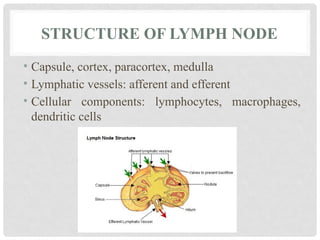
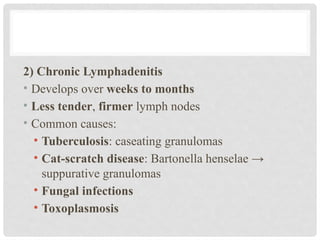
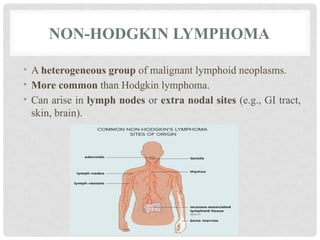
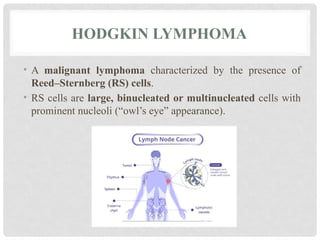
The **lymph node** is a small, bean-shaped organ of the lymphatic system that plays a crucial role in immune surveillance and response. Structurally, it is composed of a cortex, paracortex, and medulla, each housing specific immune cells like lymphocytes and macrophages. **Lymphadenopathy** refers to the abnormal enlargement of lymph nodes, often due to infection, autoimmune disease, or malignancy. **Lymphadenitis** is the inflammation of lymph nodes, commonly resulting from bacterial or viral infections. **Lymphoid neoplasms** are cancers arising from lymphoid tissues, including **Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL)** and **Hodgkin lymphoma (HL)**. NHL represents a diverse group of lymphoid malignancies with variable prognosis, while HL is characterized by the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells and often follows a more predictable clinical course. **Metastatic carcinoma** involves the spread of malignant epithelial cells from a primary tumor to the lymph nodes, indicating disease progression and often affecting prognosis and treatment strategies.