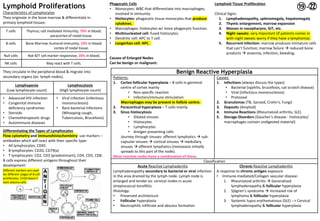
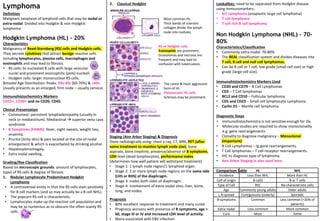
Lymphoid proliferations can be benign or malignant. Benign causes include infections while malignant causes include lymphomas. Lymphomas are divided into Hodgkin's lymphoma and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Hodgkin's lymphoma is characterized by Reed-Sternberg cells while non-Hodgkin's lymphoma can be of B-cell or T-cell origin. Investigation of lymph node enlargement includes history, examination, blood tests, imaging and biopsy to determine if the cause is benign reactive hyperplasia, infection, or malignancy such as lymphoma or metastatic carcinoma.