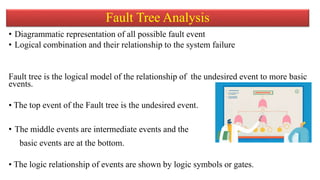
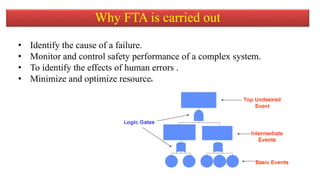
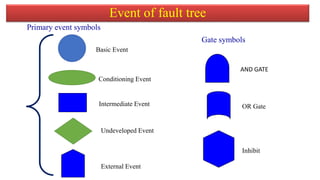
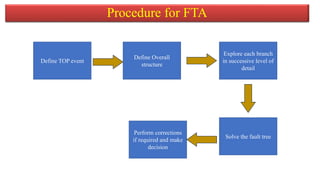
The document discusses fault tree analysis (FTA), which uses logic diagrams to identify the causes of failures in complex systems. FTA breaks down an undesired event into a logical combination of intermediate and basic events. The document provides an example of constructing a fault tree to calculate the expected frequency of injury to a steam boiler operator based on failure rates of components like water level detectors, pressure switches, and relief valves.