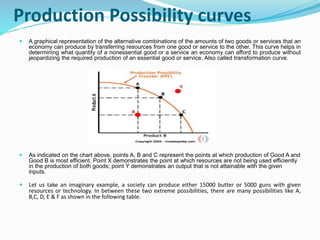
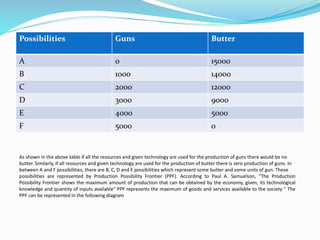
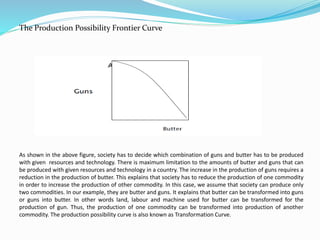
This document provides an overview of macroeconomics and its development. It discusses the classical, Keynesian, post-Keynesian, monetarist, and new Keynesian schools of macroeconomic thought. The classical school holds that markets always clear and unemployment is voluntary. Keynesians focus on managing aggregate demand and believe governments can stabilize business cycles through fiscal and monetary policy. Monetarists believe the role of government is controlling inflation through money supply and that markets typically clear. New Keynesians add microeconomic foundations to traditional Keynesian theories while recognizing some market rigidities. The document also outlines the divisions of microeconomics and macroeconomics and provides examples of areas studied in each field.






















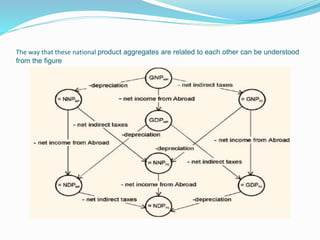
![ We can sum up the differences between gross and net, market
prices and factor cost and national and domestic concepts in the
following way:
Gross=Net + Depreciation
Market Prices=Factor Cost + [Indirect Taxes - Subsidies]
National=Domestic + Net Factor Income from Abroad
There are some national product aggregates that are more
frequently met with and we have several ways of ordering them.
One of these is as follows:
i. Gross domestic product at market price + net factor income
from abroad equals
ii. Gross national product at market prices - net indirect taxes
(indirect taxes - subsidies) equals
iii. Gross national product at factor cost - capital consumption
(depreciation) equalsiv. Net national product at factor cost,
which is popularly known as national income.
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mba2-170729105606/85/Mba-2-27-320.jpg)



