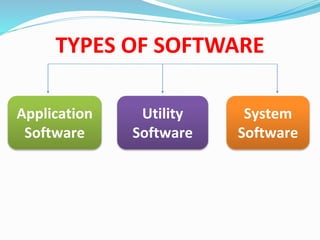
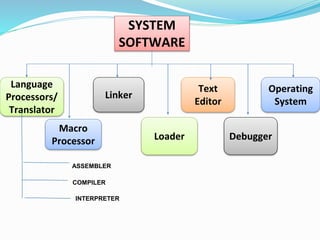
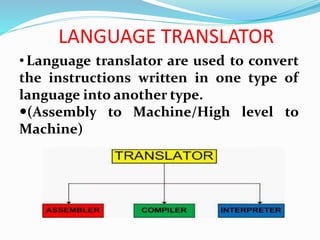
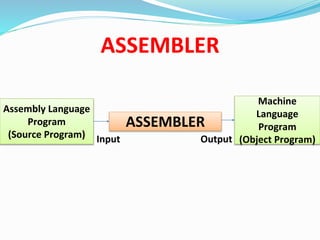
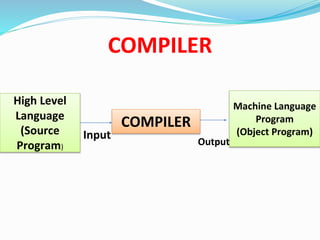
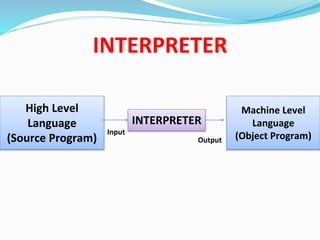
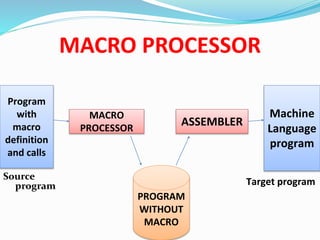
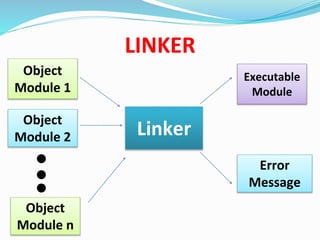
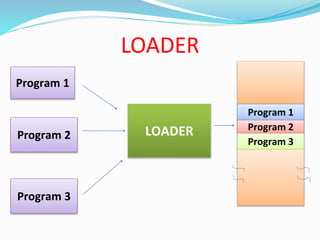
This document discusses different types of software and system software. It defines hardware as the physical components of a computer and software as programs that enhance hardware capabilities. There are three main types of software: application software designed for specific tasks, utility software for system maintenance, and system software that controls computer operations but does not solve specific problems. System software includes language translators like assemblers, compilers, and interpreters; macro processors; linkers; loaders; text editors; debuggers; and the operating system.