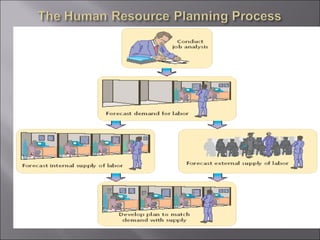
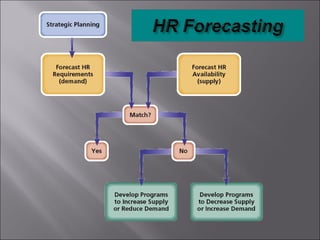
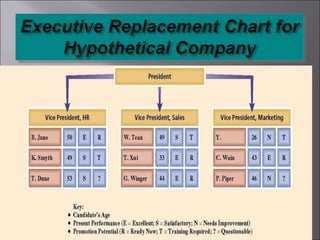
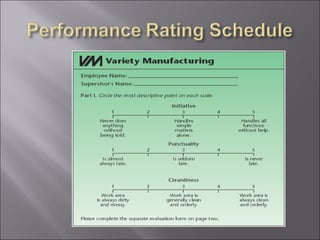
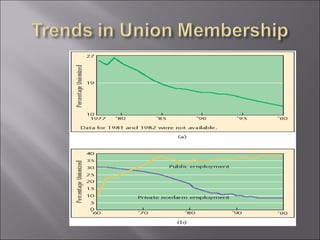
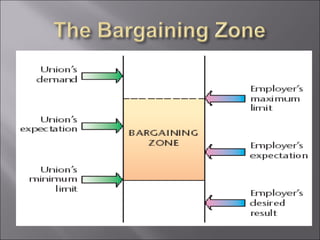
The document discusses key topics in human resource management including staffing the organization, developing the workforce, compensation and benefits, the legal context of HR, and dealing with organized labor and collective bargaining. It covers job analysis and forecasting labor supply for staffing, as well as recruiting, selecting, training, and evaluating employees. Compensation topics include wages, salaries, bonuses, and benefits. Legal issues around discrimination, equal employment opportunity, and workplace safety are also addressed. The document concludes by covering trends in unions, collective bargaining issues, and types of labor actions and dispute resolution.