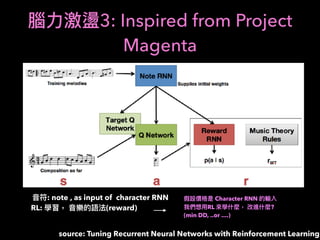
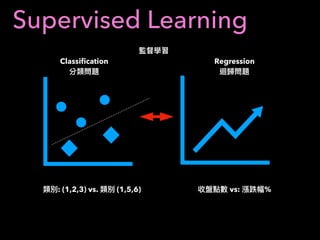
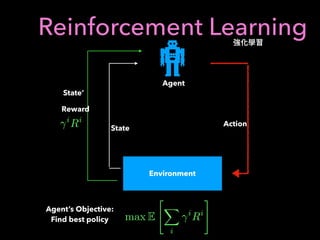
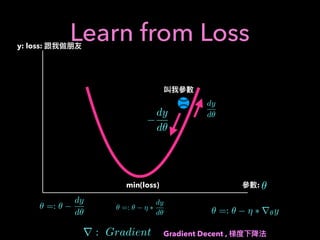
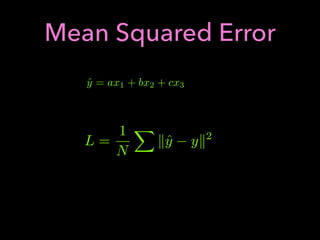
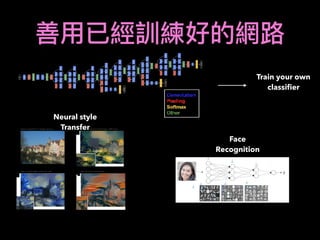
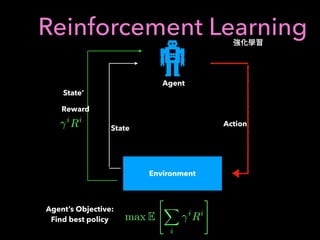
1. The document discusses using machine learning and deep learning techniques for trading, including classification, regression, clustering, and time series modeling with RNNs.
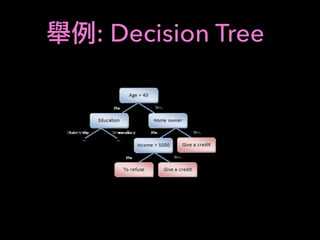
2. It provides an overview of different ML algorithms like decision trees, random forests, CNNs, RNNs and reinforcement learning and how they could be applied to problems in trading like predicting stock prices, generating trading signals, and portfolio optimization.
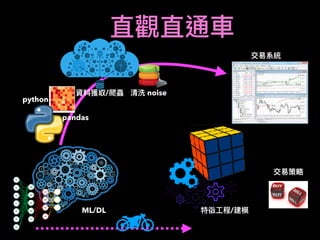
3. It presents some ideas for modeling trading problems using technical indicators or fundamental factors as inputs to classifiers, regressors or sequence models, and using reinforcement learning to optimize trading strategies.












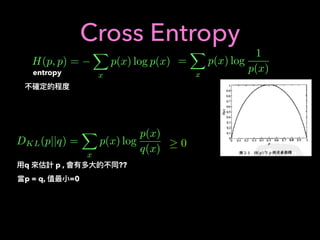




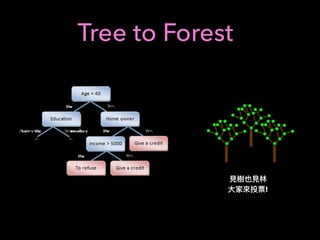



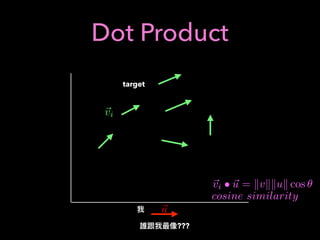

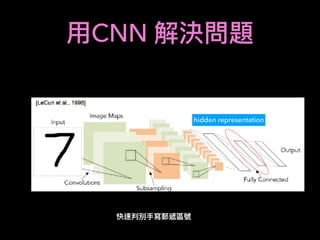




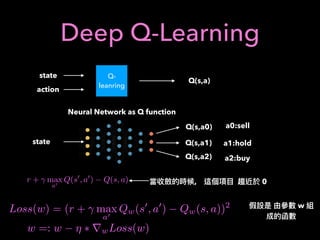
![Q-learning
action discrete finite set
a : epsilon greedy a =
(
random, prob(✏)
arg max
x
Q(s, x), prob(1 ✏)
new old learning
rate
state s, action a, state s’, reward r
a’: state s’, action
Q(s, a) Q(s, a) + (↵) ⇤ [r + max
a0
Q(s0
, a0
) Q(s, a)]
, 0r + max
a0
Q(s0
, a0
) Q(s, a)
Value Iteration](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mlfortradig180328-180911051602/85/Machine-Learning-for-Trading-52-320.jpg)

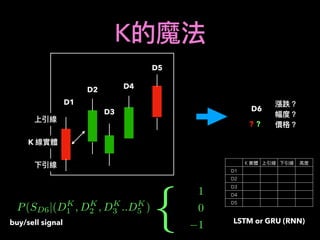
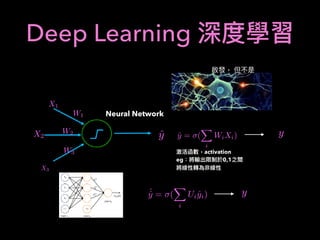
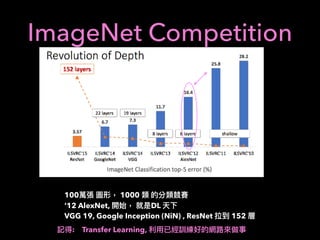
![RNN(LSTM)
label: [1,0,0] ( /long day 6 close - day 5 close > threshold)
label: [0,0,1] ( /short day 6 close - day 5 close < - threshold)
K
D1
D2
DD3
D4
D5
D1: (K )
D2: (K )
D5: (K )
.
.
LSTM
Input
LSTM
(LSTM)
fully connected
ˆy0, ˆy1, ˆy2,
X
= 1
y,y2, y3
cross entropy
one-hot
(Keras: 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mlfortradig180328-180911051602/85/Machine-Learning-for-Trading-57-320.jpg)

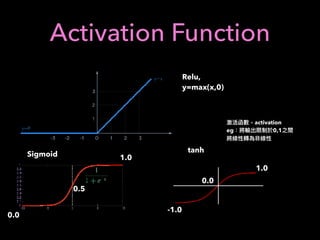
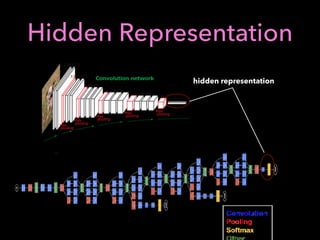
![Using CNN
Input
CNN
(CNN)
fully connected
ˆy0, ˆy1, ˆy2,
X
= 1
y,y2, y3
cross entropy
K
D1
D2
DD3
D4
D5
D1: (K )
D2: (K )
D5: (K )
.
.
CNN Sliding window
Self Define Features
label: [1,0,0] ( /long day 6 close - day 5 close > threshold)
label: [0,0,1] ( /short day 6 close - day 5 close < - threshold)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mlfortradig180328-180911051602/85/Machine-Learning-for-Trading-60-320.jpg)

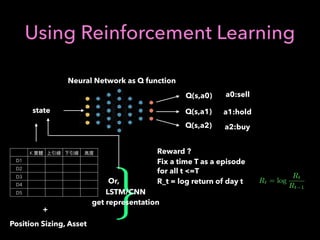

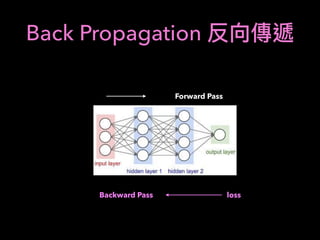
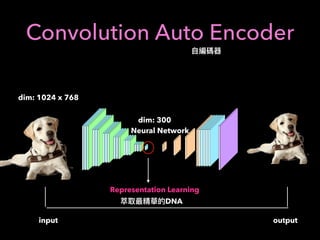
![2: Using RL for Portfolio
Optimization
Asset : [S1, S2]
S1, S2 : Stocks with predicted growth
Use RL to Optimize Portfolio
A = w1S1 + w2S2
w1 + w2 = 1
Consider action: w1 : {0.10, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 0.9}
Reward: Rt = log
At
At 1
How about n-stocks ?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mlfortradig180328-180911051602/85/Machine-Learning-for-Trading-64-320.jpg)