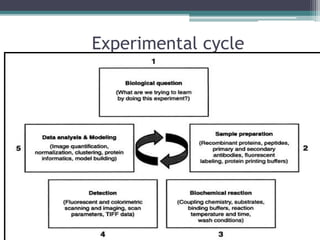
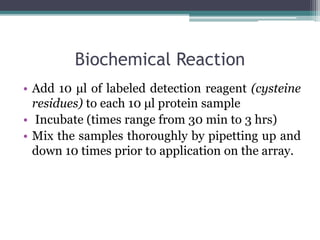
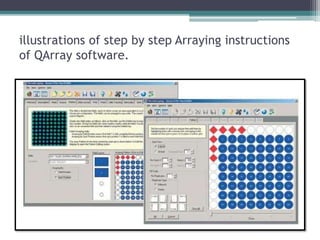
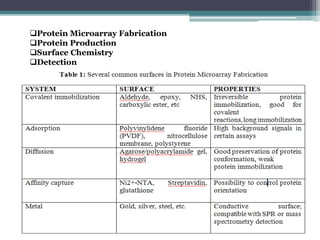
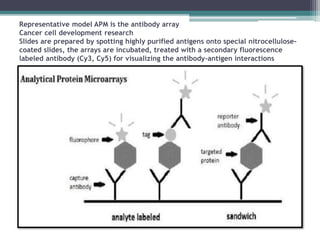
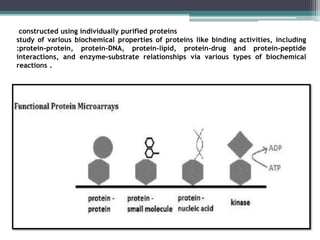
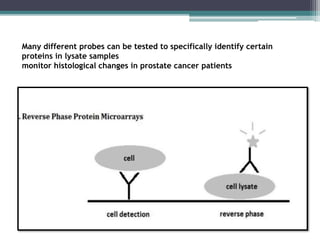
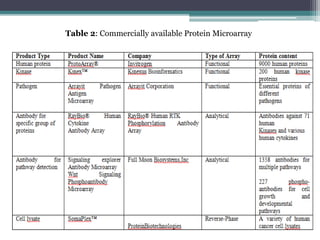
This document discusses protein microarrays, which allow high-throughput analysis of thousands of protein interactions. It describes the basic principles and experimental process of protein microarrays, including sample preparation, printing, incubation, washing, and data analysis. Protein microarrays have applications in detecting protein binding properties, profiling antibody specificity, studying post-translational modifications, and identifying biomarkers for clinical research applications like cancer. While powerful for proteomics research, protein microarrays also have some limitations like high costs.