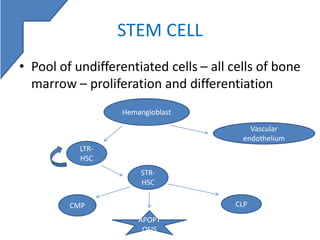
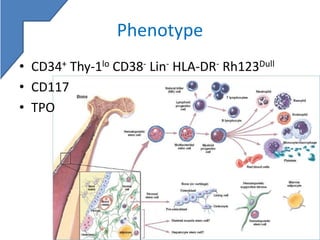
Stem cell enumeration involves quantifying stem cells, typically through CD34+ cell counting. Key methods include mononuclear cell counts, colony forming unit assays, and CD34+ enumeration via flow cytometry. For flow cytometry, the ISHAGE protocol is commonly used and involves sequential gating of lymphocytes, CD34+ cells, and viable cells. Accurate stem cell quantification is important for determining transplant timing and adequacy.