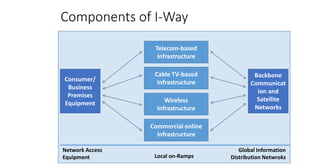
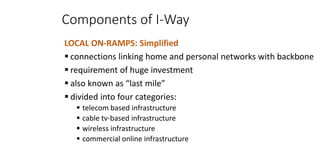
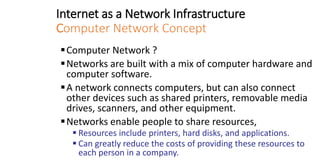
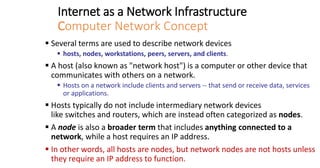
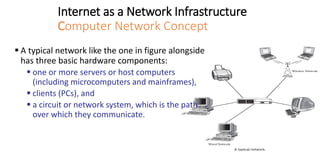
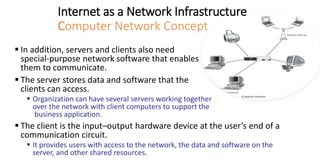
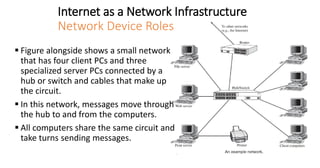
The document discusses network infrastructure for e-commerce. It covers topics like the components of the information superhighway including local on-ramps, backbone networks, and global distribution networks. It also discusses broadband technologies, definitions of the information superhighway, introduction to the I-Way, market forces influencing it, and components like telecom infrastructure, cable TV infrastructure, and wireless infrastructure. Finally, it covers internet as a network infrastructure, including computer network concepts, network device roles like hubs, switches and routers, and understanding client and server systems.