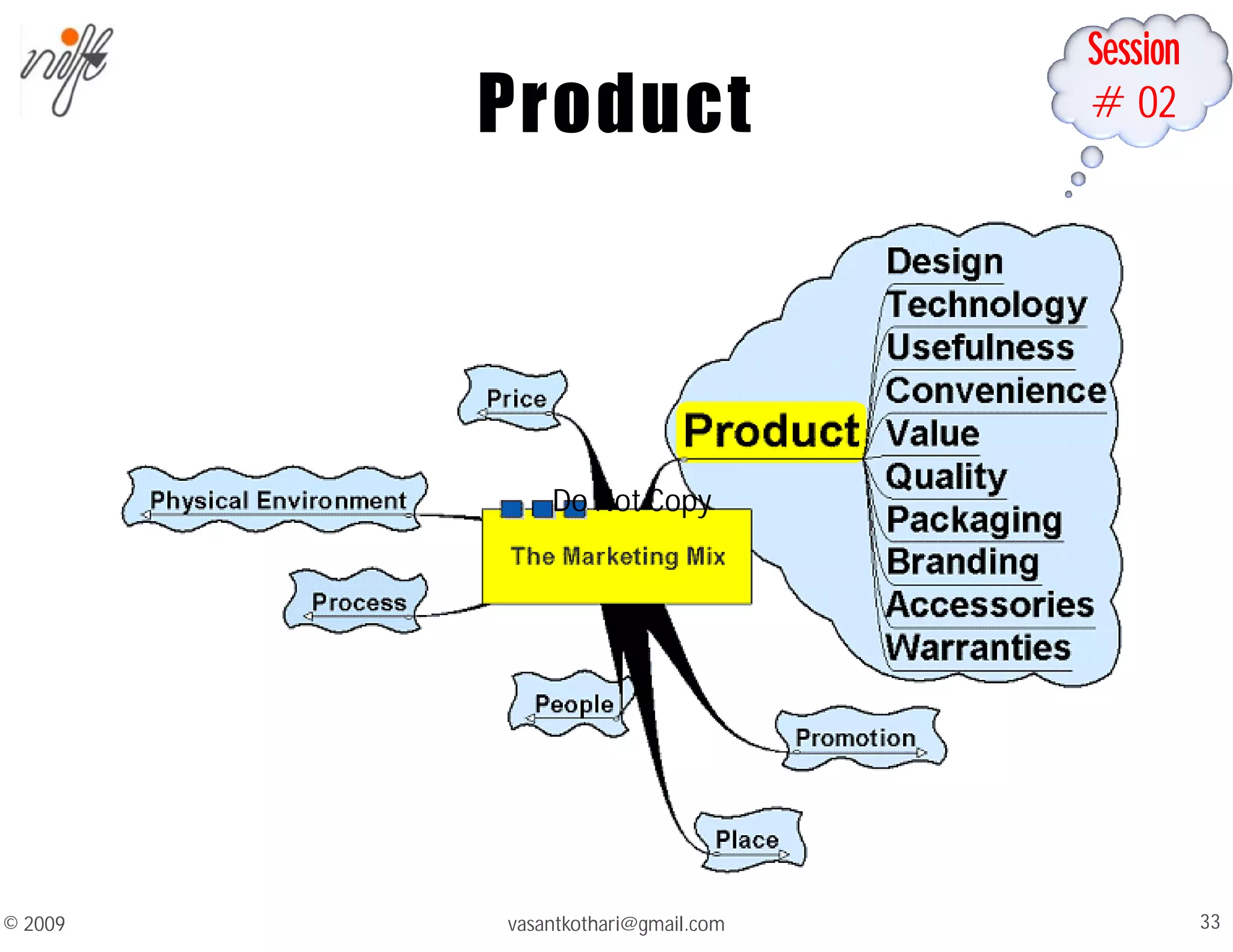
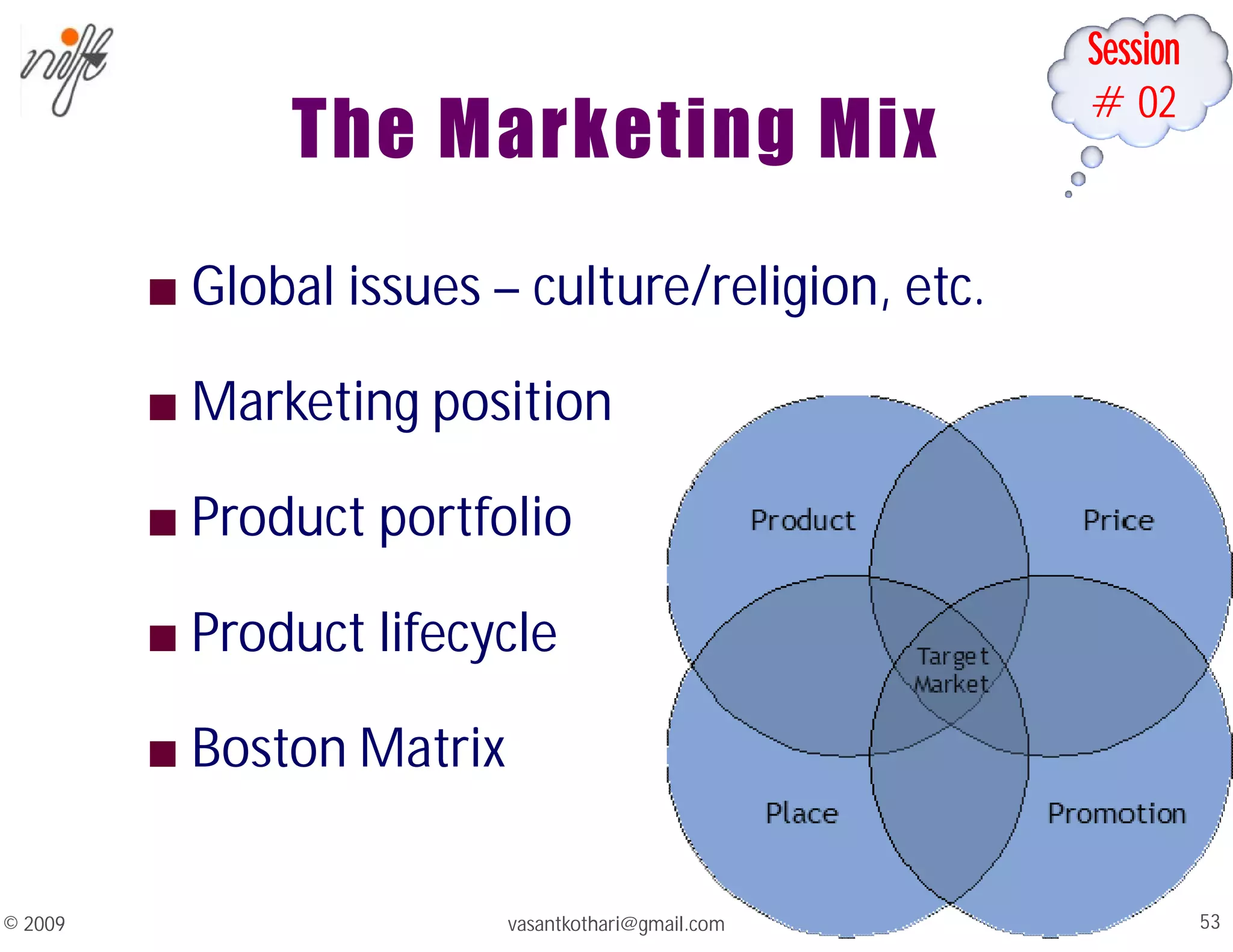
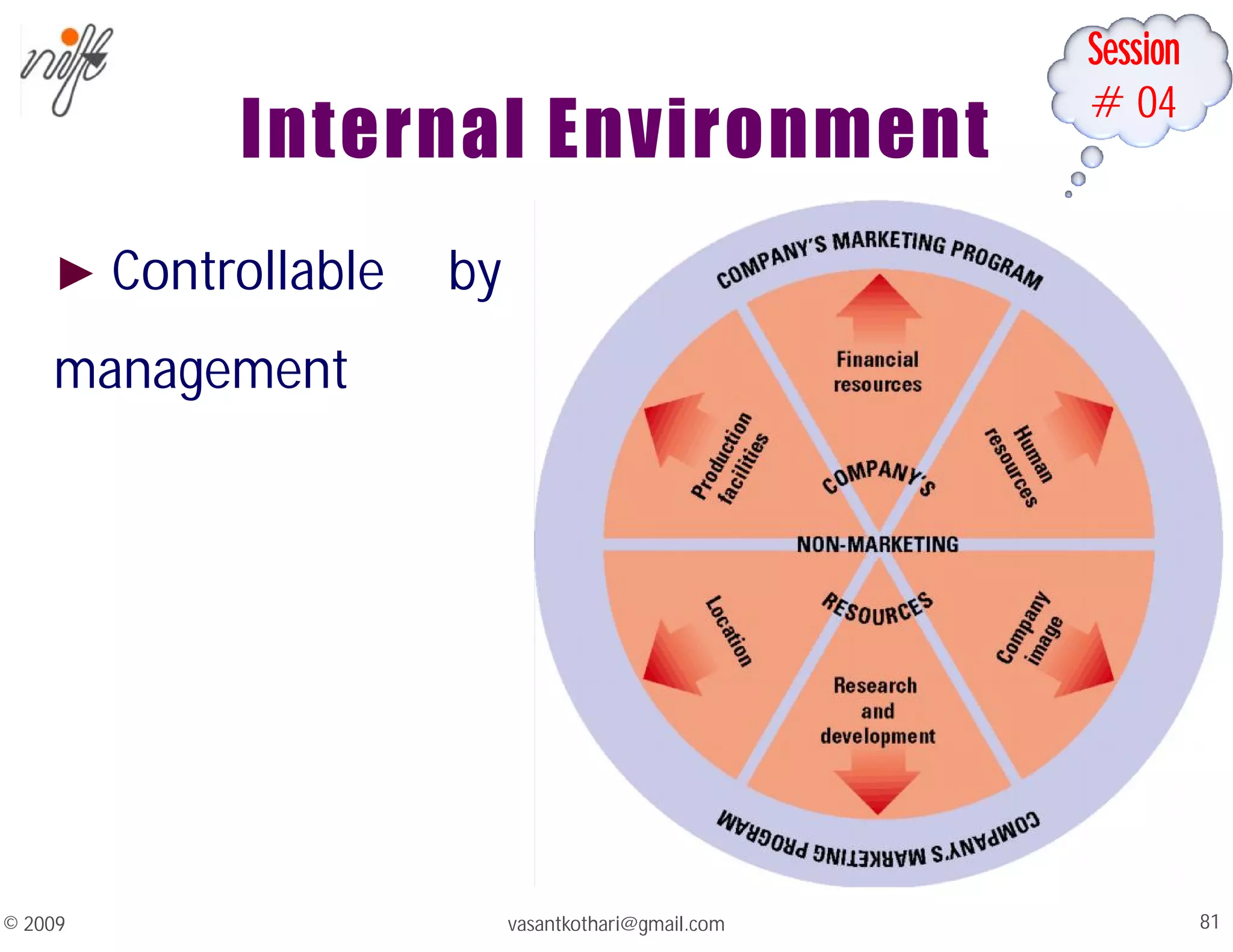
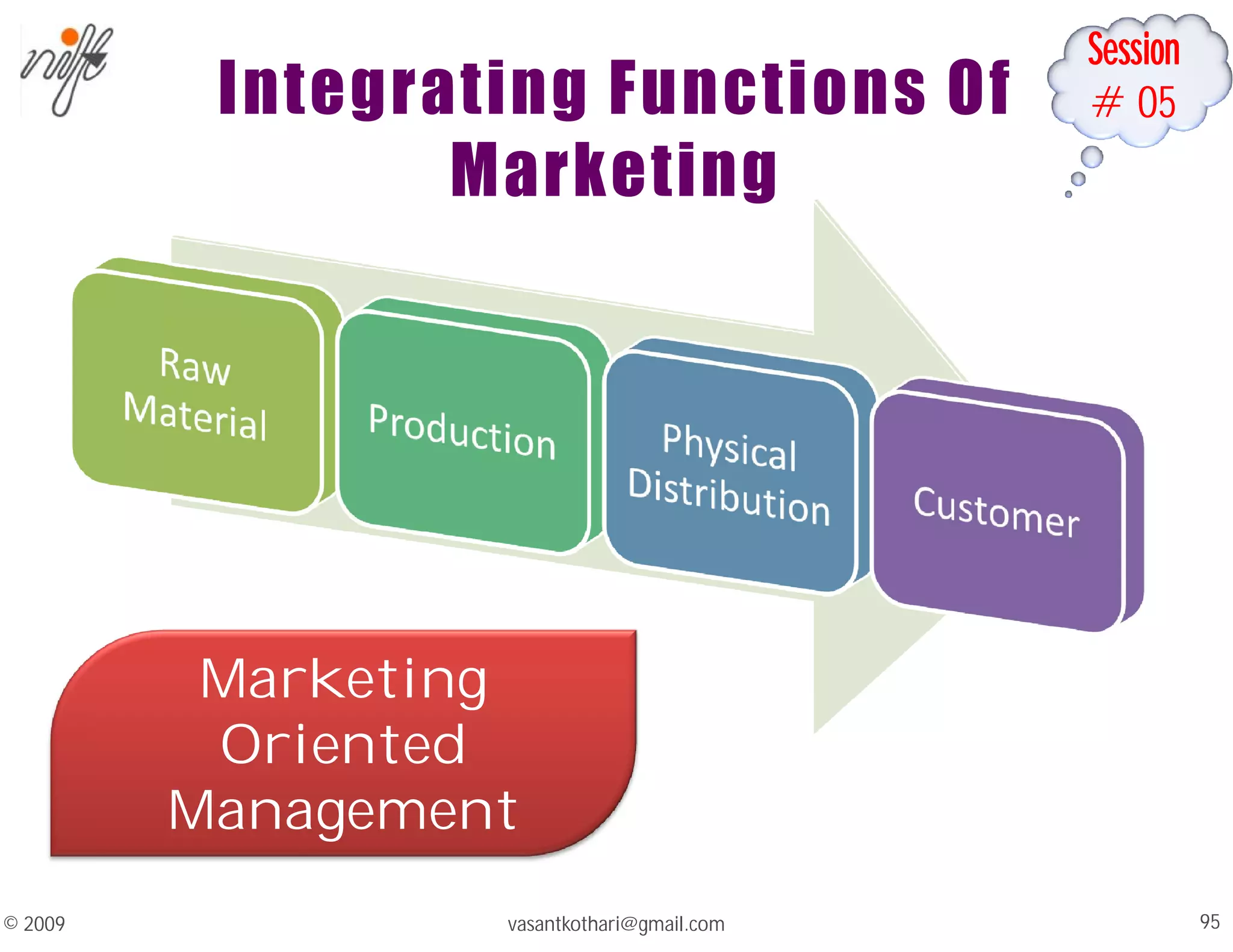
This document contains a syllabus and lecture slides for a marketing course. The syllabus covers topics like the marketing mix, selling vs marketing, and the marketing environment. The lecture slides define key marketing concepts such as needs, wants, demands and the marketing mix which includes the traditional 4Ps of product, price, place and promotion as well as expanded versions. It also discusses the differences between selling and marketing, with selling focusing on products and short-term profits, while marketing focuses on understanding customer needs and achieving long-term customer satisfaction.