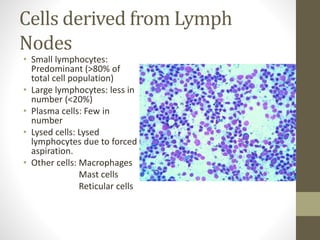
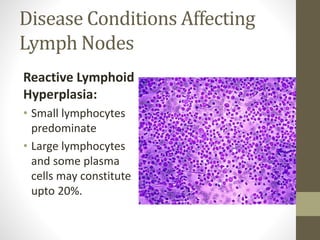
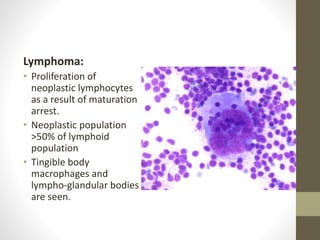
This document discusses lymph node impression smear cytology, a technique used to identify the cause of lymphadenopathy. It involves collecting a lymph node, making a smear of its cut section on a slide, staining it, and examining it under a microscope. The cells normally seen include small and large lymphocytes, plasma cells, and macrophages. Various disease conditions can be identified based on the abnormal cell types and proportions seen, such as reactive hyperplasia characterized by small lymphocytes, lymphoma showing proliferating neoplastic lymphocytes, and lymphadenitis with increased inflammatory cells. Metastatic neoplasms can also be detected by the presence of abnormal cell types within the lymph node.