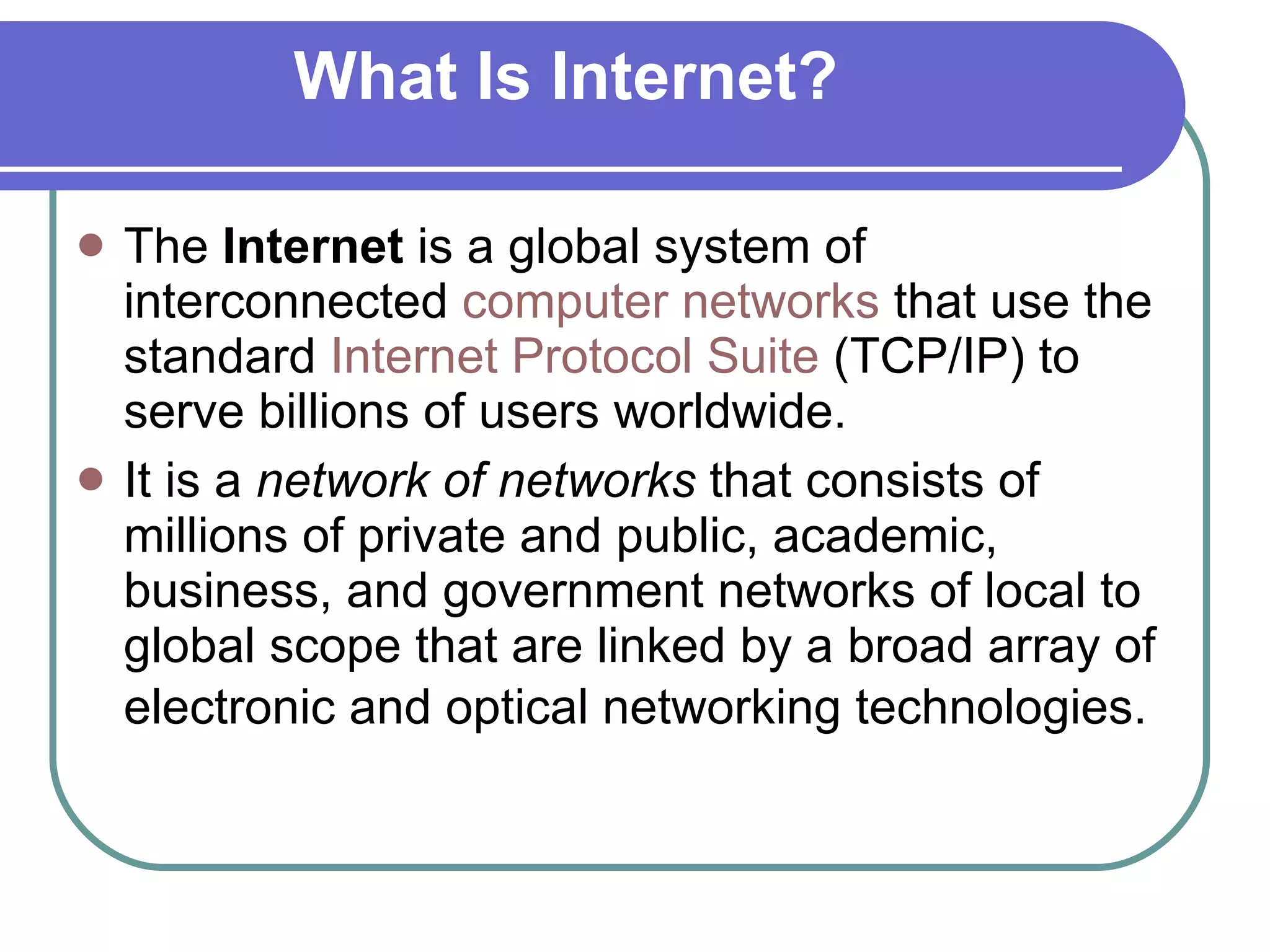
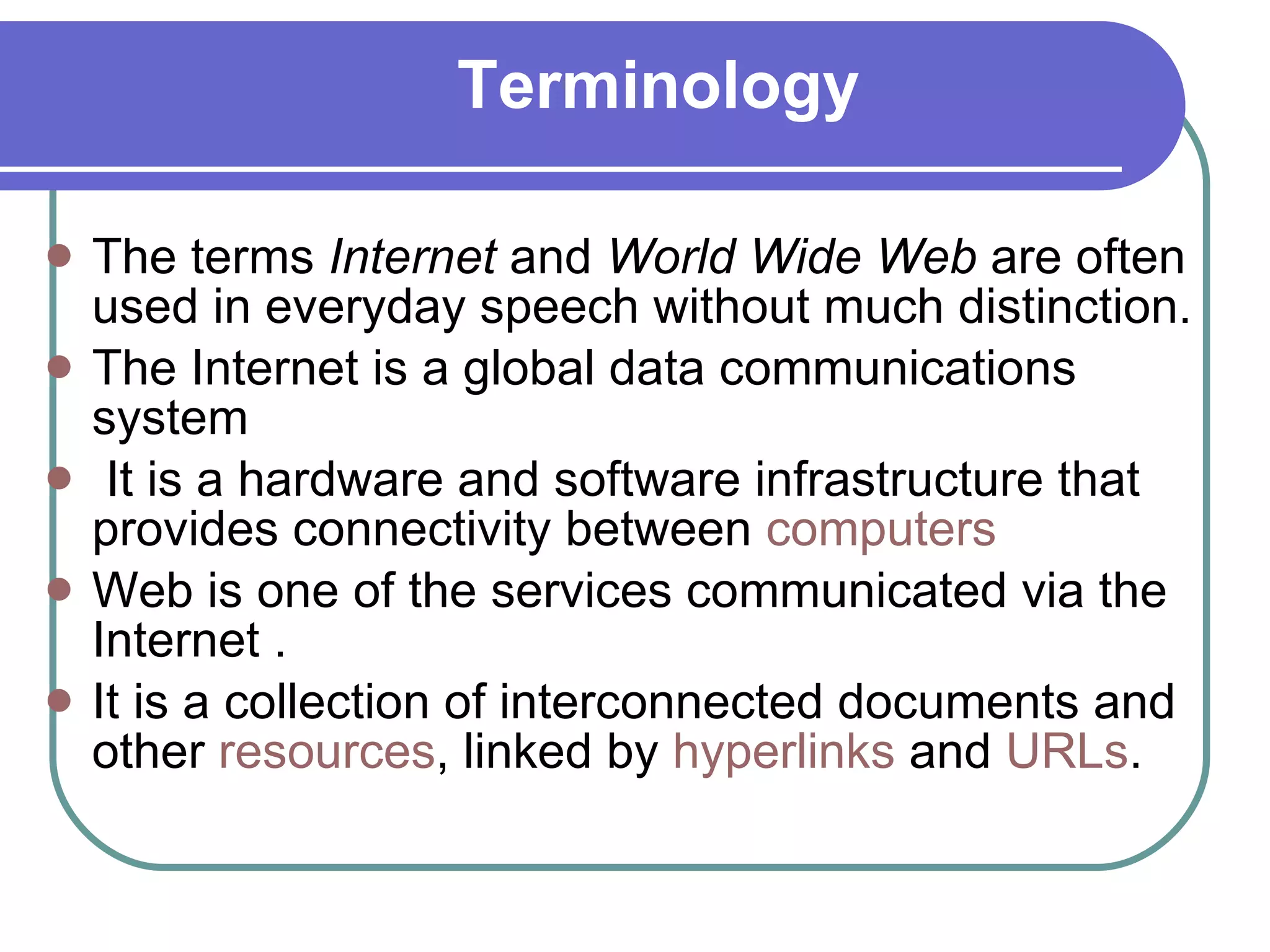
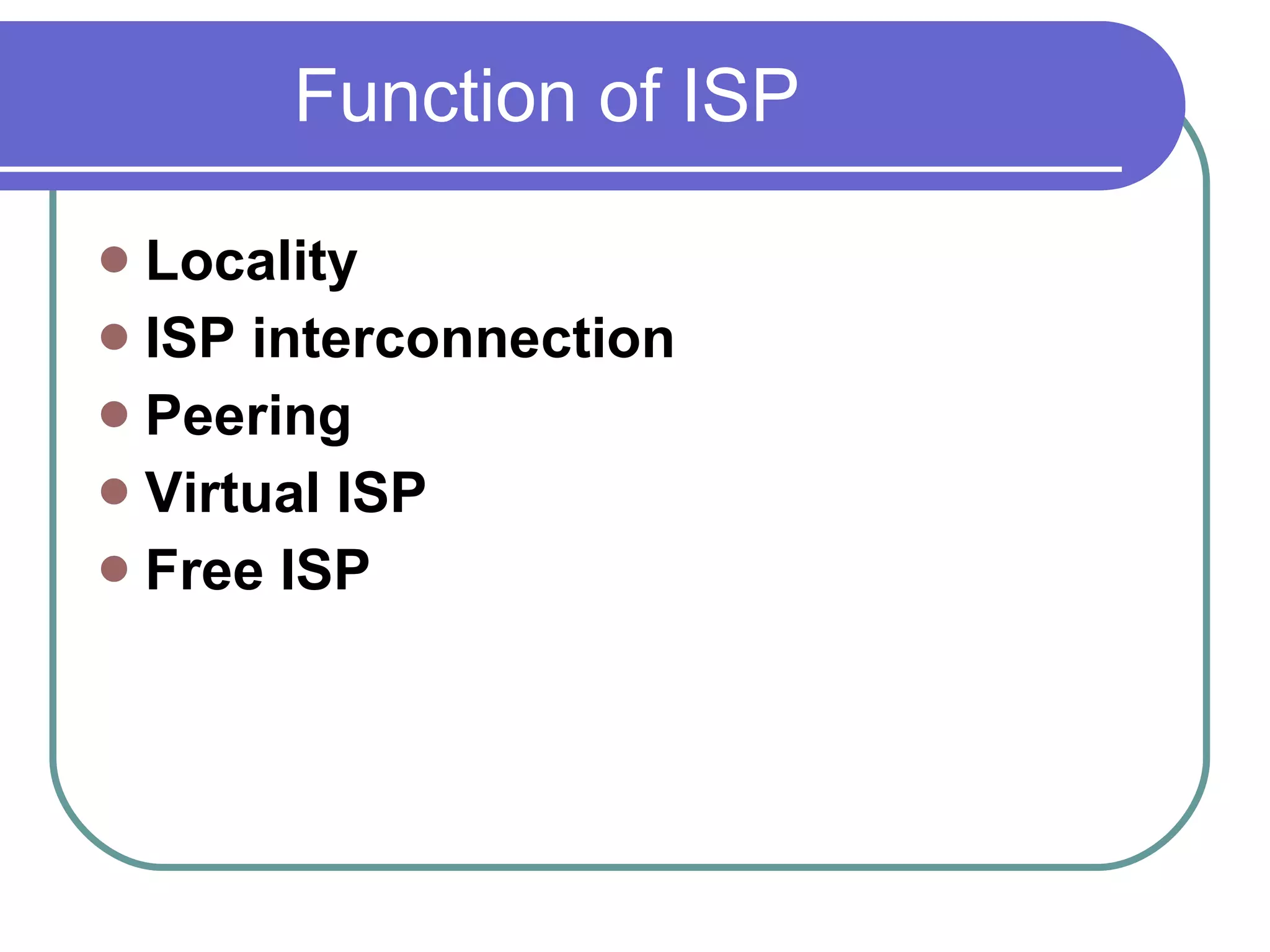
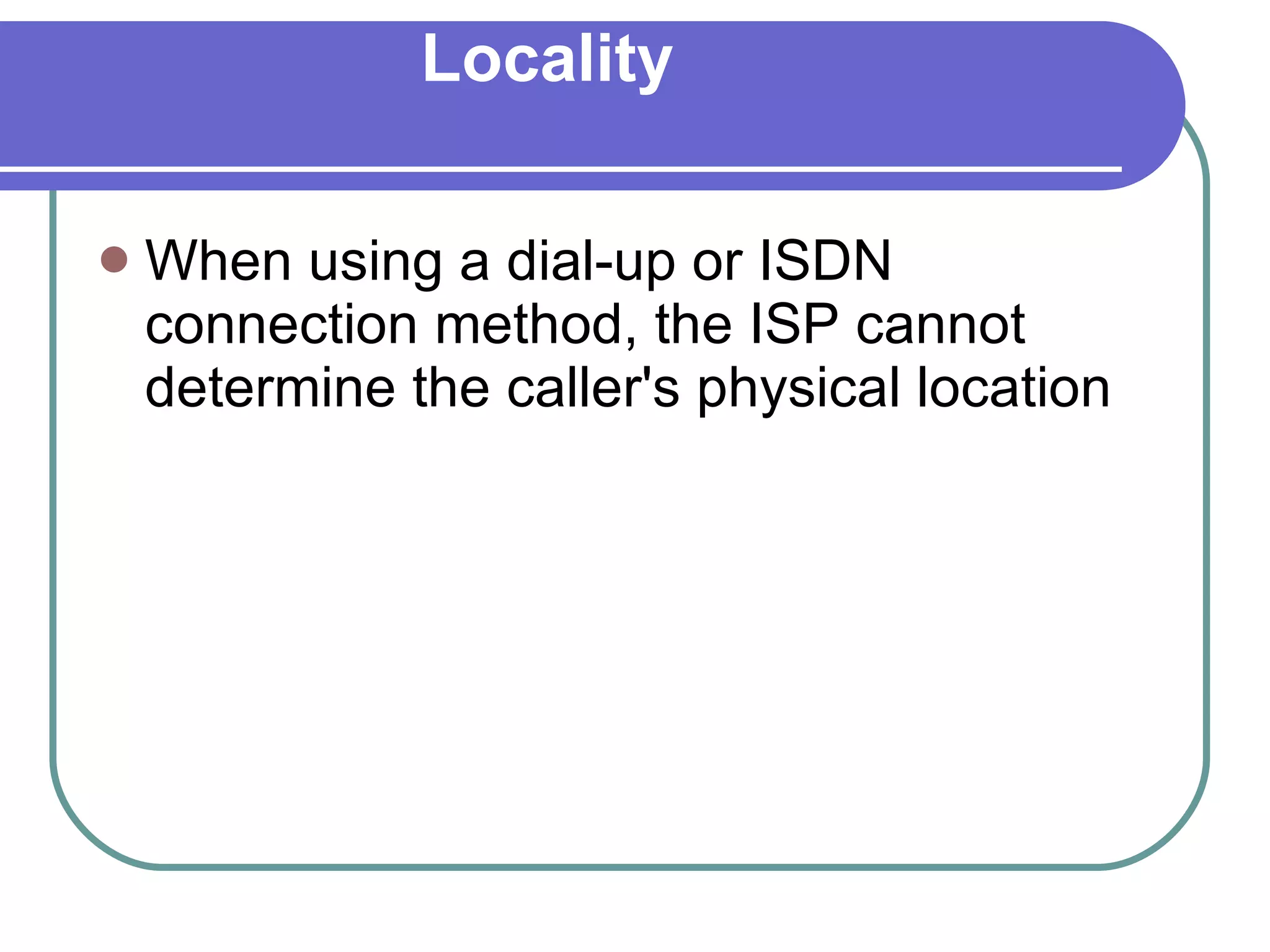
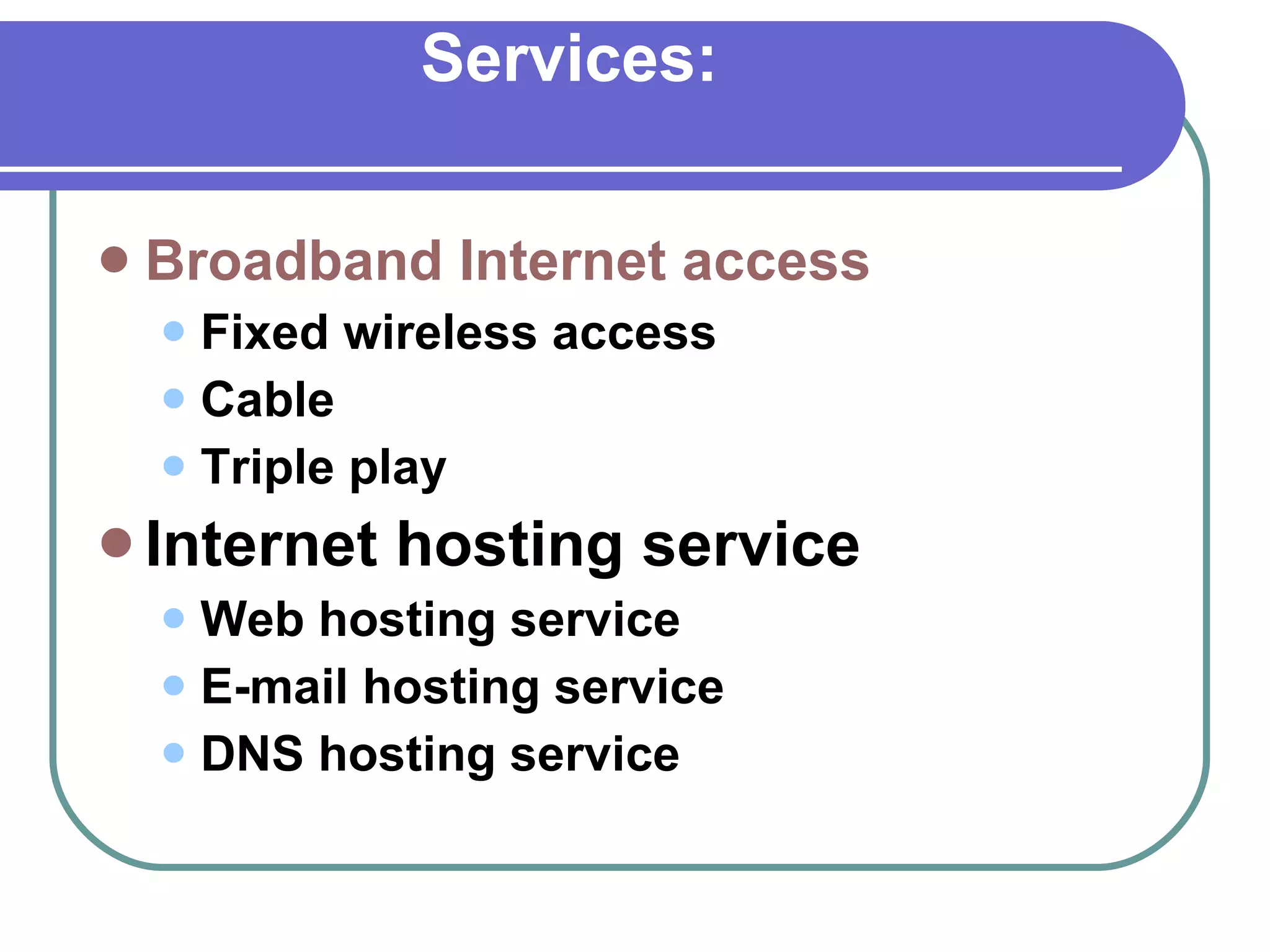
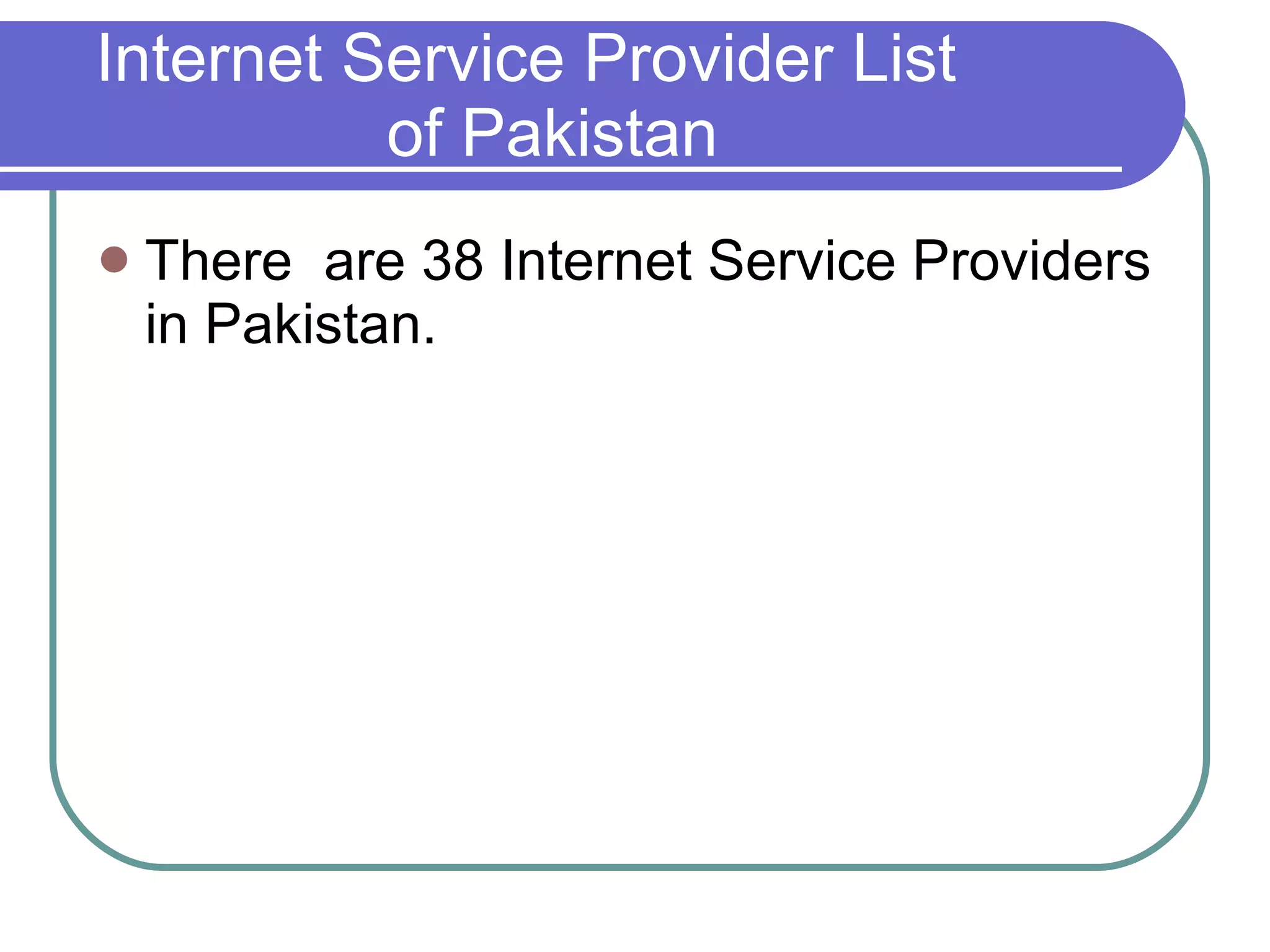
The document provides information about the internet including its history, structure, governance and modern uses. It discusses how the internet began as a US military program and was commercialized in the late 1980s. It also describes internet protocols, the scale-free network structure, and governance by ICANN. Internet service providers are defined as companies that provide customers access to the internet using various connection technologies. Common ISPs in Pakistan are also listed.