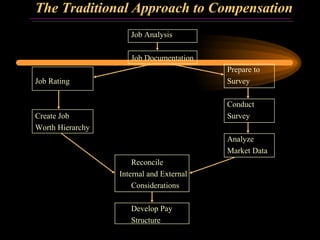
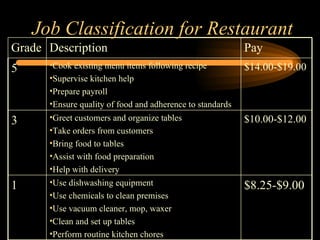
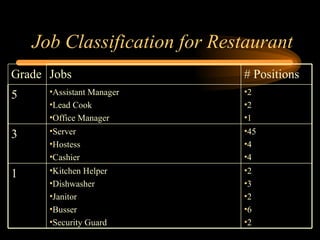
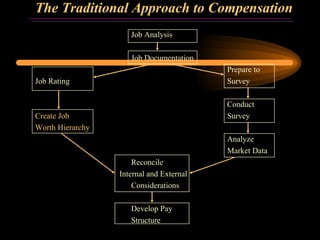
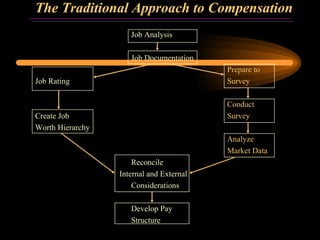
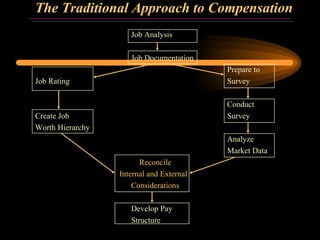
The document discusses traditional approaches to compensating employees, including achieving internal and external equity. It describes job evaluation methods like ranking, classification, and point factor analysis to determine the relative worth of jobs. Market data is then analyzed and internal job worth is reconciled with external market pay to develop an organizational pay structure. Emerging approaches to compensation like broadbanding, team-based pay, and skill-based pay are also mentioned.