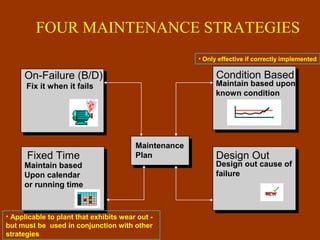
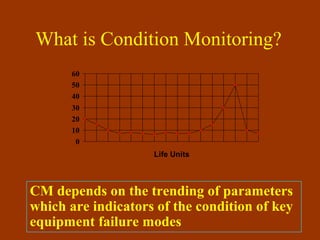
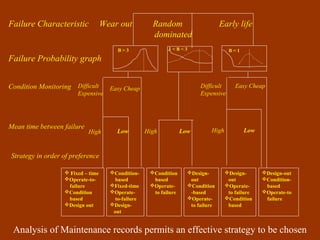
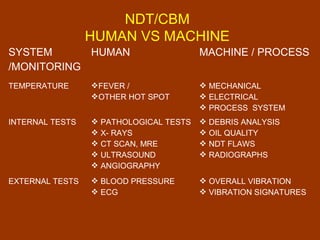
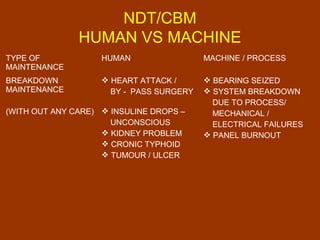
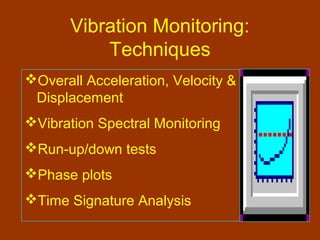
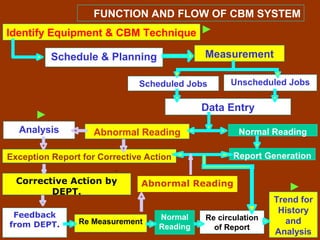
Condition-based maintenance (CBM) involves monitoring key parameters that can indicate equipment failure. CBM allows maintenance to be planned before severe damage occurs. The document discusses CBM techniques like vibration analysis, thermography, performance monitoring, lubricant analysis, and non-destructive testing. It provides examples of applying techniques like vibration, temperature, and flow measurements to monitor fans, pumps and detect issues like imbalance, bearing damage, cavitation. A successful CBM program incorporates monitoring, data analysis, reporting, and corrective actions.