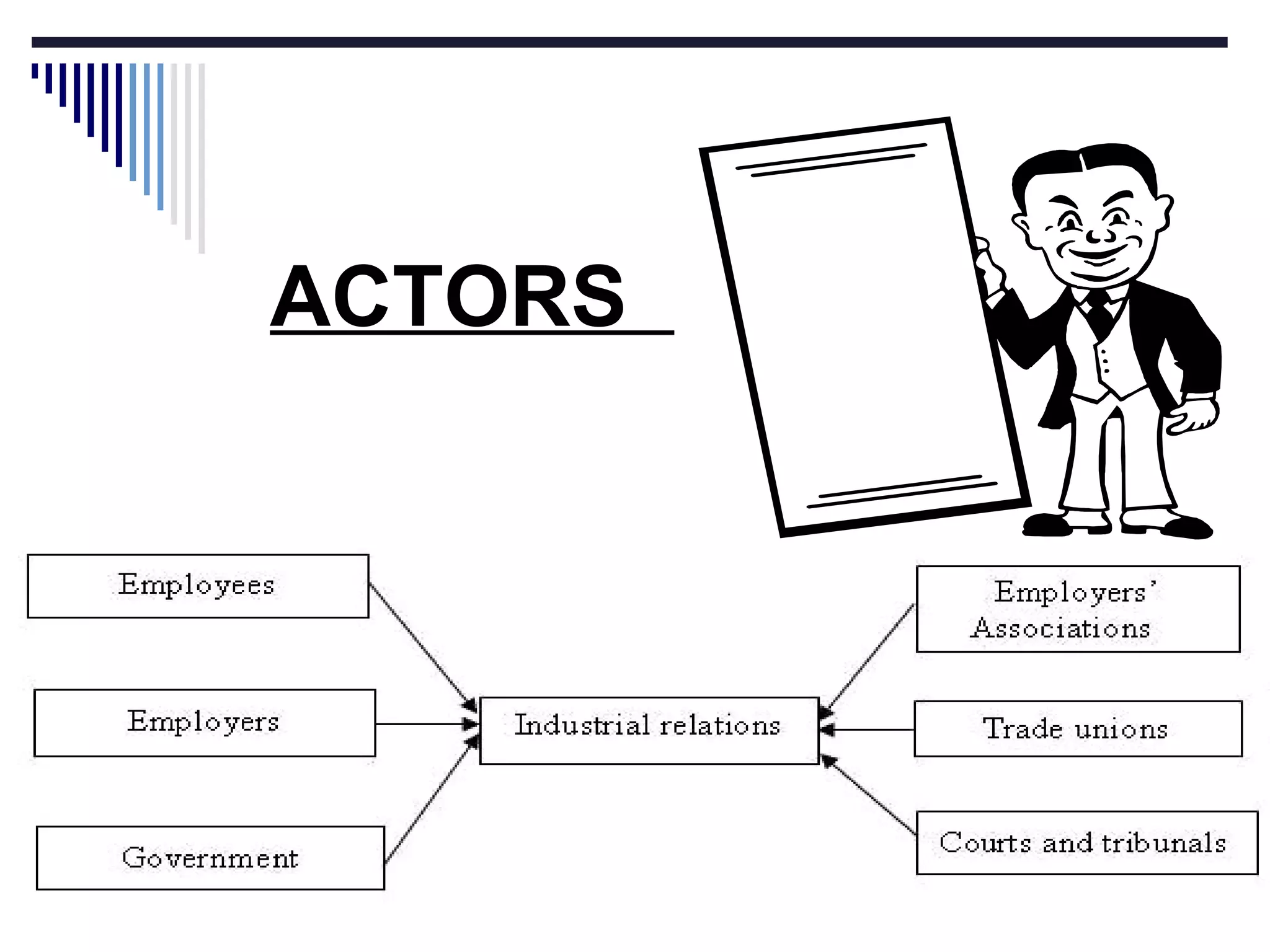
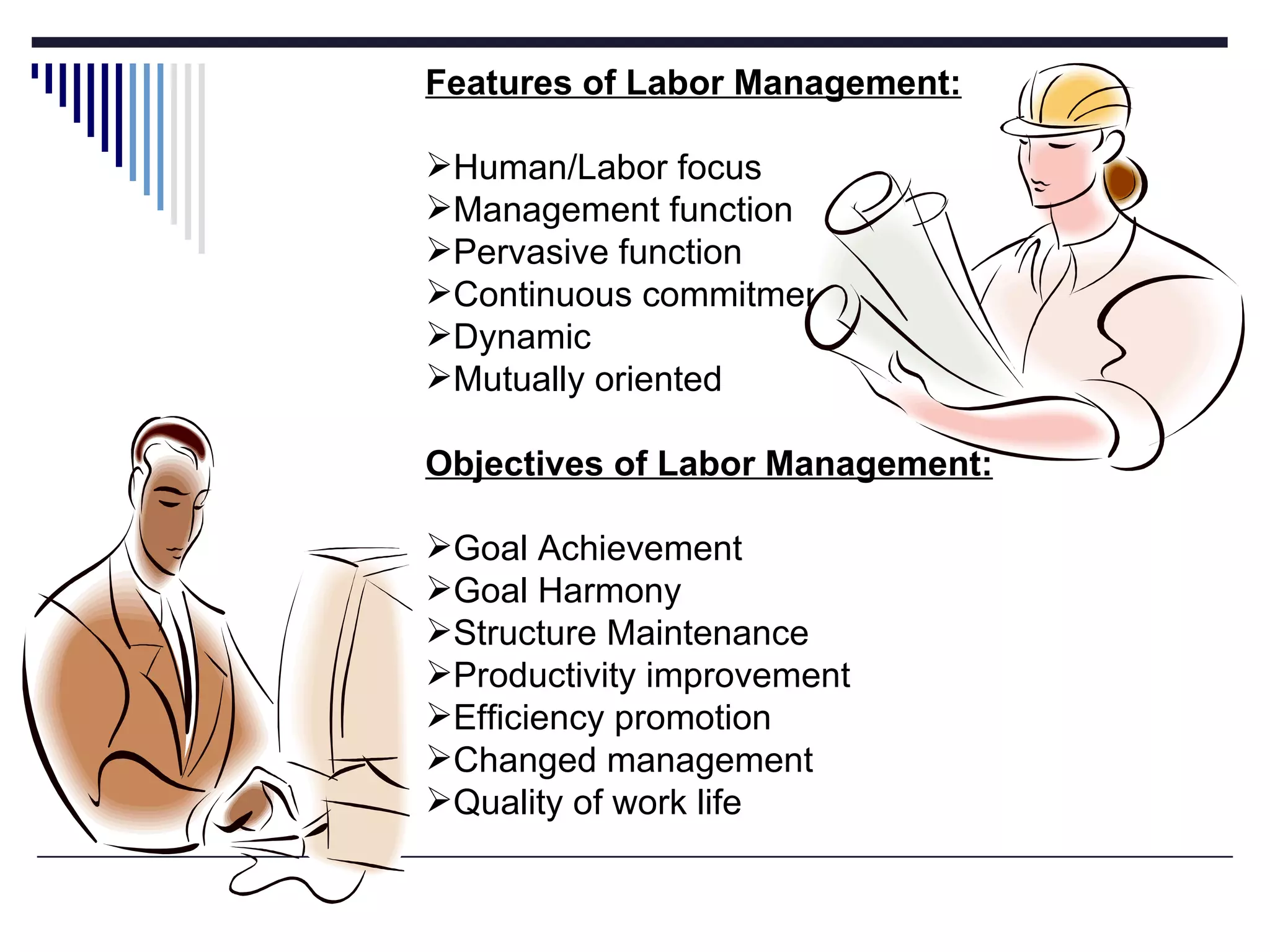
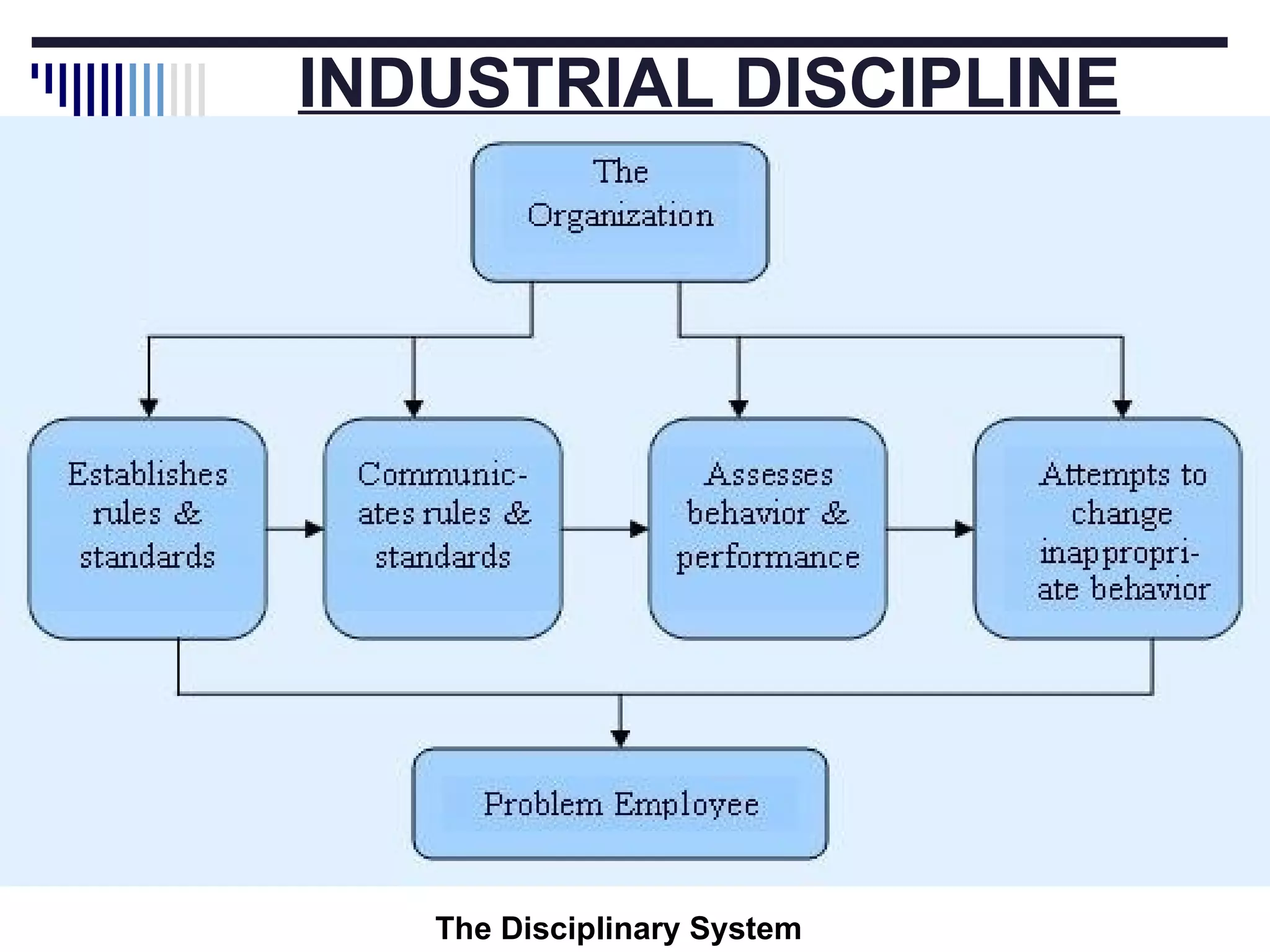
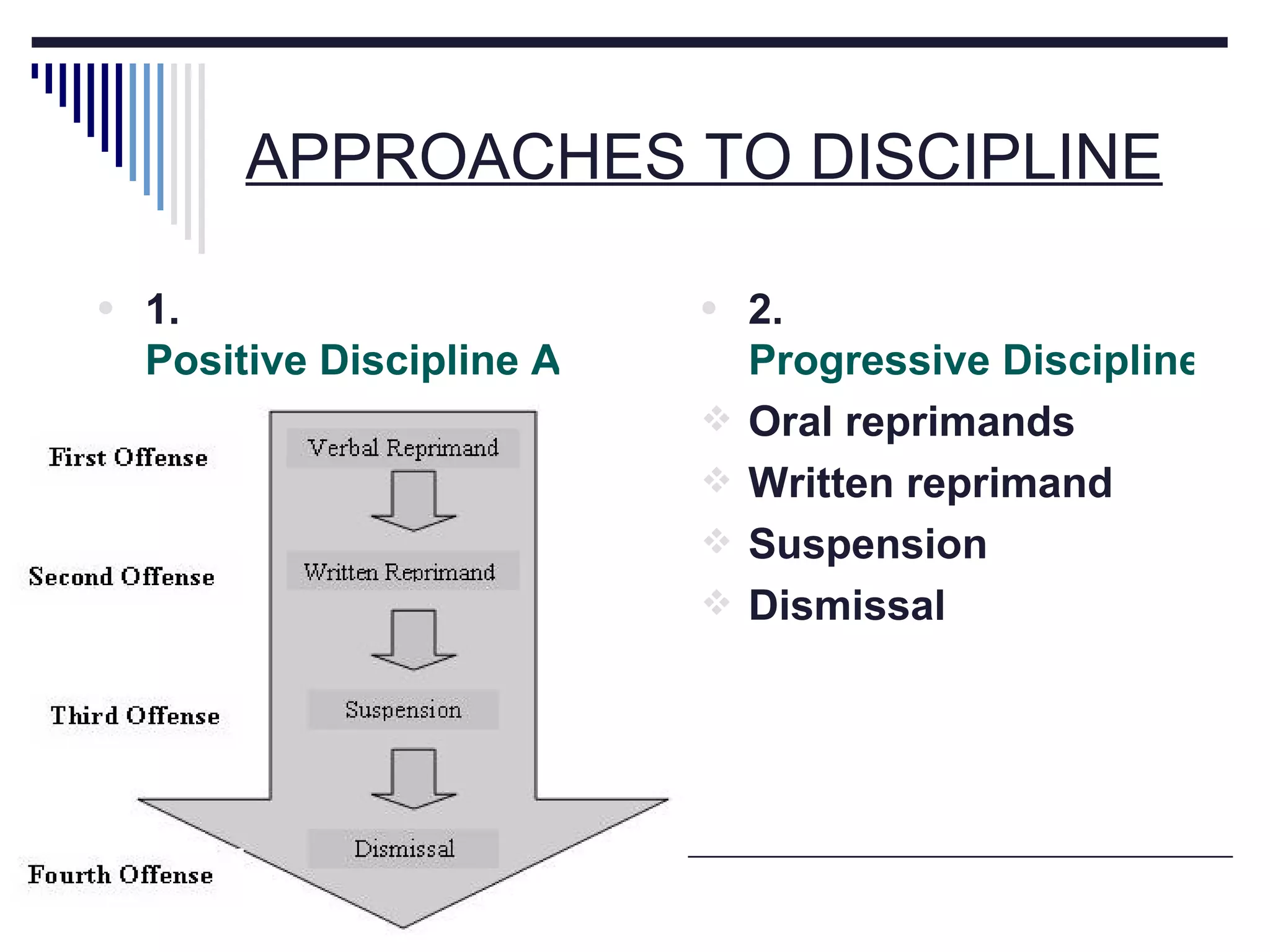
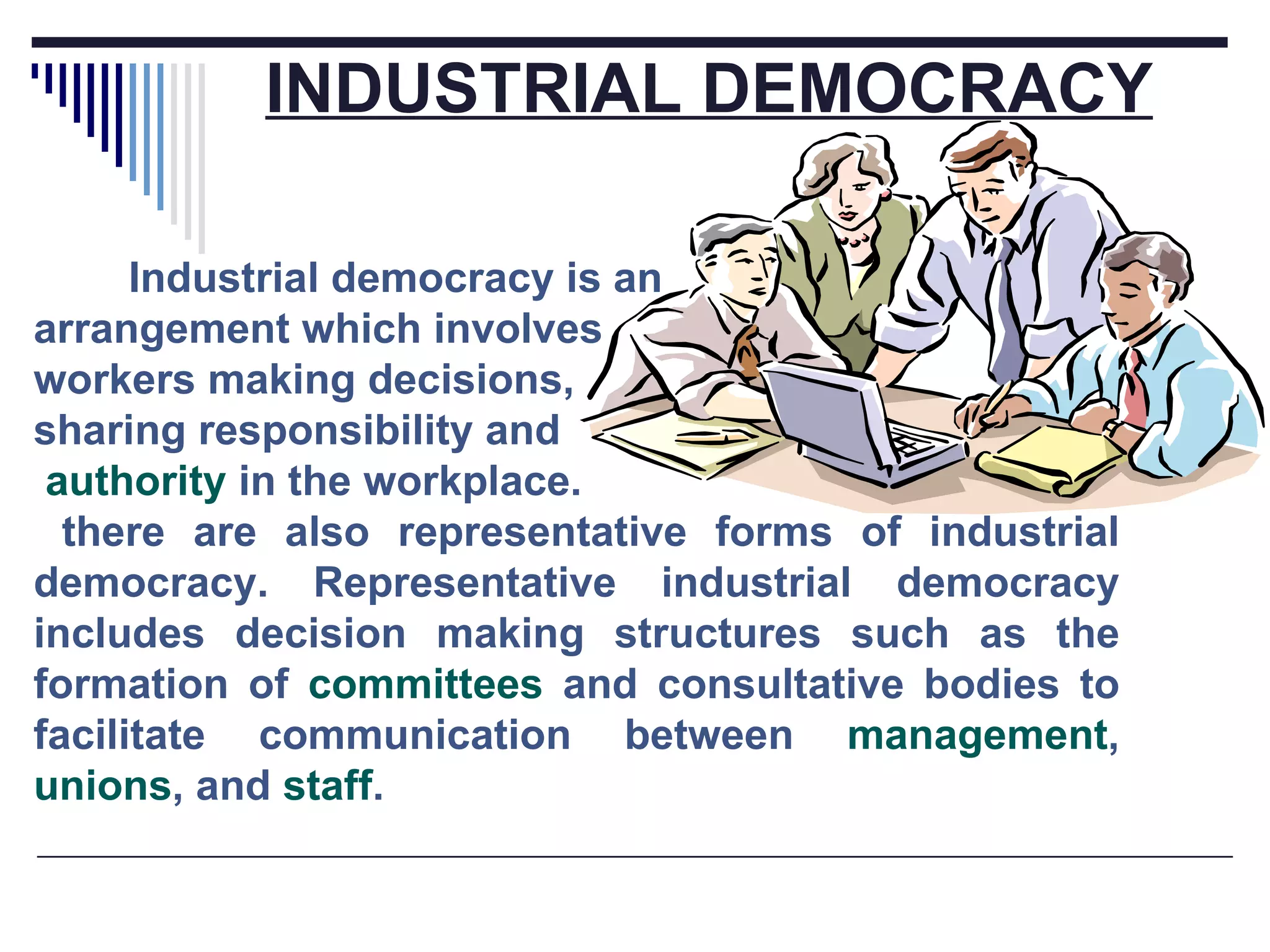
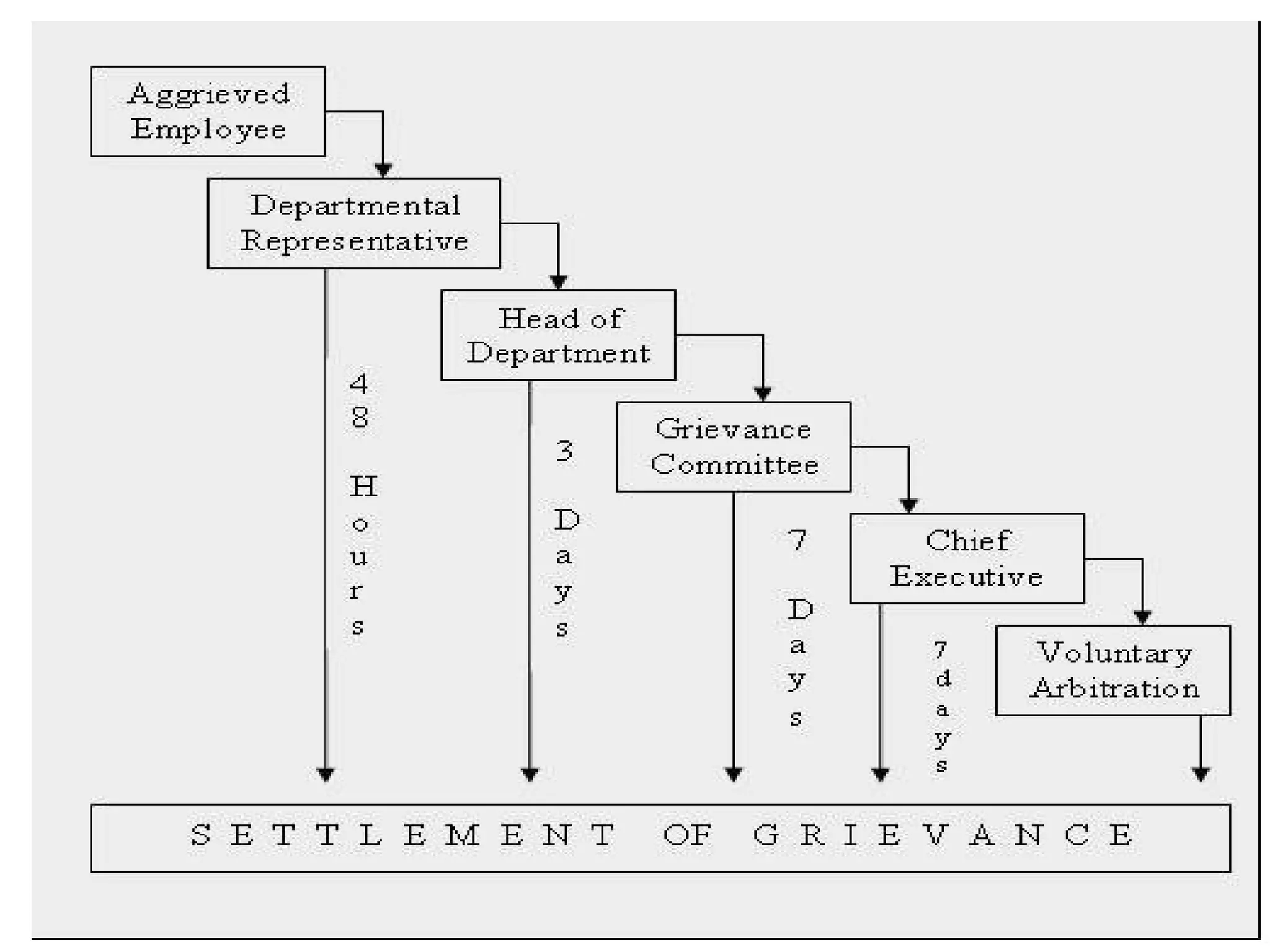
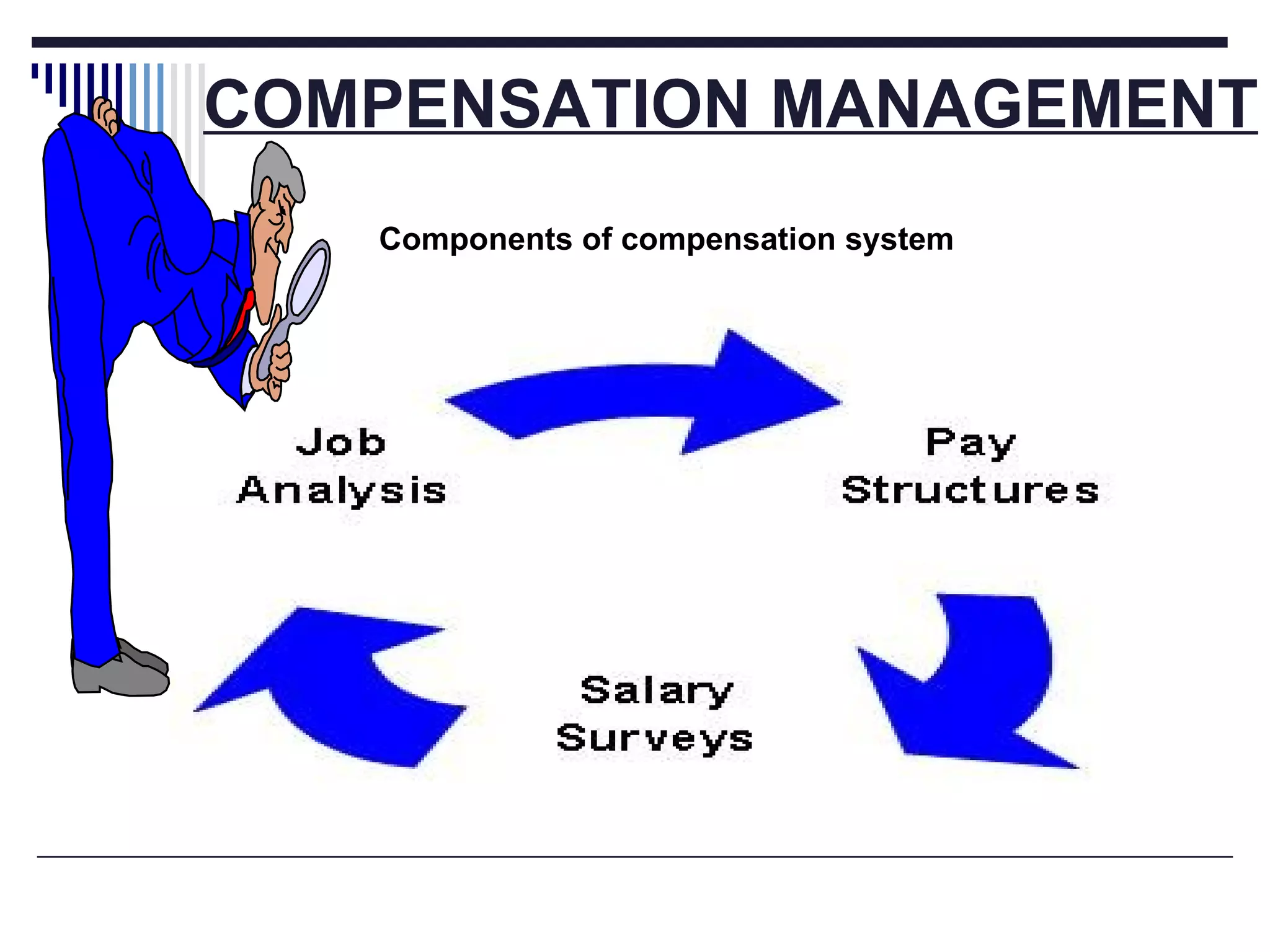
The document discusses several aspects of labor management including its key features, objectives, and the relationship between management and workers. It also describes approaches to industrial discipline, forms of industrial democracy, common causes of industrial disputes and grievances, and components of an effective compensation system. The goal of labor management is to achieve objectives through cooperation and mutual understanding between workers and management.