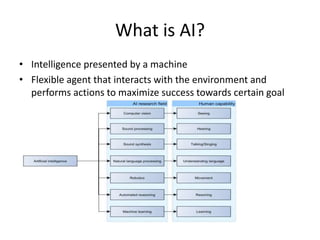
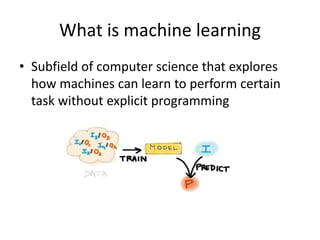
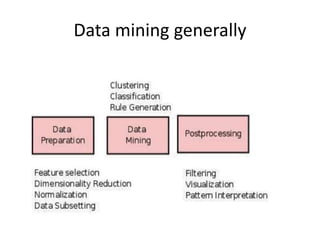
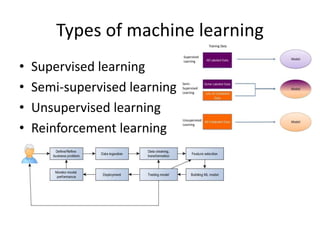
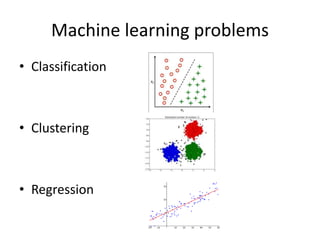
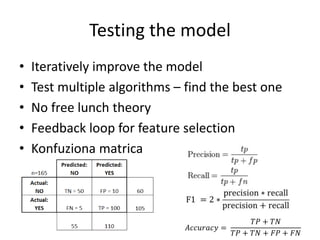
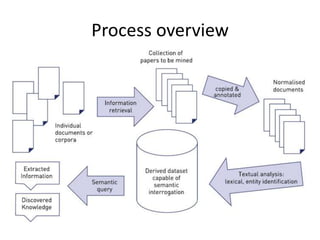
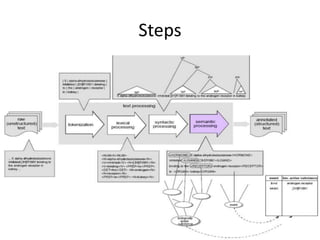
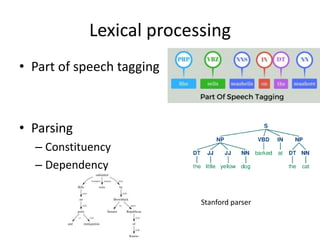
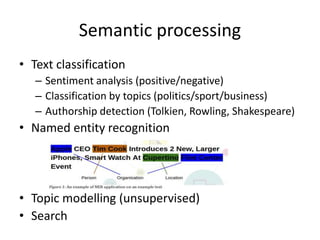
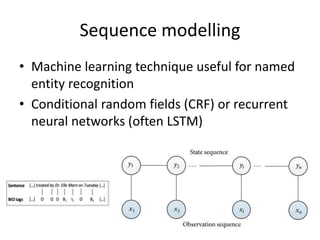
The document discusses artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, defining AI as a machine's ability to interact with the environment and emphasizing machine learning as a subfield of computer science focused on learning tasks without explicit programming. It outlines various types of machine learning, challenges of analyzing text data, and the steps involved in lexical and semantic processing. Additionally, it mentions frameworks and tools for machine learning and natural language processing, including Sci-kit Learn and Keras, while highlighting the importance of feature engineering and search techniques in extracting information from unstructured data.