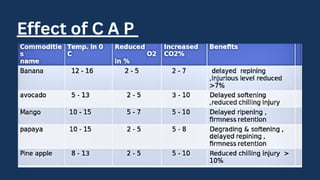
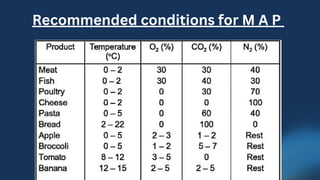
Controlled atmospheric (CA) and modified atmospheric packaging (MAP) can preserve quality and reduce losses of tropical fruits and vegetables during transport and storage by maintaining optimal temperature and humidity. CA and MAP reduce respiration and ethylene production to delay ripening. MAP involves flushing out air from packaging and replacing it with gases like carbon dioxide and nitrogen to extend shelf life while maintaining sensory attributes. The gases inhibit microbial growth and reduce the need for preservatives. Equipment like gas analyzers and packaging machines are required to implement CA and MAP.