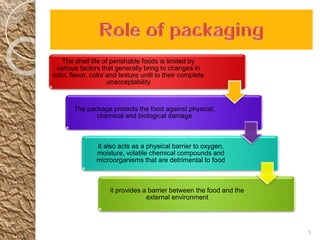
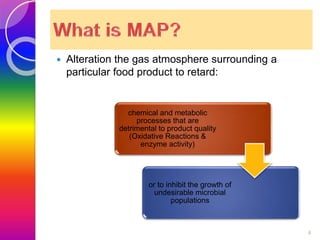
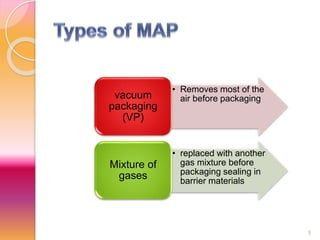
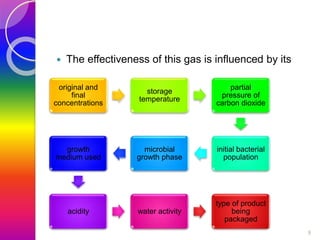
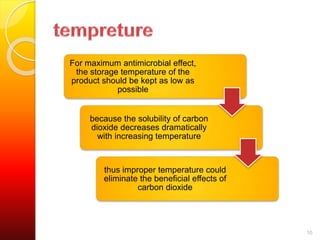
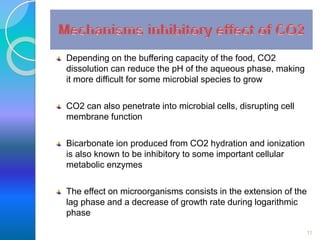
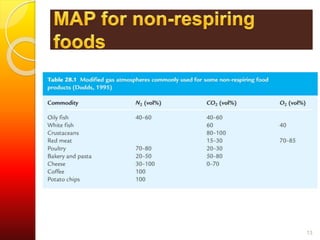
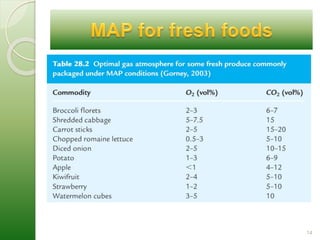
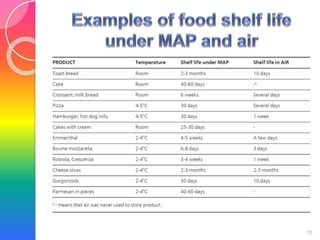
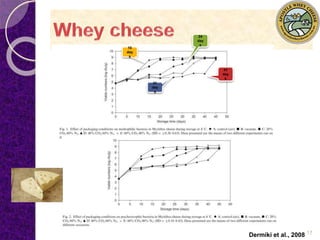
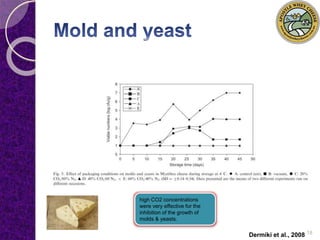
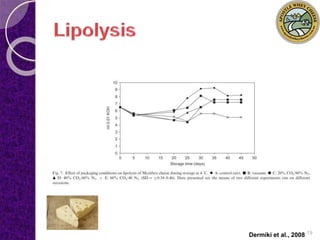
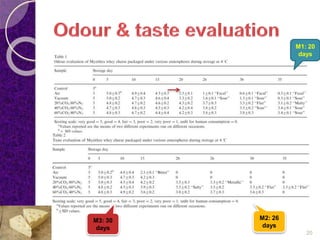
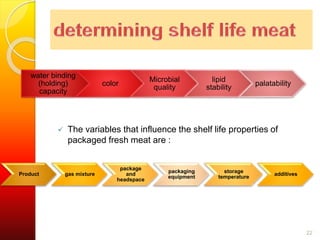
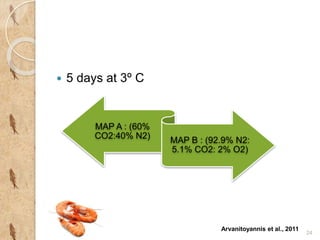
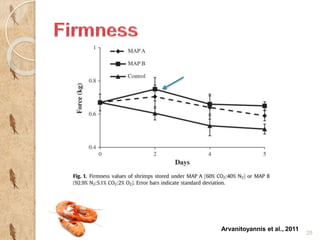
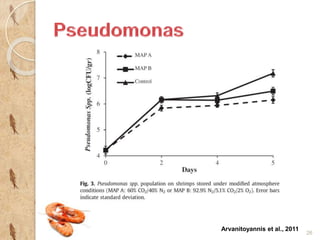
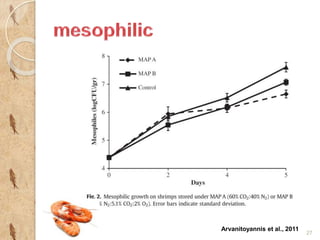
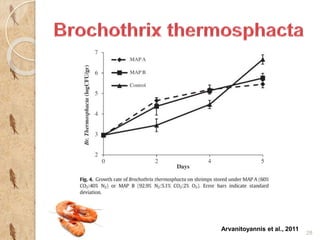
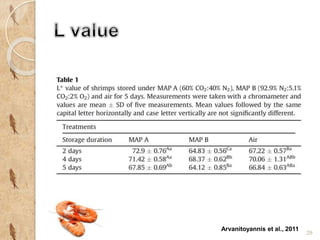
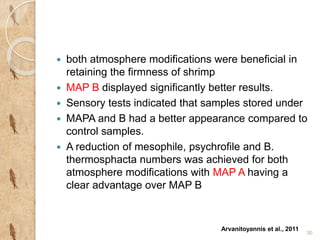
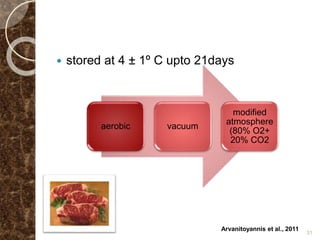
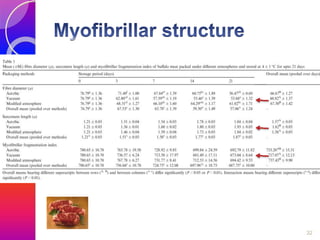
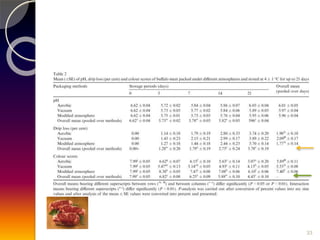
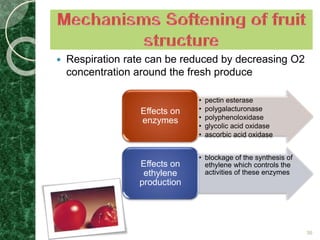
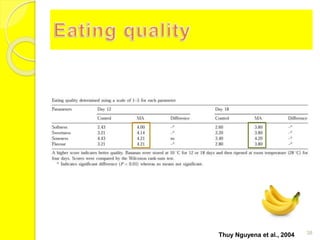
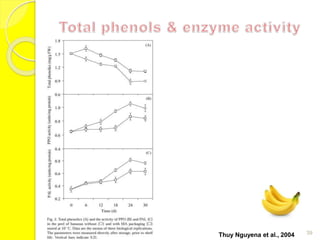
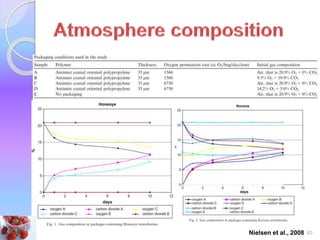
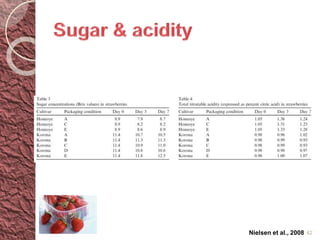
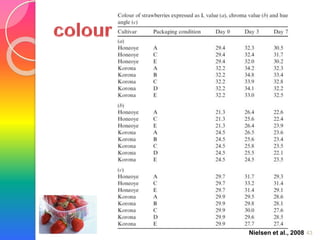
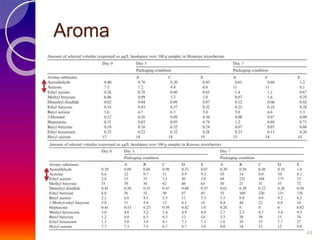
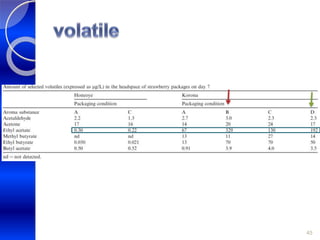
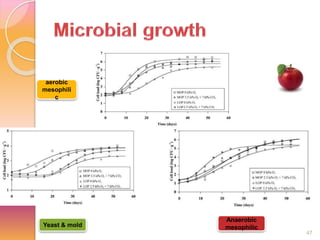
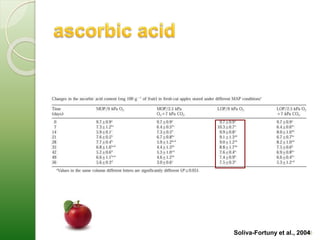
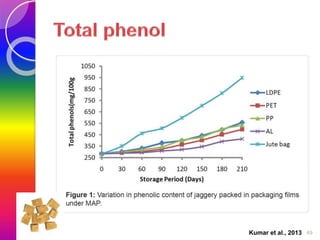
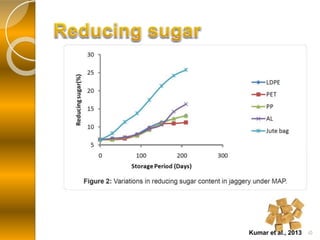
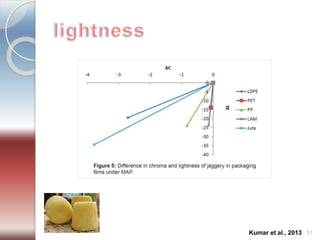
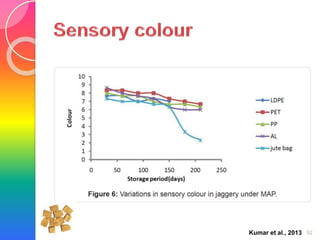
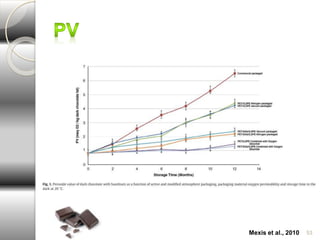
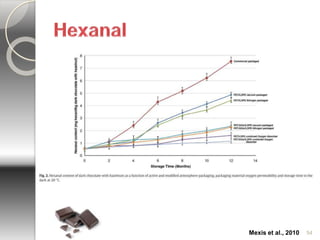
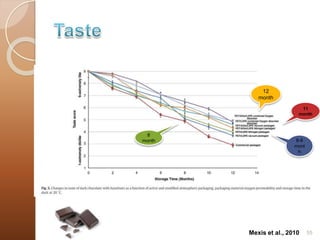
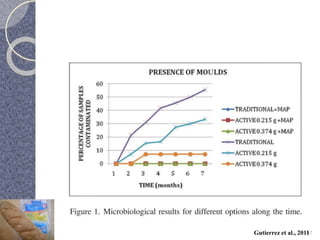
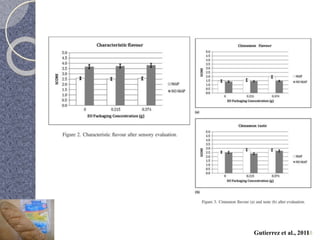
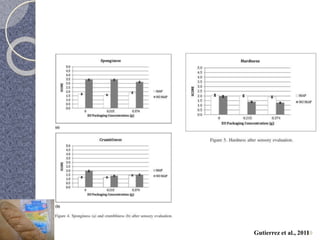
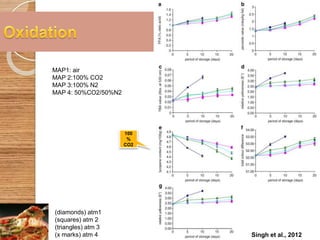
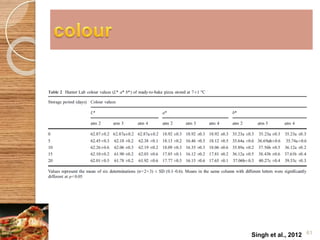
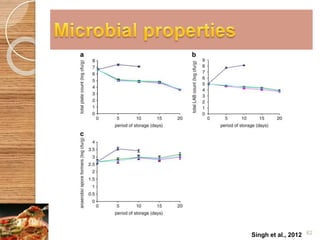
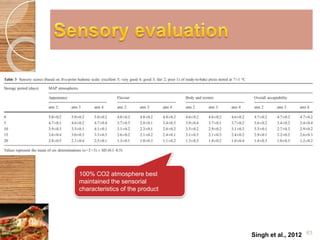
MAP involves altering the gas atmosphere surrounding food products to inhibit microbial growth and deteriorative chemical/enzymatic reactions. It extends shelf life by slowing respiration and ethylene production rates. The document discusses MAP applications for various foods like dairy, meat, produce and bakery products. It also examines how different gas mixtures, storage temperatures and other factors influence MAP effectiveness for specific foods. Overall, MAP is shown to increase shelf life and reduce waste while maintaining quality attributes like color, texture and aroma compared to traditional packaging methods.