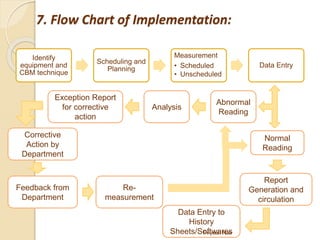
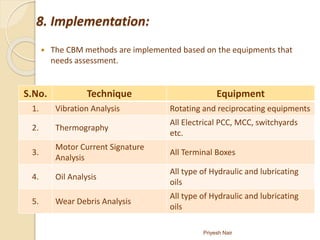
This document discusses condition based monitoring (CBM), also known as predictive maintenance. It compares monitoring machines to monitoring the human body, using techniques like vibration analysis, thermography, oil analysis, and wear debris analysis to detect abnormalities. The advantages of CBM include allowing planned maintenance to minimize downtime and equipment damage. CBM is most effective for equipment where downtime costs are high, safety risks exist, or accurate maintenance planning is essential. The document provides a flow chart and techniques for implementing a CBM program, including scheduling measurements and analyzing data to take corrective actions.