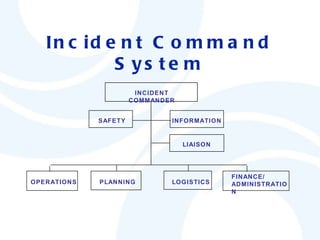
The document discusses OSHA requirements for emergency response and preparedness in the construction industry according to 29 CFR 1926. It outlines general requirements for all workplaces including developing emergency action plans, ensuring means of egress, and providing fire protection. It also details additional requirements for specific workplaces and operations such as excavations, underground construction, and power transmission. The standards aim to ensure workplaces establish procedures, training, and equipment to effectively respond to emergencies.