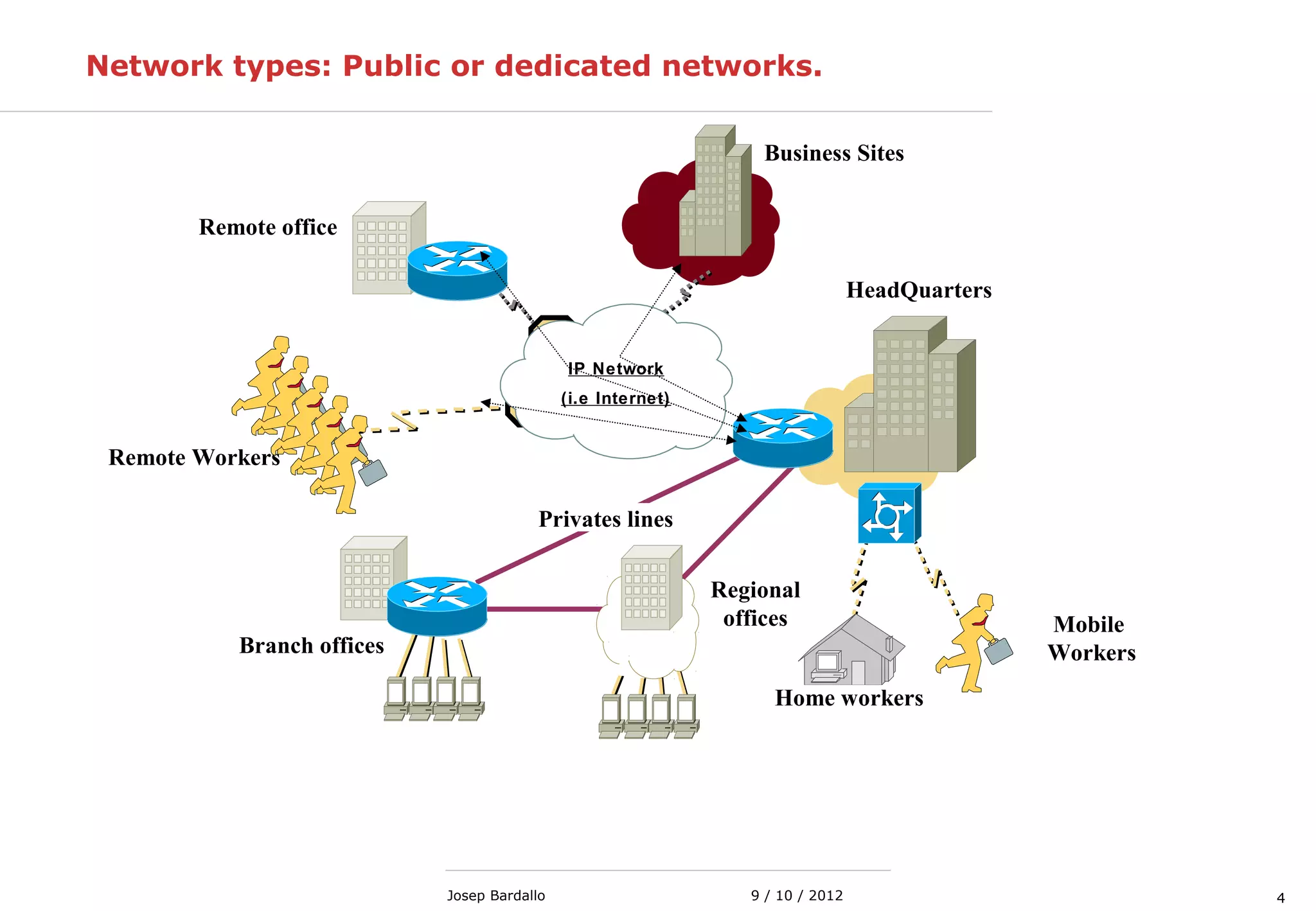
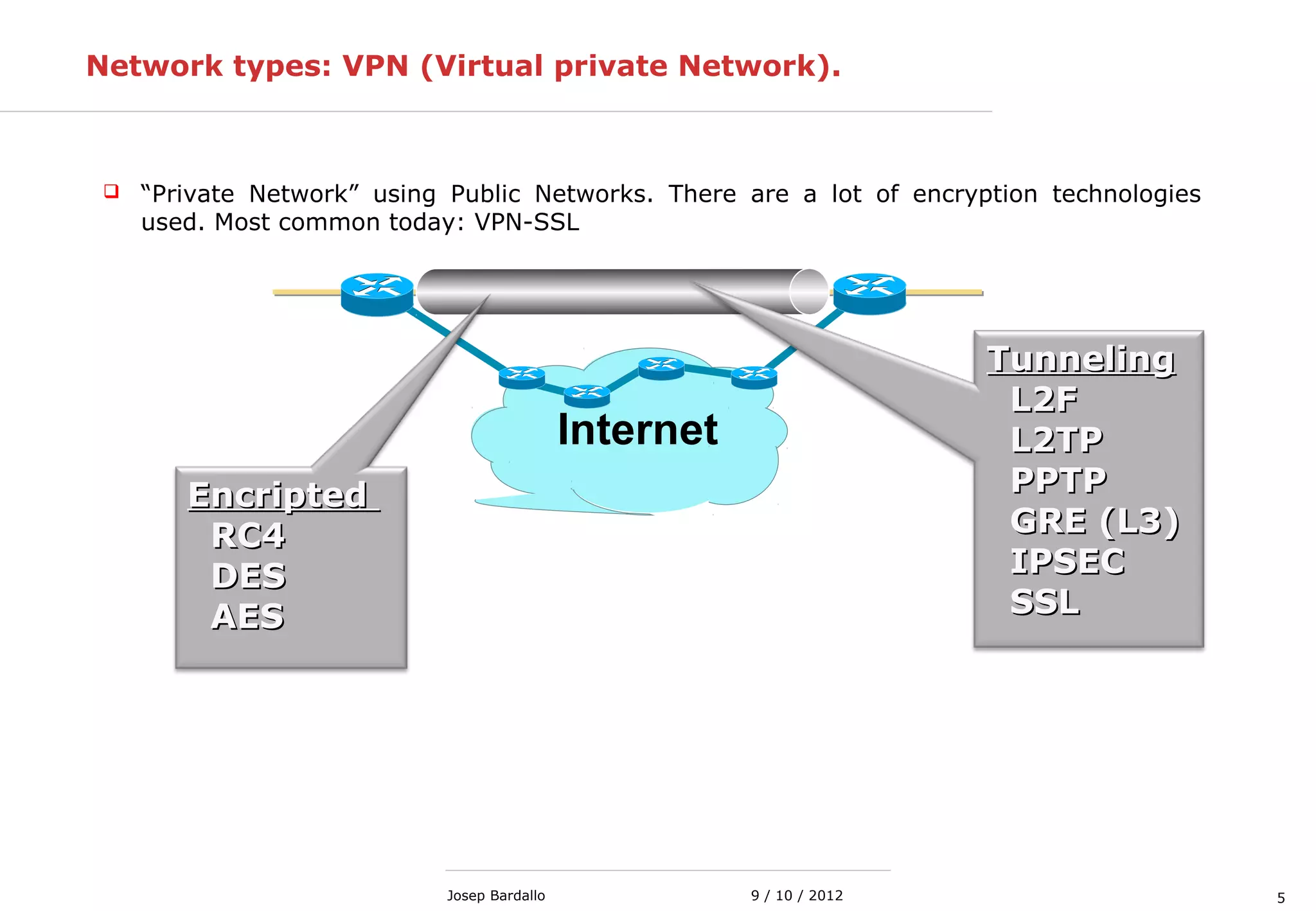
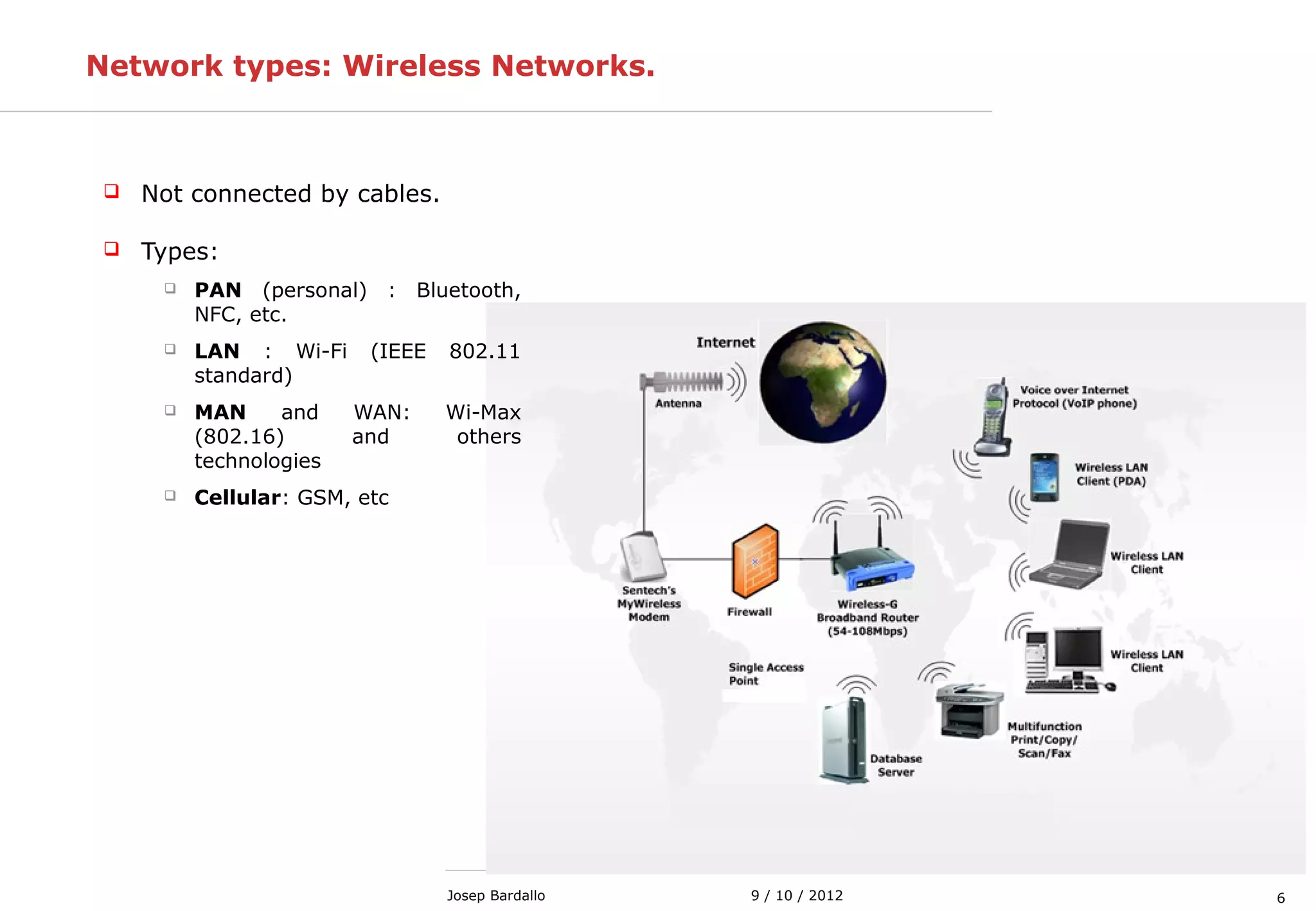
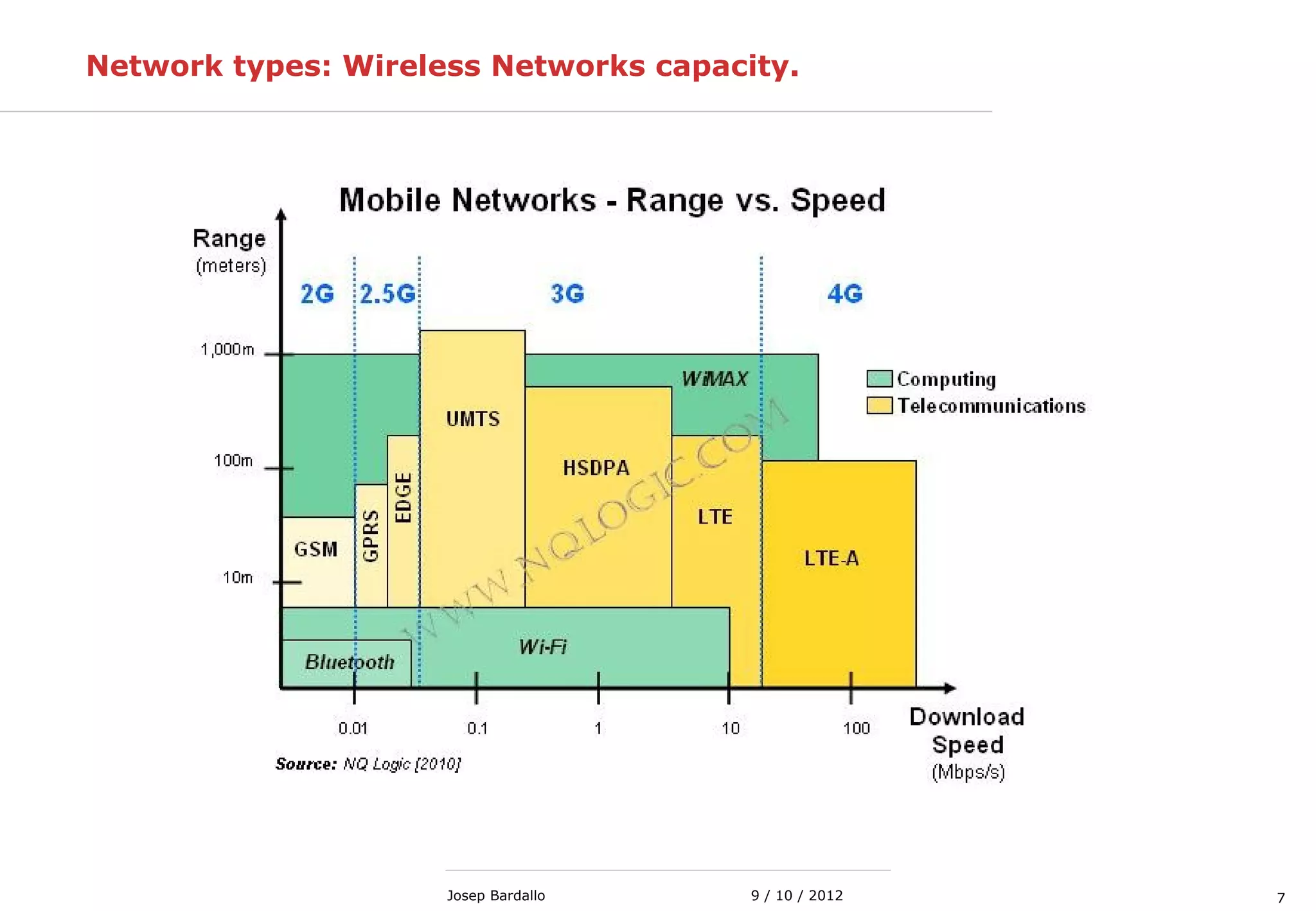
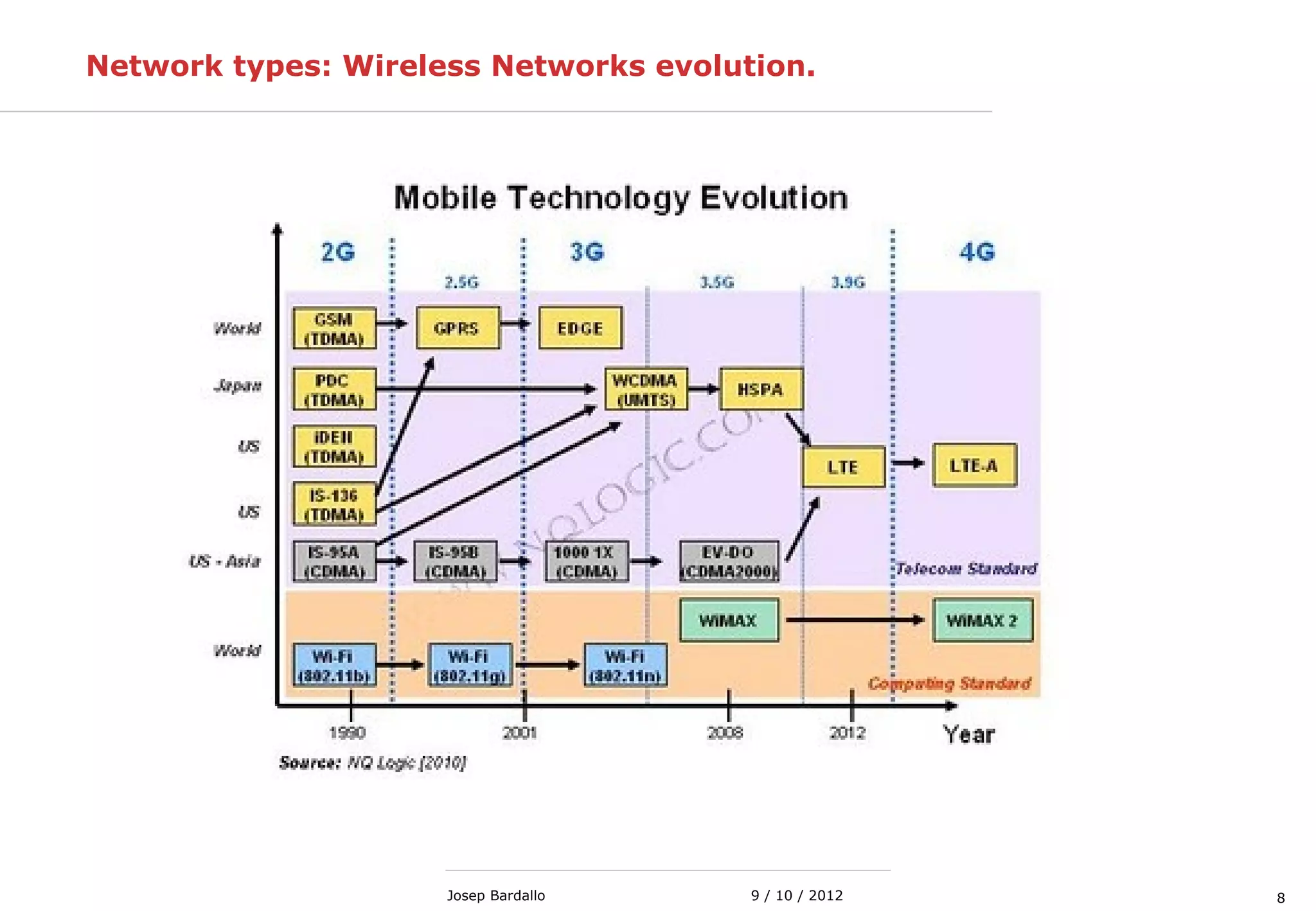
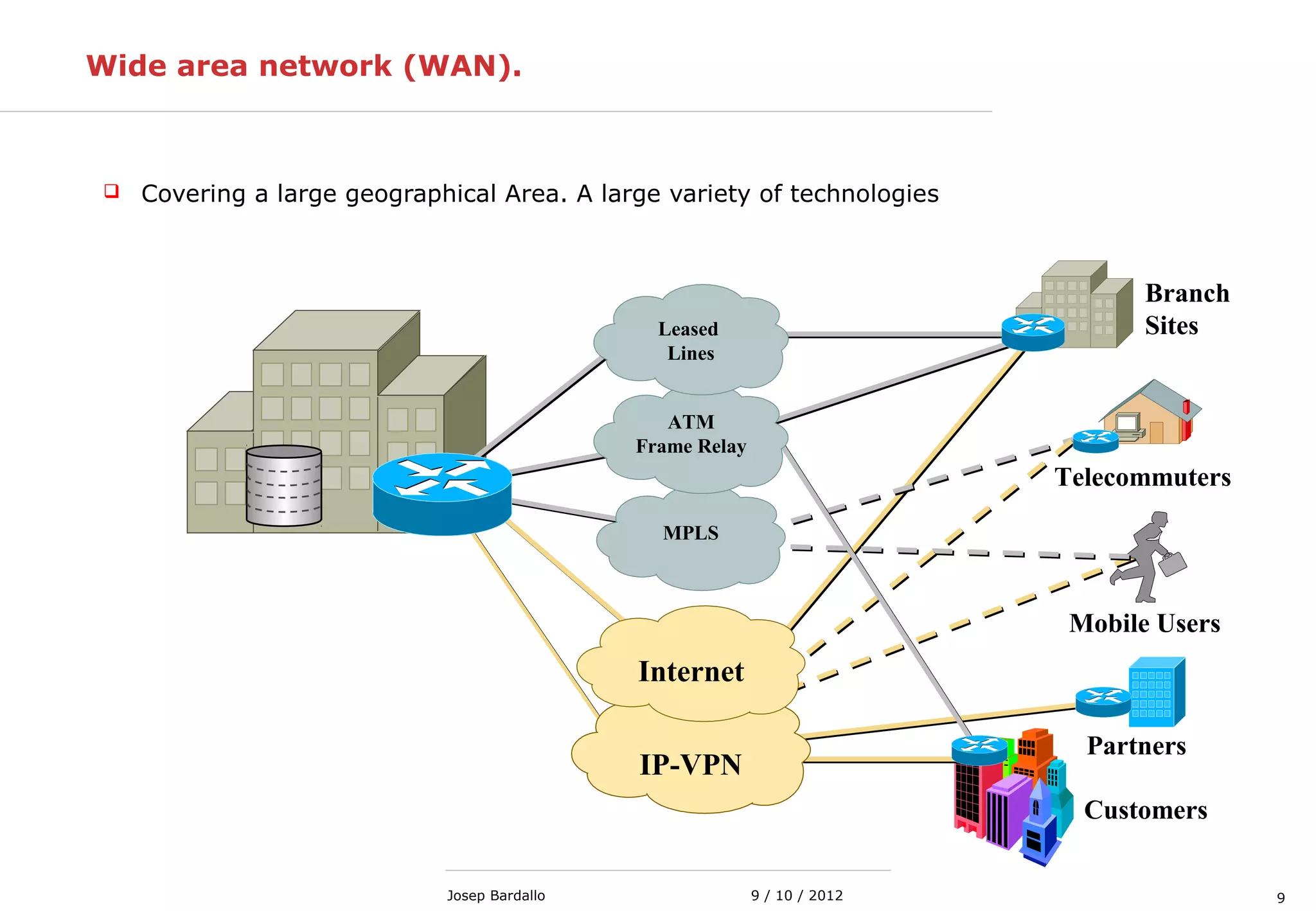
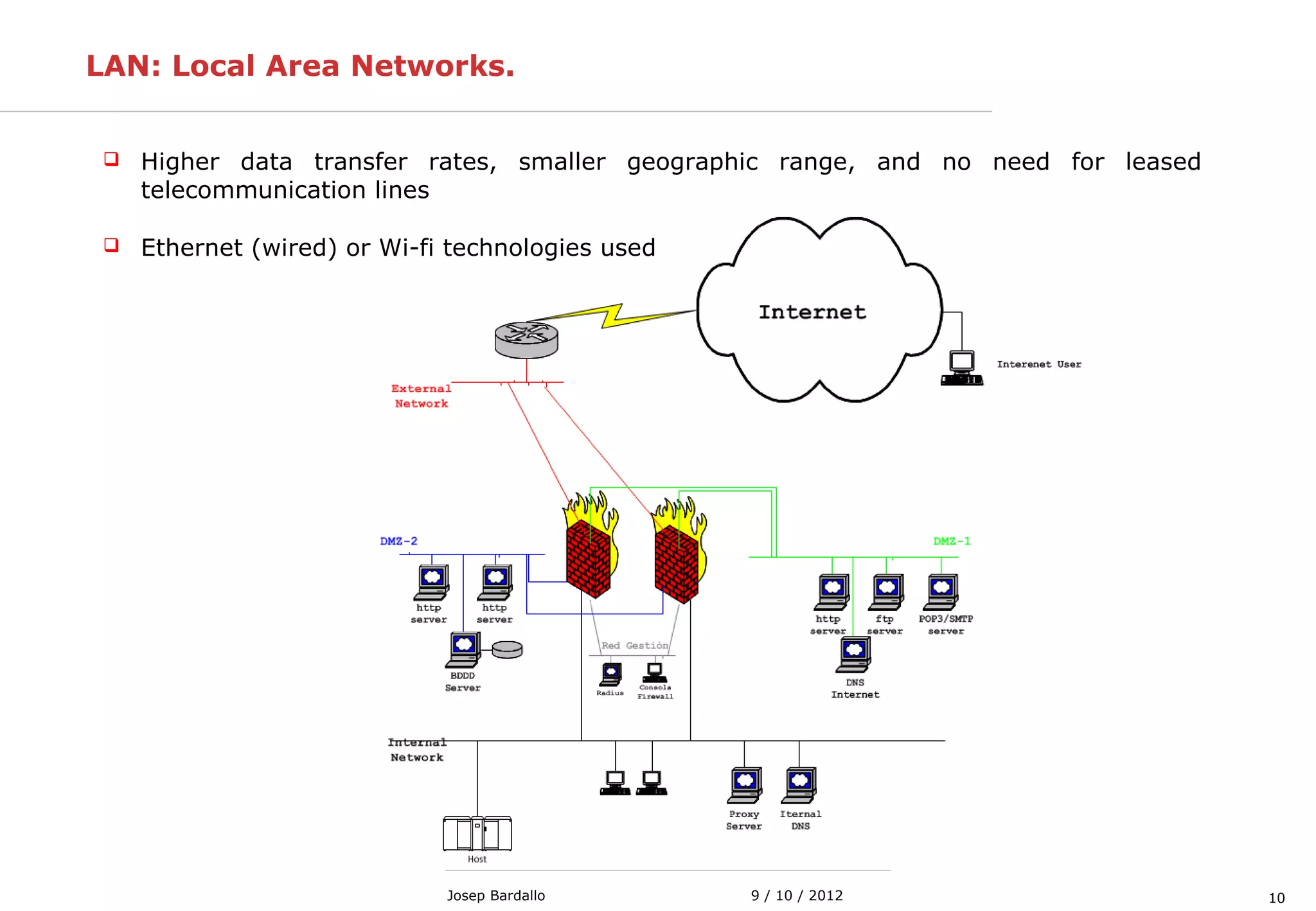
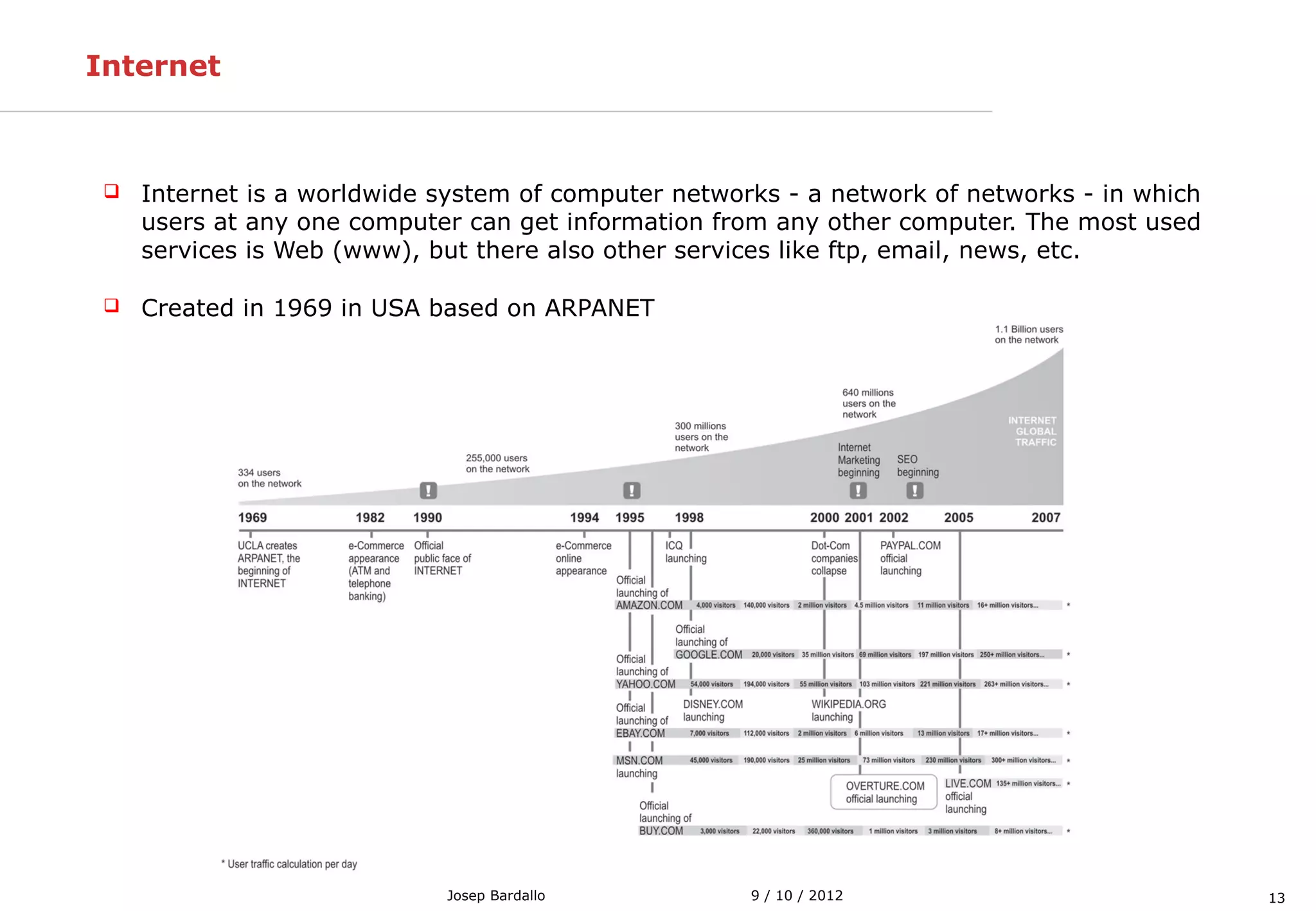
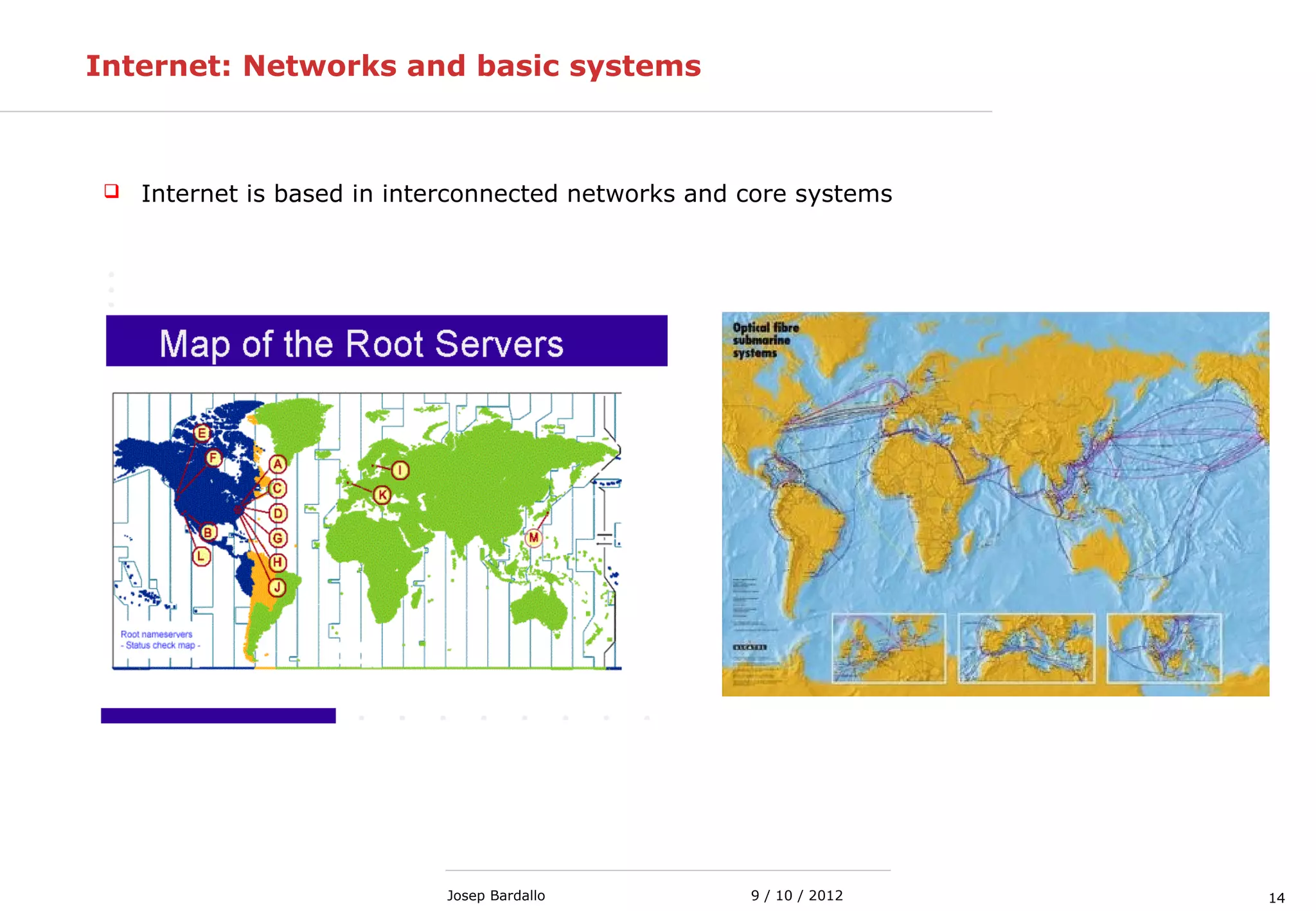
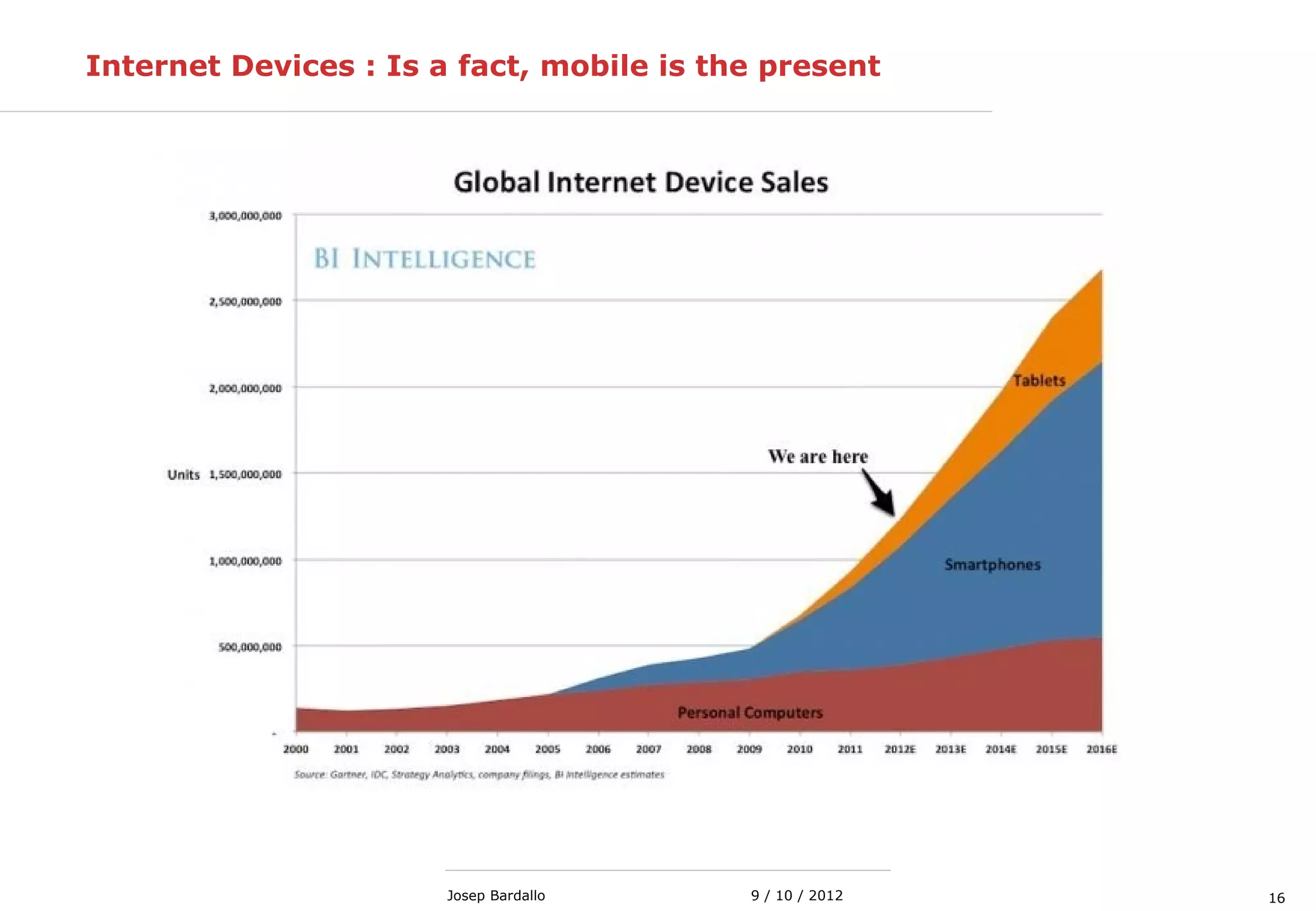
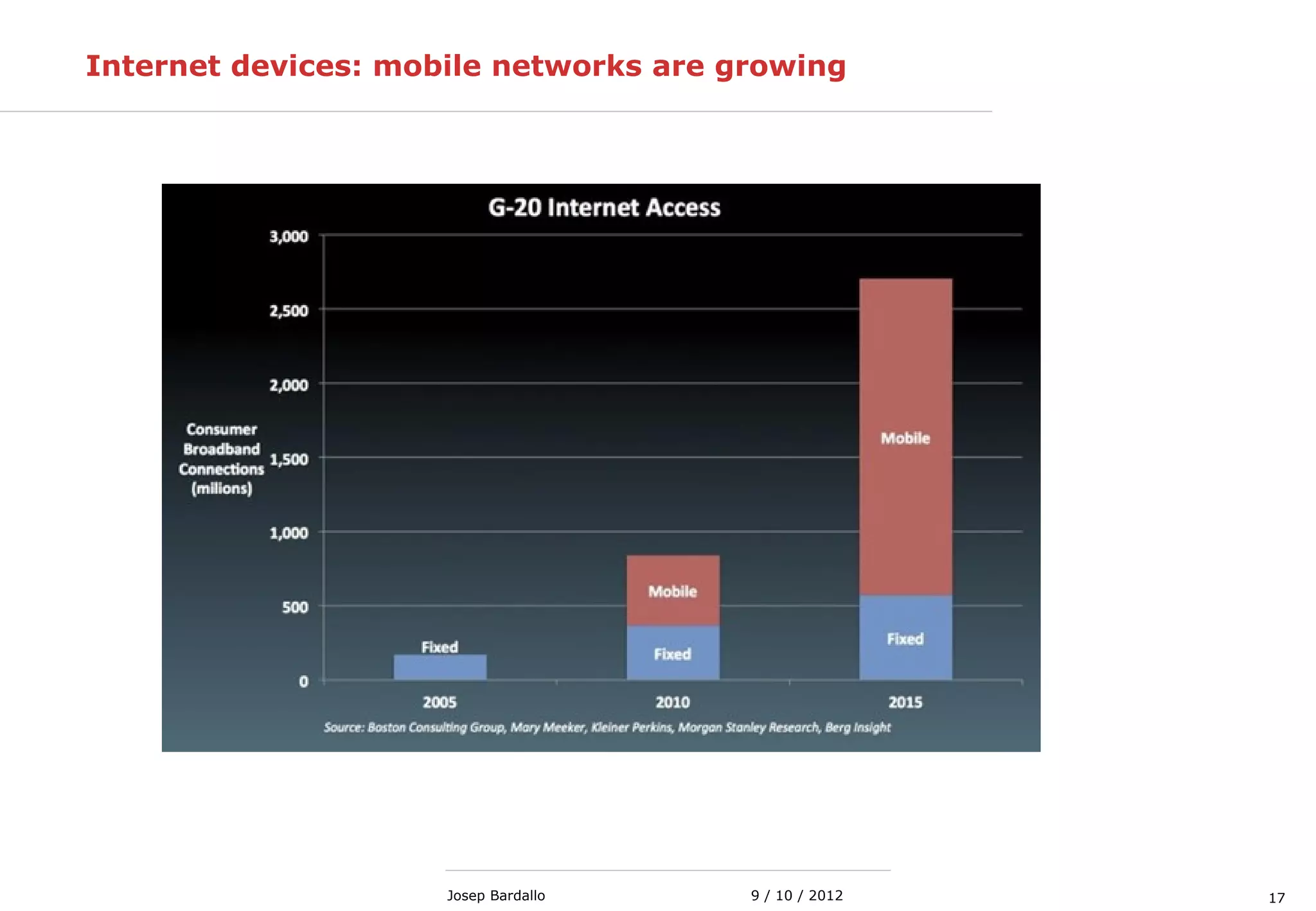
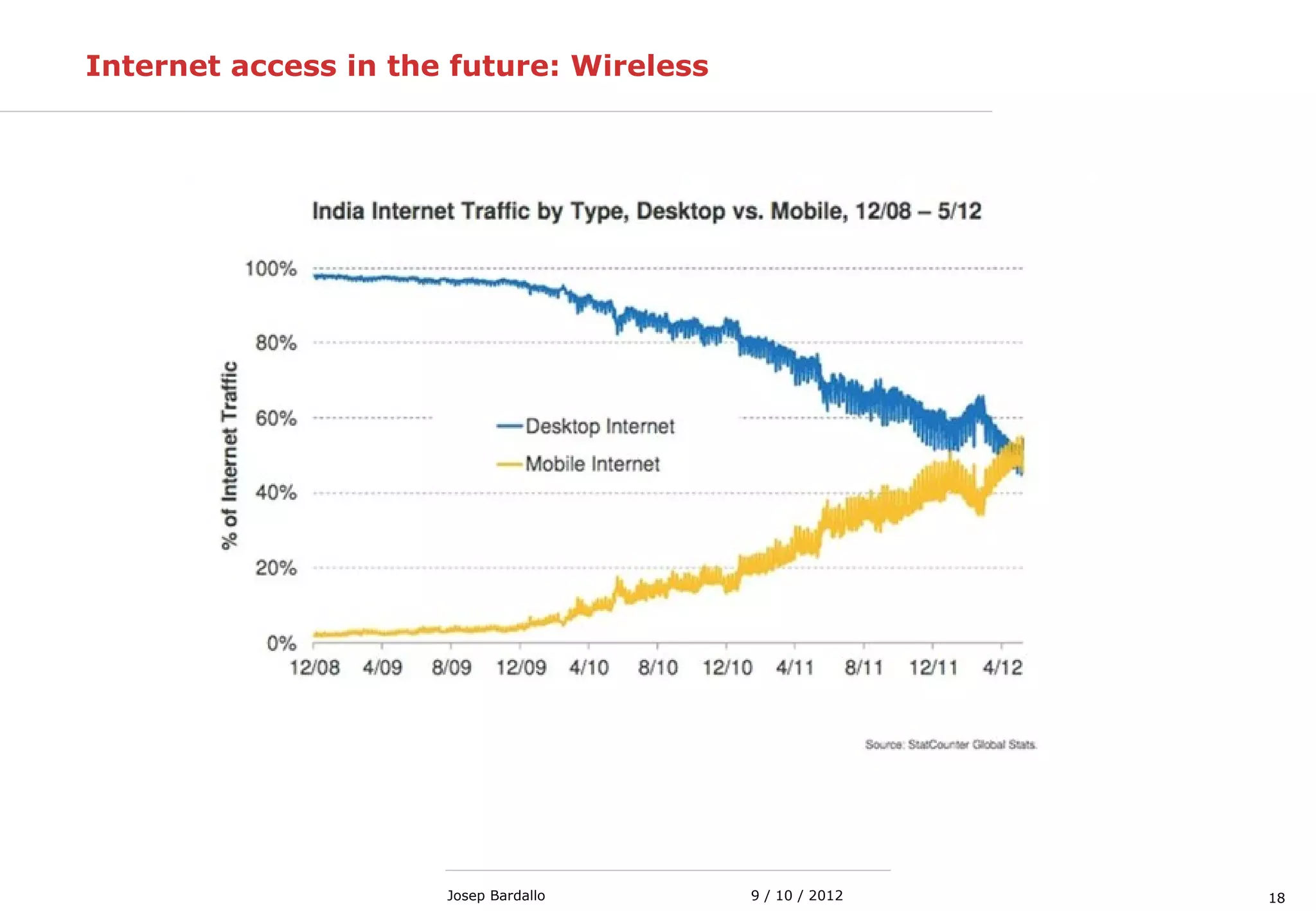
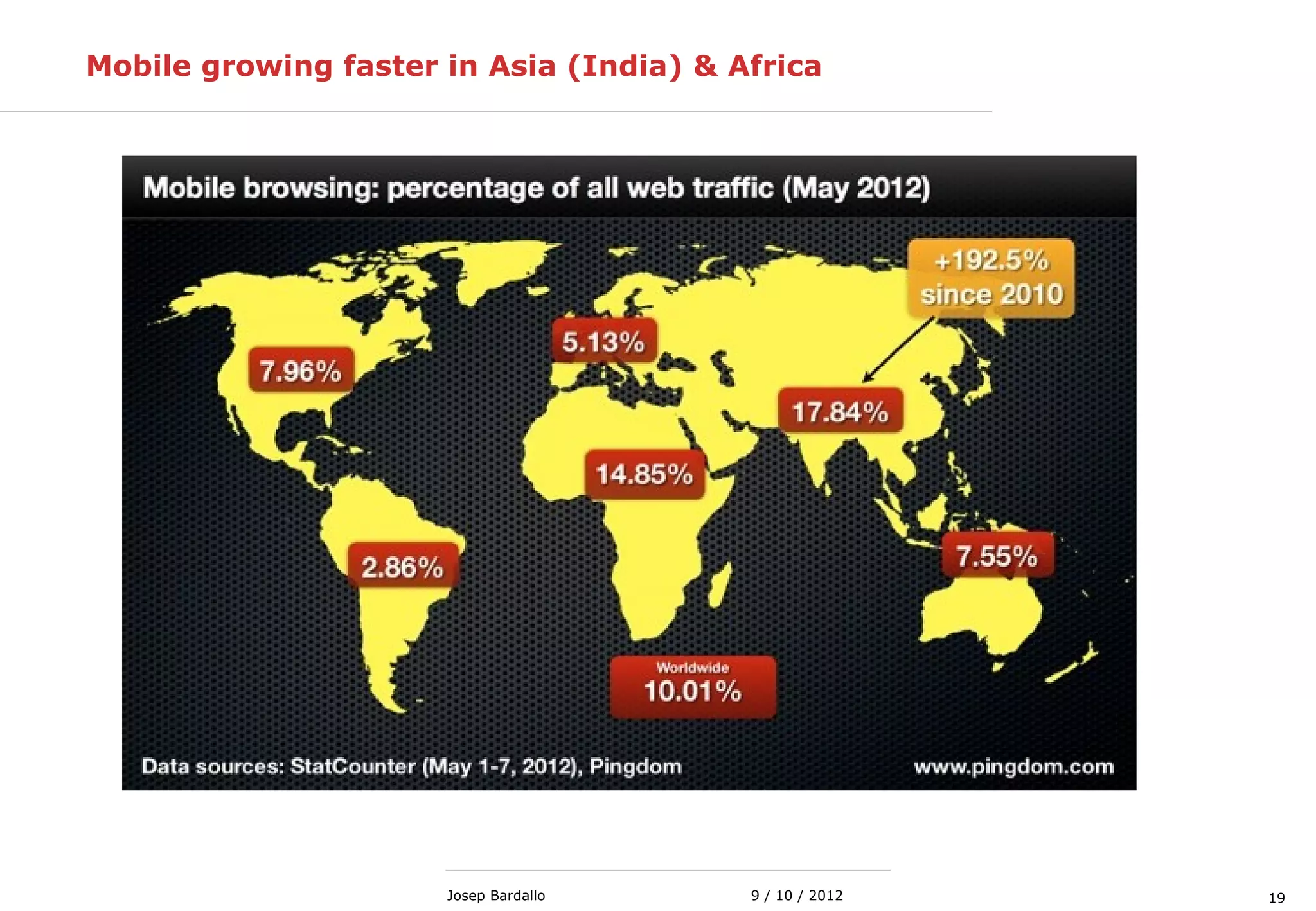
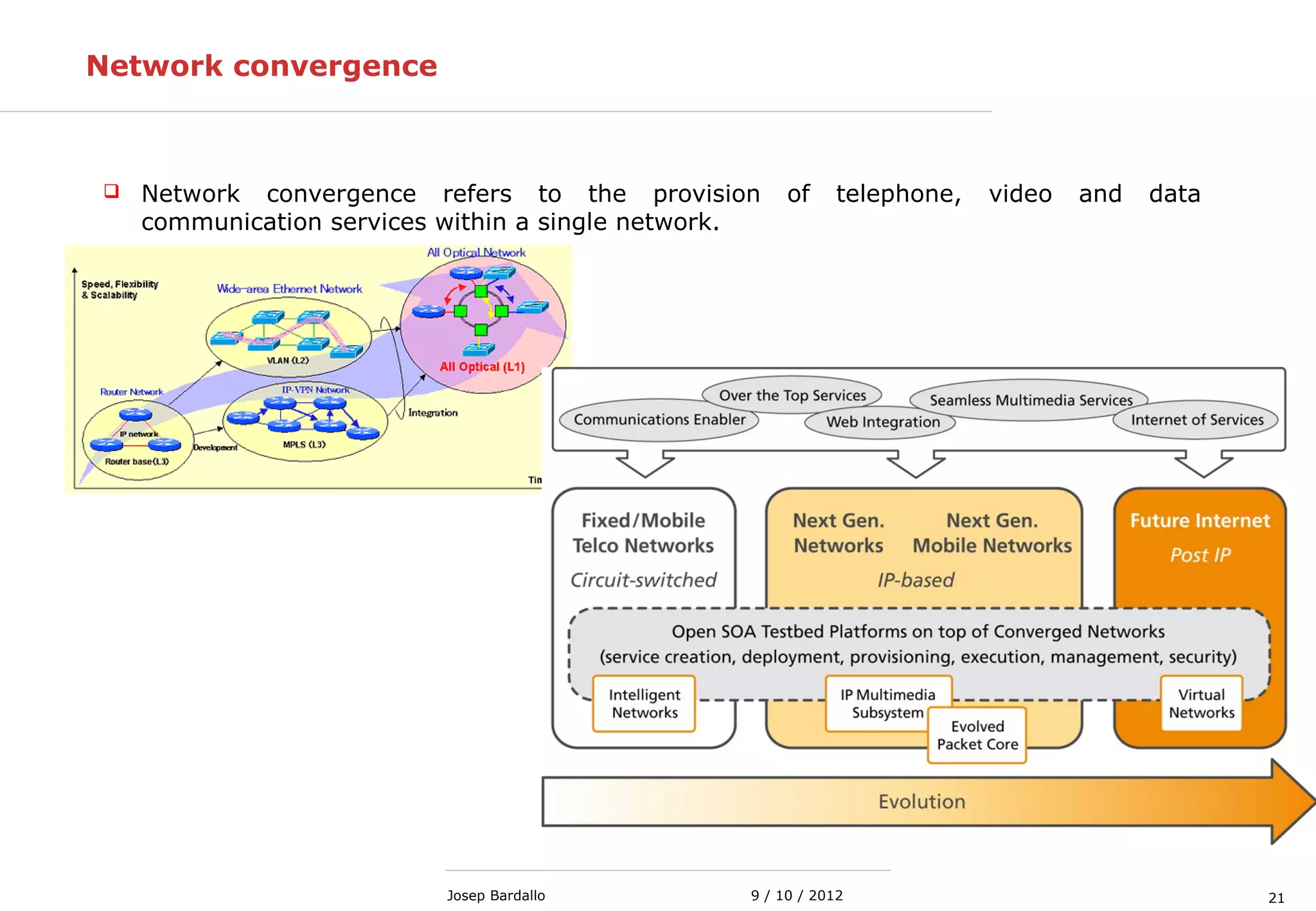
This document discusses different types of computer networks. It describes local area networks (LANs) that connect devices within a small geographic area like a home or office using technologies like Ethernet or WiFi. Wide area networks (WANs) are discussed as covering a larger geographic area using technologies like MPLS, ATM, or Frame Relay. The document also summarizes wireless networks including personal (PAN), local (LAN), and metropolitan/wide area networks. The Internet is introduced as a worldwide system of interconnected computer networks that allows users to access information from any computer.