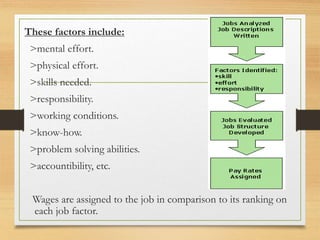
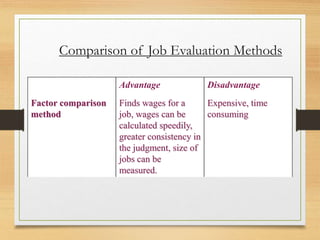
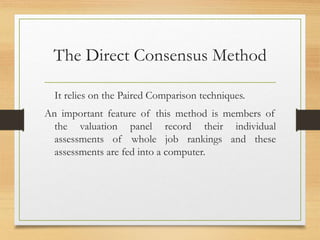
The document outlines job evaluation as a systematic process for determining the relative worth of jobs within an organization, centering on job content, required skills, and market value. It details various job evaluation methods, including conventional and innovative approaches, and emphasizes the importance of stakeholder involvement and establishing a job evaluation committee. The benefits of job evaluation include linking pay with job requirements, creating equitable wage structures, and facilitating improved workforce utilization.