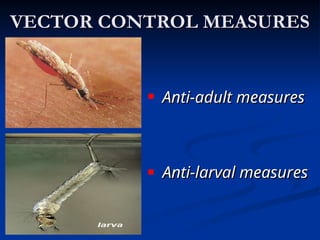
Malaria affects 1.8 billion people worldwide and poses significant economic challenges. The document outlines various strategies for prevention, treatment, and eradication, including active interventions, vector control, and chemoprophylaxis. Historical context and progress in malaria control programs, especially in India, are also discussed, highlighting the importance of continued efforts to combat this preventable and curable disease.